| 1 |
刘仙花, 余英豪, 叶显宗. 林奇综合征临床病理筛查的相关进展[J]. 实用肿瘤杂志, 2018,33(3):277-282.
|
| 2 |
王晓乐, 何淼龙, 宁方玲, 等. 林奇综合征的基因学、诊断及治疗相关进展[J]. 中国医药科学, 2021,11(7):56-59.
|
| 3 |
WATSON P, VASEN H, MECKLIN J P, et al.. The risk of extra-colonic, extra-endometrial cancer in the Lynch syndrome[J]. Int. J. Cancer, 2008,123(2):444-449.
|
| 4 |
谢天赐, 徐向上. 林奇综合征发生发展的研究进展[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2022,30(6):1102-1108.
|
| 5 |
MOLLER P, SEPPALA T, BERNSTEIN I, et al.. Cancer incidence and survival in Lynch syndrome patients receiving colonoscopic and gynaecological surveillance: first report from the prospective Lynch syndrome database[J]. Gut, 2017,66(3):464-472.
|
| 6 |
The Cancer Genome Atlas Network.Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer[J]. Nature, 2012,487(7407):330-337.
|
| 7 |
SCHWITALLE Y, KLOOR M, EIERMANN S, et al.. Immune response against frameshift-induced neopeptides in HNPCC patients and healthy HNPCC mutation carriers[J]. Gastroenterology, 2008,134(4):988-997.
|
| 8 |
EDGAR R, DOMRACHEV M, LASH A E. Gene expression omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository[J]. Nucl. Acids Res., 2002,30(1):207-210.
|
| 9 |
ORY L, NAZIH E H, DAOUD S, et al.. Targeting bioactive compounds in natural extracts-development of a comprehensive workflow combining chemical and biological data[J]. Anal. Chim. Acta, 2019,1070:29-42.
|
| 10 |
SZKLARCZYK D, GABLE A L, NASTOU K C, et al.. The STRING database in 2021: customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets[J]. Nucl. Acids Res, 2021,49(D1):D605-D612.
|
| 11 |
JANG B S, CHANG J H. Socioeconomic status and survival outcomes in elderly cancer patients: a national health insurance service-elderly sample cohort study[J]. Cancer Med., 2019,8(7):3604-3613.
|
| 12 |
LIU J, ZHOU S, LI S, et al.. Eleven genes associated with progression and prognosis of endometrial cancer (EC) identified by comprehensive bioinformatics analysis[J/OL]. Cancer Cell Int., 2019,19:136[2022-12-25]. .
|
| 13 |
HUANG D W, SHERMAN B T, TAN Q, et al.. The DAVID gene functional classification tool: a novel biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large gene lists[J]. Genome Biol., 2007,8(9):1-16.
|
| 14 |
文家治, 朱腾, 韩春晨, 等. 易感基因在林奇综合征相关结直肠癌、腺瘤筛查中应用研究[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2018,46(8):972-973.
|
| 15 |
许赟, 徐烨. 林奇综合征的病因研究及临床诊治现状[J]. 医学新知杂志, 2019,29(6):585-588.
|
| 16 |
SINICROPE F A. Lynch Syndrome-associated colorectal cancer[J]. N. Engl. J. Med., 2018,379(8):764-773.
|
| 17 |
李小会, 赵文婕, 刘变英. 林奇综合征诊疗进展[J]. 中华结直肠疾病电子杂志, 2016,5(6):512-517.
|
| 18 |
COHEN S A, LEININGER A. The genetic basis of Lynch syndrome and its implications for clinical practice and risk management[J]. Appl. Clin. Genet., 2014,7:147-158.
|
| 19 |
王红格. PARP抑制剂与土木香内酯所致DNA氧化损伤在肿瘤细胞中形成的合成致死作用研究[D]. 吉林:吉林大学, 2020.
