Current Biotechnology ›› 2025, Vol. 15 ›› Issue (3): 446-455.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2025.0015
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Studies on the Immunological Effects of Dinotefuran Exposure on Zebrafish Juveniles
Yunshuo CHENG( ), Zixu LI, Guanghua MAO(
), Zixu LI, Guanghua MAO( ), Xiangyang WU(
), Xiangyang WU( )
)
- School of Environment and Safety Engineering,Jiangsu University,Jiangsu Zhenjiang 212013,China
-
Received:2025-02-13Accepted:2025-03-10Online:2025-05-25Published:2025-07-01 -
Contact:Guanghua MAO,Xiangyang WU
呋虫胺暴露对斑马鱼幼鱼的免疫毒性研究
- 江苏大学环境与安全工程学院,江苏 镇江 212013
-
通讯作者:茆广华,吴向阳 -
作者简介:程云硕 E-mail: 2916579457@qq.com -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(22276079)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yunshuo CHENG, Zixu LI, Guanghua MAO, Xiangyang WU. Studies on the Immunological Effects of Dinotefuran Exposure on Zebrafish Juveniles[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(3): 446-455.
程云硕, 李子旭, 茆广华, 吴向阳. 呋虫胺暴露对斑马鱼幼鱼的免疫毒性研究[J]. 生物技术进展, 2025, 15(3): 446-455.
share this article
| 基因 | 引物序列(5'→3') |
|---|---|
| tlr4a | F: 5'-CAATGGCTTGGGTACTTTGC-3' |
| R: 5'-GATTTGAGGAGTGCCGGATA-3' | |
| myd88 | F: 5'-TCCGAAAGAAACTGGGTCTG-3' |
| R: 5'-CGGAATAACGGAGTTCAGCTTGTG-3' | |
| irak4 | F: 5'-CAGAGAGGATTGTGGGAACGA-3' |
| R: 5'-GAGGAAGCCCAGACAAAACCT-3' | |
| traf6 | F: 5'-AAGCCGGTCAGCCTATTGTC-3' |
| R: 5'-CTGGCTGTCAAACTCACCCT-3' | |
| ikkβ | F: 5'-GTGGCGGTGGATTATTGG-3' |
| R: 5'-GCACGGGTTGCCAGTTTG-3' | |
| il-6 | F: 5'-TGGACGTAAAGAGTCTCCTTGG-3' |
| R: 5'-TCATGTTCACCATCTCTCTGAAA-3' | |
| il-1β | F: 5'-CATTTGCAGGCCGTCACA-3' |
| R: 5'-GGACATGCTGAAGCGCACTT-3' | |
| tnf-α | F: 5'-GCTGGATCTTCAAAGTCGGGTGTA-3' |
| R: 5'-TGTGAGTCTCAGCACACTTCCATC-3' | |