|
| 20 |
ALJAŽ G, BRIGITA L, MIHA P. Current view on EpCAM structural biology[J/OL]. Cells, 2020,9(6):1361[2022-12-25]. .
|
| 21 |
丁颖, 王聪, 方海生, 等. EPCAM基因缺失导致的林奇综合征相关卵巢癌一例[J/OL]. 中国临床案例成果数据库, 2022,4(1):E132[2022-12-25]. .
|
| 22 |
HUTH C, KLOOR M, VOIGT A Y, et al.. The molecular basis of EPCAM expression loss in Lynch syndrome-associated tumors[J]. Modern Pathol., 2012,25(6):911-916.
|
| 23 |
BENDRIS N, LEMMERS B, BLANCHARD J M. Cell cycle, cytoskeleton dynamics and beyond: the many functions of cyclins and CDK inhibitors[J]. Cell Cycle, 2015,14(12):1786-1798.
|
| 24 |
MUSGROVE E A, CALDON C E, BARRACLOUGH J, et al.. Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in cancer[J]. Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2011,11(8): 558-572.
|
| 25 |
KRISHNAN R, PATEL P S, HAKEM R. BRCA1 and metastasis: outcome of defective DNA repair[J/OL]. Cancers, 2021,14(1) 108[2022-12-25]..
|
| 26 |
MAGRIN L, FANALE D, BRANDO C, et al.. POLE, POLD1, and NTHL1: the last but not the least hereditary cancer-predisposing genes[J]. Oncogene, 2021,40(40):5893-5901.
|
| 27 |
ORANS J, MCSWEENEY E A, IYER R R, et al.. Structures of human exonuclease 1 DNA complexes suggest a unified mechanism for nuclease family[J]. Cell, 2011,145(2):212-223.
|
| 28 |
SZANKASI P, SMITH G R. A DNA exonuclease induced during meiosis of Schizosaccharomyces pombe [J]. J. Biol. Chem., 1992,267(5):3014-3023.
|
| 29 |
NAGUIB A, BENCZE G, CHO H, et al.. PTEN functions by recruitment to cytoplasmic vesicles[J]. Mol. Cell, 2015,58(2):255-268.
|
| 30 |
HOLLANDER M C, BLUMENTHAL G M, DENNIS P A. PTEN loss in the continuum of common cancers, rare syndromes and mouse models[J]. Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2011,11(4):289-301.
|
| 31 |
SCRUGGS A M, KOH H B, TRIPATHI P, et al.. Loss of CDKN2B promotes fibrosis via increased fibroblast differentiation rather than proliferation[J]. Am. J. Respir Cell Mol. Biol., 2018,59(2):200-214.
|
| 32 |
YANG L, MA D W, CAO Y P, et al.. PRMT5 functionally associates with EZH2 to promote colorectal cancer progression through epigenetically repressing CDKN2B expression[J]. Theranostics, 2021,11(8):3742-3759.
|
| 33 |
YUAN J, YI K, YANG L. TGFBR2 regulates hedgehog pathway and cervical cancer cell proliferation and migration by mediating SMAD4[J]. J. Proteome Res., 2020,19(8):3377-3385.
|
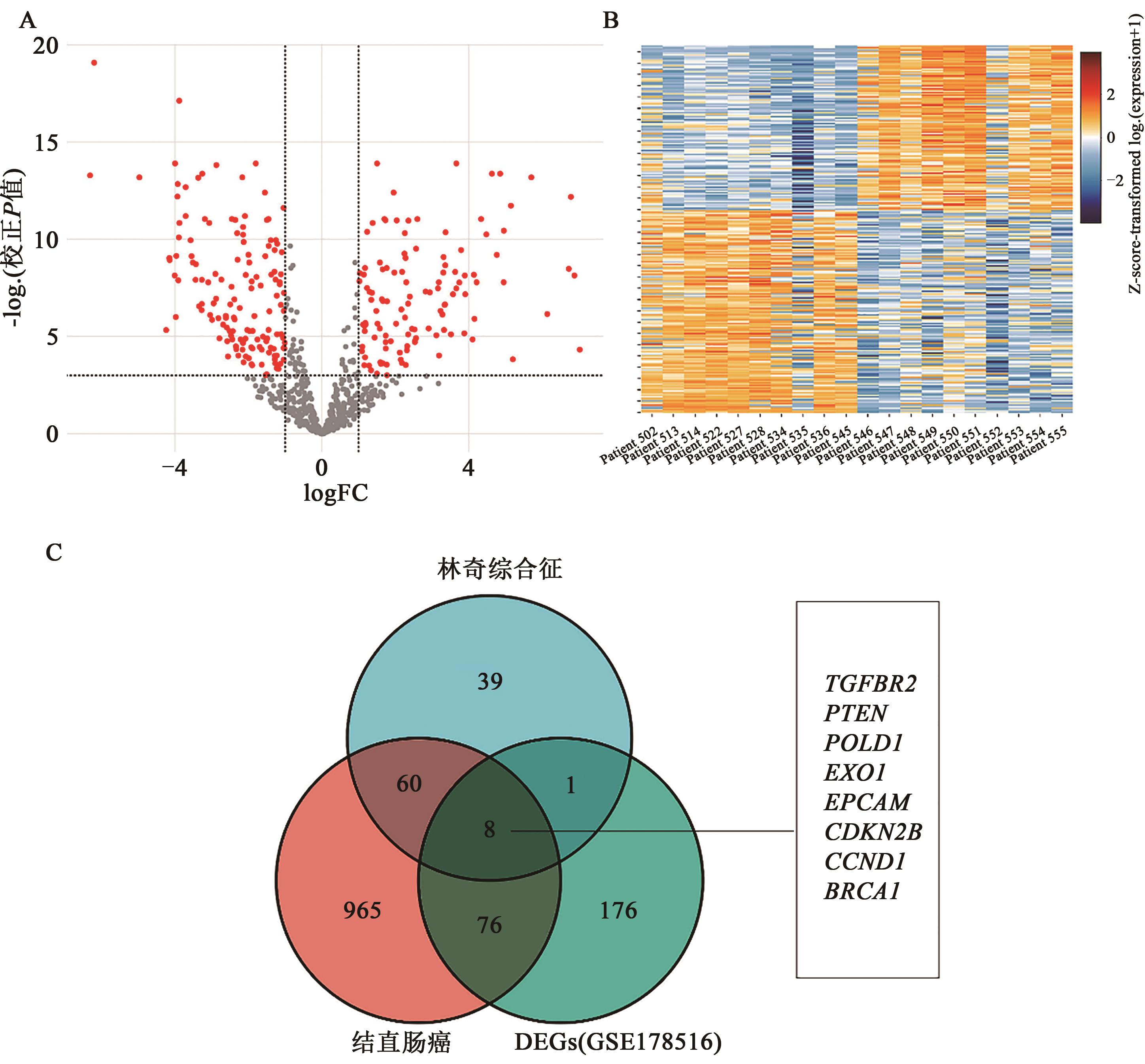
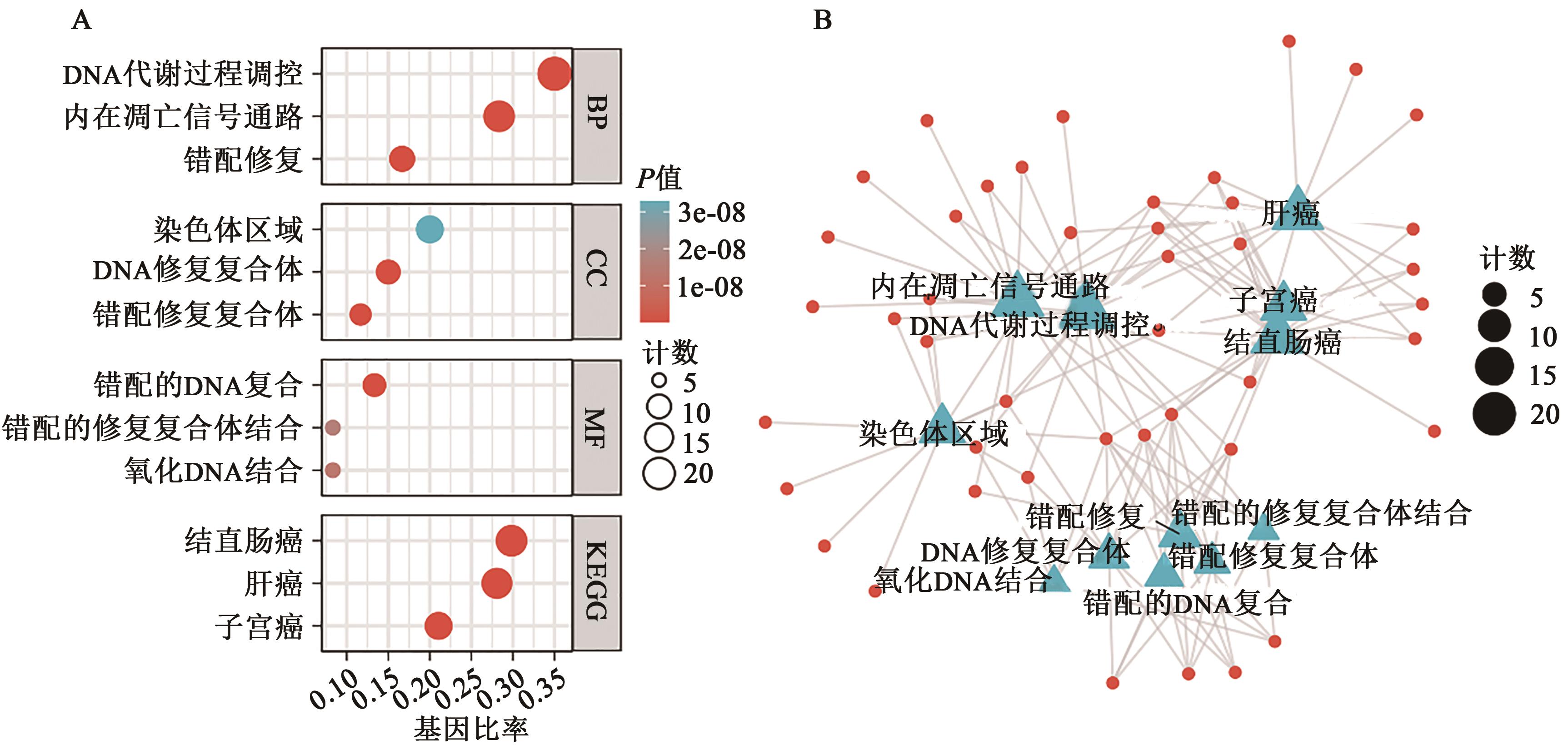
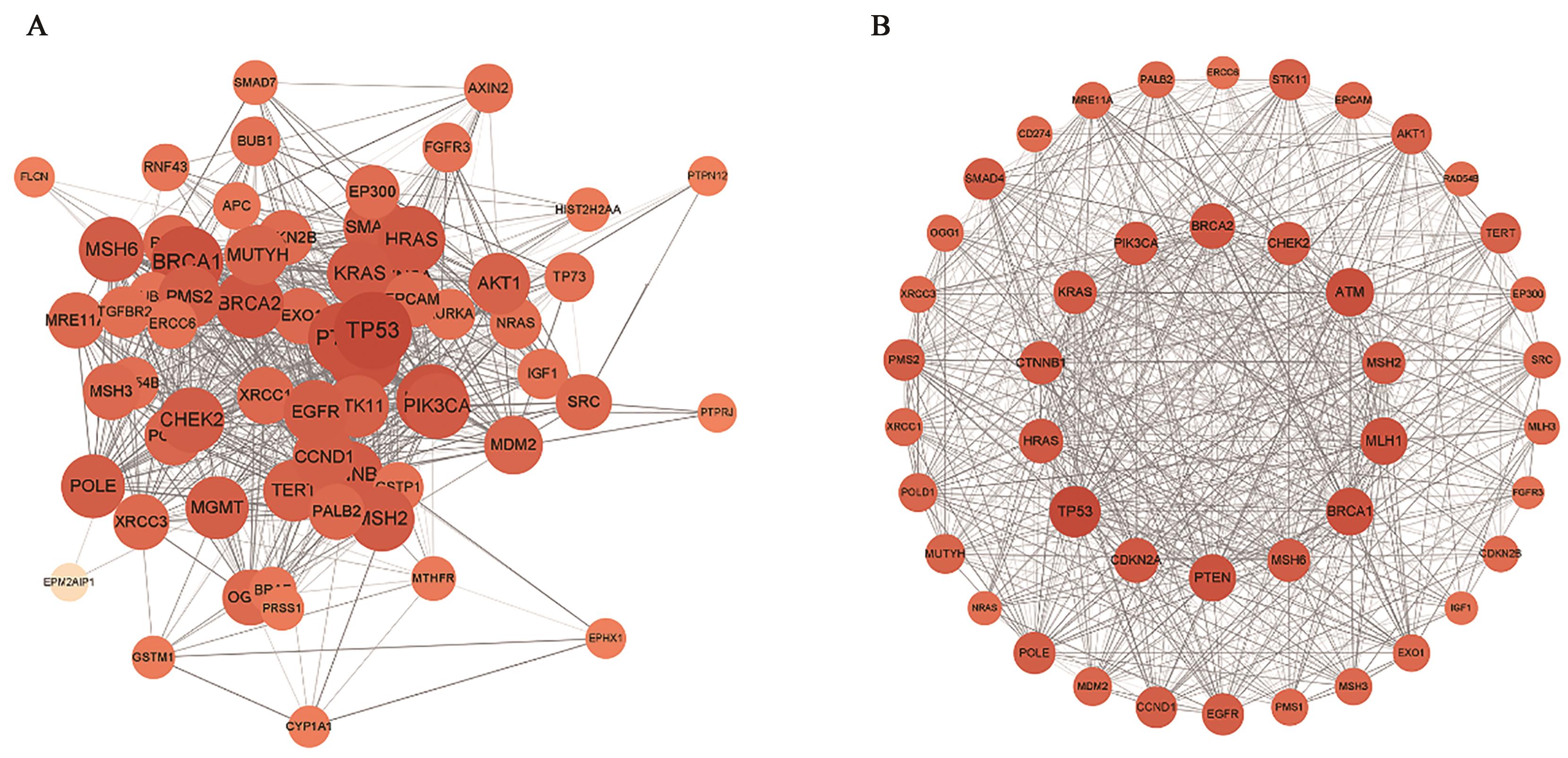