| nfκb p65 | F: 5'-TATGAAGCAGACCTACAG-3' |
| R: 5'-TCTTGGCATCAGGAATA-3' | |
| keap1 | F: 5'-TGTGATCTGGTTCTGCATGTC-3' |
| R: 5'-ACTCCTTGAAGTTGCTGGTG-3' | |
| ho-1 | F: 5'-ATGCCCTTGTTTCCAGTCAGC-3' |
| R: 5'-CTCGGAGGAGATGGAAGGAAG-3' | |
| cat | F:5'-AGGGCAACTGGGATCTTACA-3' |
| R: 5'-TTTATGGGACCAGACCTTGG-3' | |
| sod | F: 5'-GTCGTCTGGCTTGTGGAGTG-3’ |
| R: 5'-TGTCAGCGGGCTAGTGCTT-3' | |
| jak1 | F: 5'-GCAGGCAACTGTGTGTGAAG-3' |
| R: 5'-AGAACTCGAGCTGGTGTGTG-3' | |
| jak2 | F: 5'-TCGCTGCTTCTTCTGTCAGG-3' |
| R: 5'-ACAGCCGTCCATTTTGGCTT-3' | |
| socs3b | F: 5'-CCTTCCATACCCACCGAGAC-3' |
| R: 5'-GCGCTGTCAAGCCTACTATG-3' | |
| stat3 | F: 5'-TGTGACACCAACGACCTGC-3' |
| R: 5'-CCAAACTGCATCAATGAATCTA-3' | |
| gapdh | F: 5'-GTGGAGTCTACTGGTGTCTTC-3' |
| R: 5'-GTGCAGGAGGCATTGCTTACA-3' |
Table 1 The sequences of primer list used in this study
| 基因 | 引物序列(5'→3') |
|---|---|
| tlr4a | F: 5'-CAATGGCTTGGGTACTTTGC-3' |
| R: 5'-GATTTGAGGAGTGCCGGATA-3' | |
| myd88 | F: 5'-TCCGAAAGAAACTGGGTCTG-3' |
| R: 5'-CGGAATAACGGAGTTCAGCTTGTG-3' | |
| irak4 | F: 5'-CAGAGAGGATTGTGGGAACGA-3' |
| R: 5'-GAGGAAGCCCAGACAAAACCT-3' | |
| traf6 | F: 5'-AAGCCGGTCAGCCTATTGTC-3' |
| R: 5'-CTGGCTGTCAAACTCACCCT-3' | |
| ikkβ | F: 5'-GTGGCGGTGGATTATTGG-3' |
| R: 5'-GCACGGGTTGCCAGTTTG-3' | |
| il-6 | F: 5'-TGGACGTAAAGAGTCTCCTTGG-3' |
| R: 5'-TCATGTTCACCATCTCTCTGAAA-3' | |
| il-1β | F: 5'-CATTTGCAGGCCGTCACA-3' |
| R: 5'-GGACATGCTGAAGCGCACTT-3' | |
| tnf-α | F: 5'-GCTGGATCTTCAAAGTCGGGTGTA-3' |
| R: 5'-TGTGAGTCTCAGCACACTTCCATC-3' | |
| nfκb p65 | F: 5'-TATGAAGCAGACCTACAG-3' |
| R: 5'-TCTTGGCATCAGGAATA-3' | |
| keap1 | F: 5'-TGTGATCTGGTTCTGCATGTC-3' |
| R: 5'-ACTCCTTGAAGTTGCTGGTG-3' | |
| ho-1 | F: 5'-ATGCCCTTGTTTCCAGTCAGC-3' |
| R: 5'-CTCGGAGGAGATGGAAGGAAG-3' | |
| cat | F:5'-AGGGCAACTGGGATCTTACA-3' |