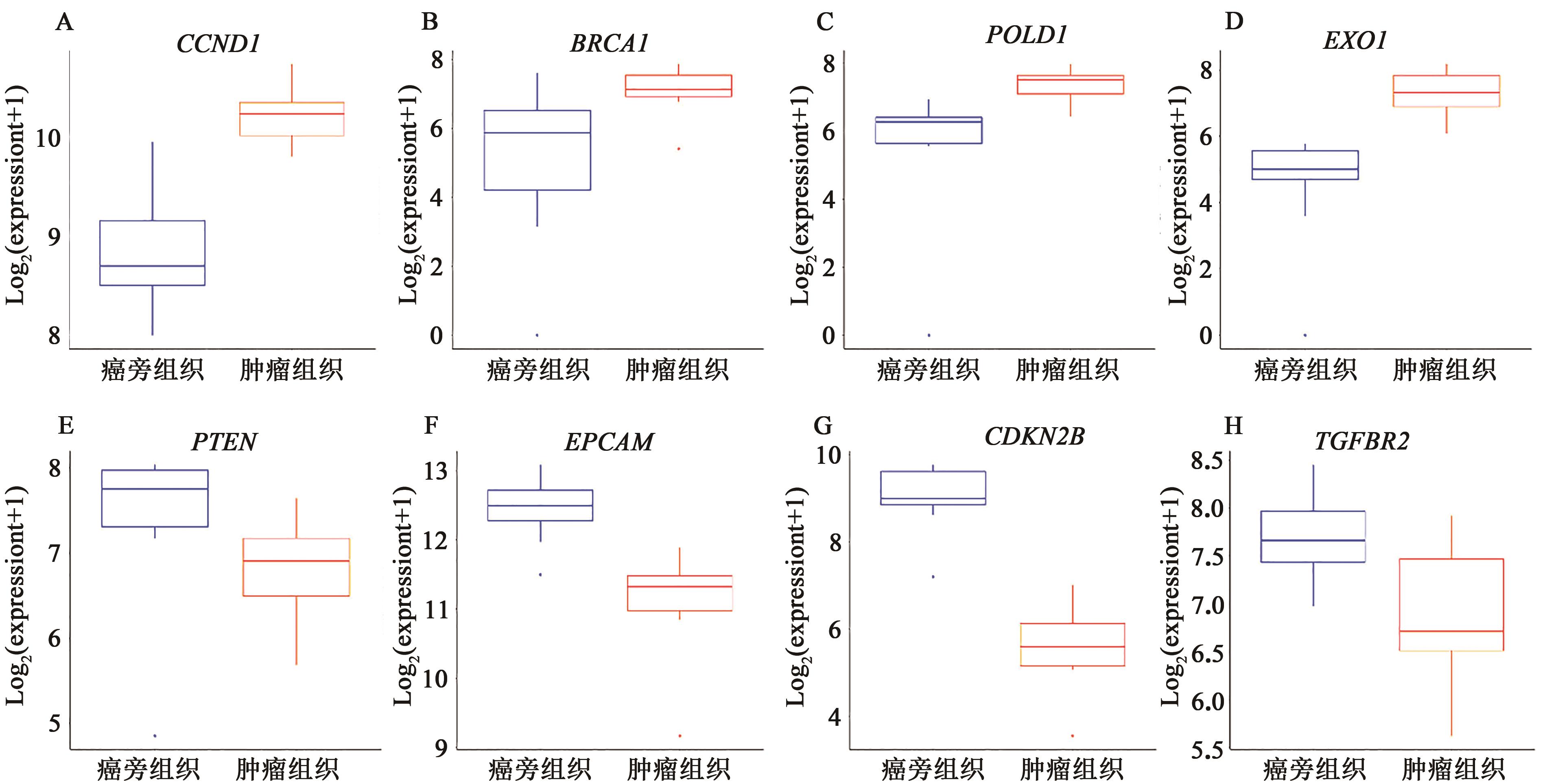
 ), Junjie HUANG1, Caiming WENG2, Wangwu LIU2, Yongyuan CHEN2, Huiyan CHEN2, Hu ZHAO2,3, Yu WANG2,3, Chengzhi LIN2,3(
), Junjie HUANG1, Caiming WENG2, Wangwu LIU2, Yongyuan CHEN2, Huiyan CHEN2, Hu ZHAO2,3, Yu WANG2,3, Chengzhi LIN2,3( )
)
 ), 黄军杰1, 翁才明2, 刘旺武2, 陈永元2, 陈惠燕2, 赵虎2,3, 王瑜2,3, 林承志2,3(
), 黄军杰1, 翁才明2, 刘旺武2, 陈永元2, 陈惠燕2, 赵虎2,3, 王瑜2,3, 林承志2,3( )
)