| R: 5'-TTTATGGGACCAGACCTTGG-3' | |
| sod | F: 5'-GTCGTCTGGCTTGTGGAGTG-3’ |
| R: 5'-TGTCAGCGGGCTAGTGCTT-3' | |
| jak1 | F: 5'-GCAGGCAACTGTGTGTGAAG-3' |
| R: 5'-AGAACTCGAGCTGGTGTGTG-3' | |
| jak2 | F: 5'-TCGCTGCTTCTTCTGTCAGG-3' |
| R: 5'-ACAGCCGTCCATTTTGGCTT-3' | |
| socs3b | F: 5'-CCTTCCATACCCACCGAGAC-3' |
| R: 5'-GCGCTGTCAAGCCTACTATG-3' | |
| stat3 | F: 5'-TGTGACACCAACGACCTGC-3' |
| R: 5'-CCAAACTGCATCAATGAATCTA-3' | |
| gapdh | F: 5'-GTGGAGTCTACTGGTGTCTTC-3' |
| R: 5'-GTGCAGGAGGCATTGCTTACA-3' |
| 1 | BARTON B, ULLAH N, KOSZELSKA K, et al.. Reviewing neonicotinoid detection with electroanalytical methods[J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int., 2024, 31(26): 37923-37942. |
| 2 | BASS C, DENHOLM I, WILLIAMSON M S, et al.. The global status of insect resistance to neonicotinoid insecticides[J]. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol., 2015, 121: 78-87. |
| 3 | 周怡彤, 李清雪, 王斌, 等. 太湖流域西北部地表水中农药的污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2020, 15(3):171-183. |
| ZHOU Y T, LI Q X, WANG B, et al.. Distribution and ecotoxicological risk assessment of pesticides in surface water of the northwest of Taihu Lake basin[J]. Asian J. Ecotoxicol., 2020, 15(3): 171-183. | |
| 4 | ZHANG C, JIN L, ZHOU S, et al.. Chiral separation of neonicotinoid insecticides by polysaccharide-type stationary phases using high-performance liquid chromatography and supercritical fluid chromatography[J]. Chirality, 2011, 23(3): 215-221. |
| 5 | HIRASE K, YAMADA E, KIRITANI Y, et al.. Dinotefuran, a novel neonicotinoid[C]. Plant Protection Towards the 21st Century-Proceedings of the XVth International Plant Protection Congress, 2004. |
| 6 | DORES E F G C, CARBO L, RIBEIRO M L, et al.. Pesticide levels in ground and surface waters of Primavera do Leste Region, Mato Grosso, Brazil[J]. J. Chromatogr. Sci., 2008, 46(7): 585-590. |
| 7 | HAYASAKA D, KOBASHI K, HASHIMOTO K. Community responses of aquatic insects in paddy mesocosms to repeated exposures of the neonicotinoids imidacloprid and dinotefuran[J]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2019, 175: 272-281. |
| 8 | 吕正标. 新烟碱类杀虫剂在水环境中的残留特征及潜在风险[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2020. |
| 9 | BRADLEY P M, JOURNEY C A, ROMANOK K M, et al.. Expanded target-chemical analysis reveals extensive mixed-organic-contaminant exposure in U.S. streams[J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2017, 51(9): 4792-4802. |
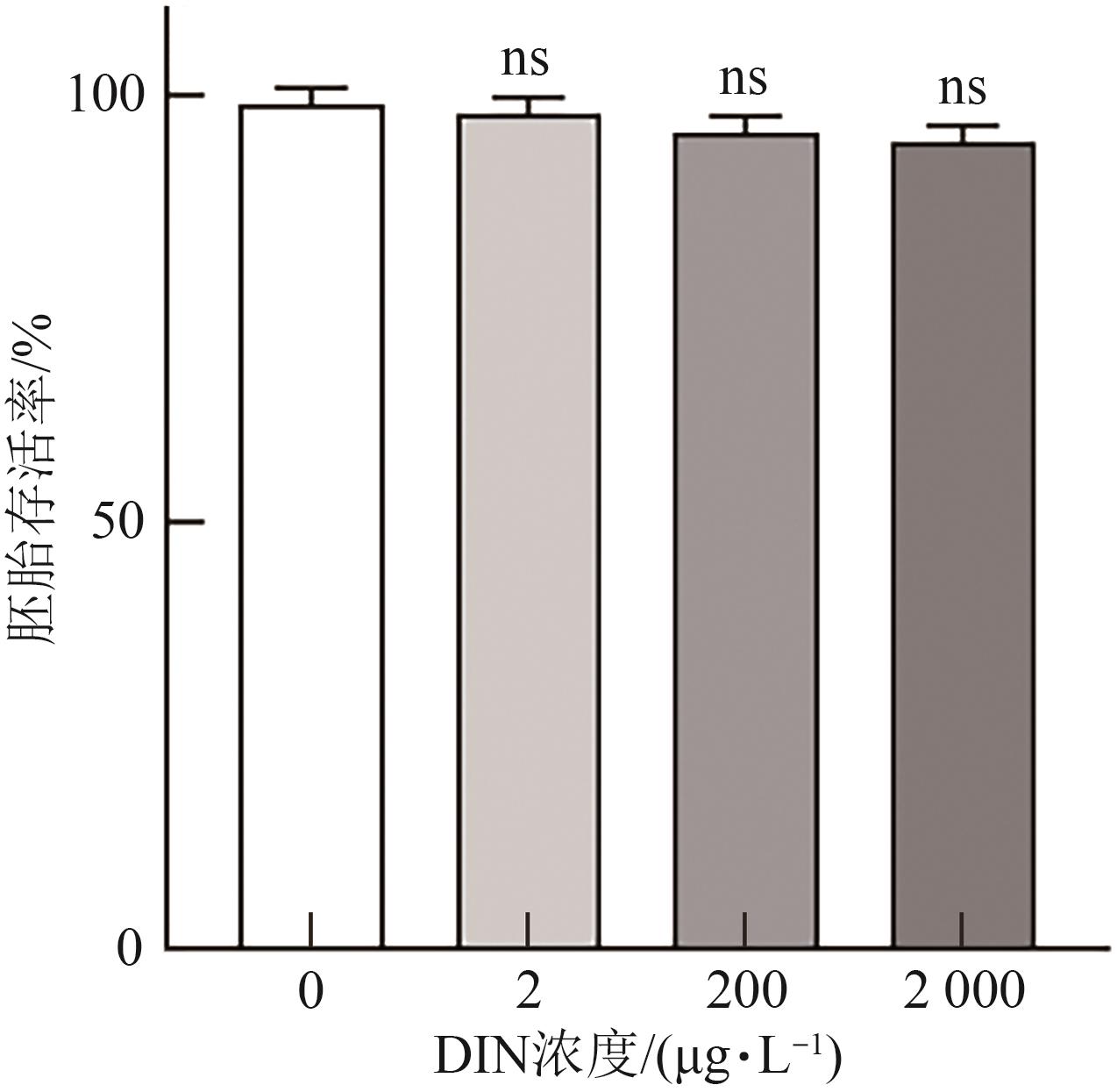
| 10 | KAKUTA I, TAKASE K. Exposure to neonicotinoid pesticides induces physiological disorders and affects color performance and foraging behavior in goldfish[J/OL]. Physiol. Rep., 2024, 12(15): e16138[2025-03-10]. . |
| 11 | TIAN X, HONG X, YAN S, et al.. Neonicotinoids caused oxidative stress and DNA damage in juvenile Chinese rare minnows (Gobiocypris rarus)[J/OL]. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2020, 197: 110566[2025-03-10]. . |
| 12 | 孙琦, 范咏梅, 赖柯华, 等. 呋虫胺对斑马鱼胚胎-幼鱼生长发育及细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2016, 11(3): 356-364. |
| SUN Q, FAN Y M, LAI K H, et al.. Effects of dinotefuran on the embryonic and larvae development and apoptosis in zebrafish (Danio rerio)[J]. Asian J. Ecotoxicol., 2016, 11(3): 356-364. | |
| 13 | ZHOU X, YANG Y, MING R, et al.. Insight into the differences in the toxicity mechanisms of dinotefuran enantiomers in zebrafish by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS[J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int., 2022, 29(47): 70833-70841. |
| 14 | 刘林, 赵群芬, 金凯星, 等. 纳米氧化锌对斑马鱼肝脏的毒性效应[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(10): 3884-3891. |
| LIU L, ZHAO Q F, JIN K X, et al.. Toxic effect of Nano-ZnO in liver of zebrafish[J]. Environ. Sci., 2015, 36(10): 3884-3891. | |
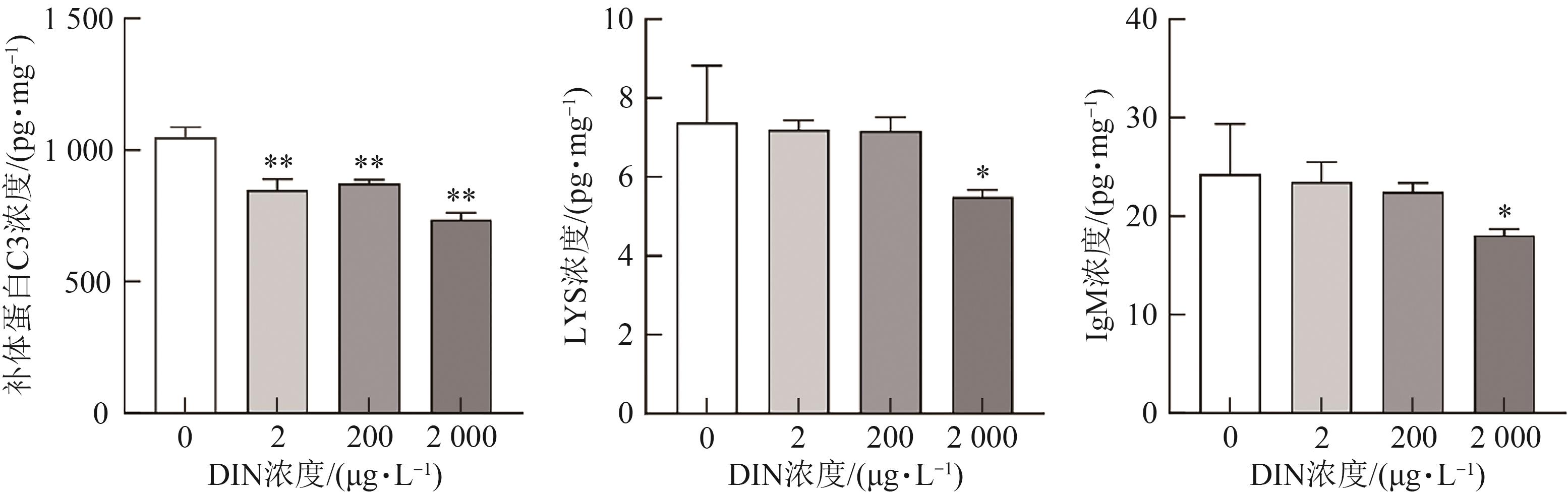
| 15 | YANG C, LIM W, SONG G. Immunotoxicological effects of insecticides in exposed fishes[J/OL]. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol., 2021, 247: 109064[2025-03-10]. . |
| 16 | BRODZKI P, GORZKOŚ H, MARCZUK J, et al.. The influence of probiotic administration on the phagocytic and oxidative burst activity of neutrophils and monocytes in the peripheral blood of dairy cows during different lactation periods[J]. J. Vet. Res., 2024, 68(3): 401-408. |
| 17 | GALLI S J, BORREGAARD N, WYNN T A. Phenotypic and functional plasticity of cells of innate immunity: macrophages, mast cells and neutrophils[J]. Nat. Immunol., 2011, 12(11): 1035-1044. |
| 18 | XIONG G, ZOU L, DENG Y, et al.. Clethodim exposure induces developmental immunotoxicity and neurobehavioral dysfunction in zebrafish embryos[J]. Fish Shellfish. Immunol., 2019, 86: 549-558. |
| 19 | XU H, DONG X, ZHANG Z, et al.. Assessment of immunotoxicity of dibutyl phthalate using live zebrafish embryos[J]. Fish Shellfish. Immunol., 2015, 45(2): 286-292. |
| 20 | 汪霞, 郜兴利, 何炳楠, 等. 拟除虫菊酯类农药的免疫毒性研究进展[J]. 农药学学报, 2017, 19(1): 1-8. |
| WANG X, GAO X L, HE B N, et al.. Research progress on the immunotoxicity of pyrethroids[J]. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci., 2017, 19(1): 1-8. | |
| 21 | GAO X Q, FEI F, HUO H H, et al.. Impact of nitrite exposure on plasma biochemical parameters and immune-related responses in Takifugu rubripes [J/OL]. Aquat. Toxicol., 2020, 218: 105362[2025-03-10]. . |
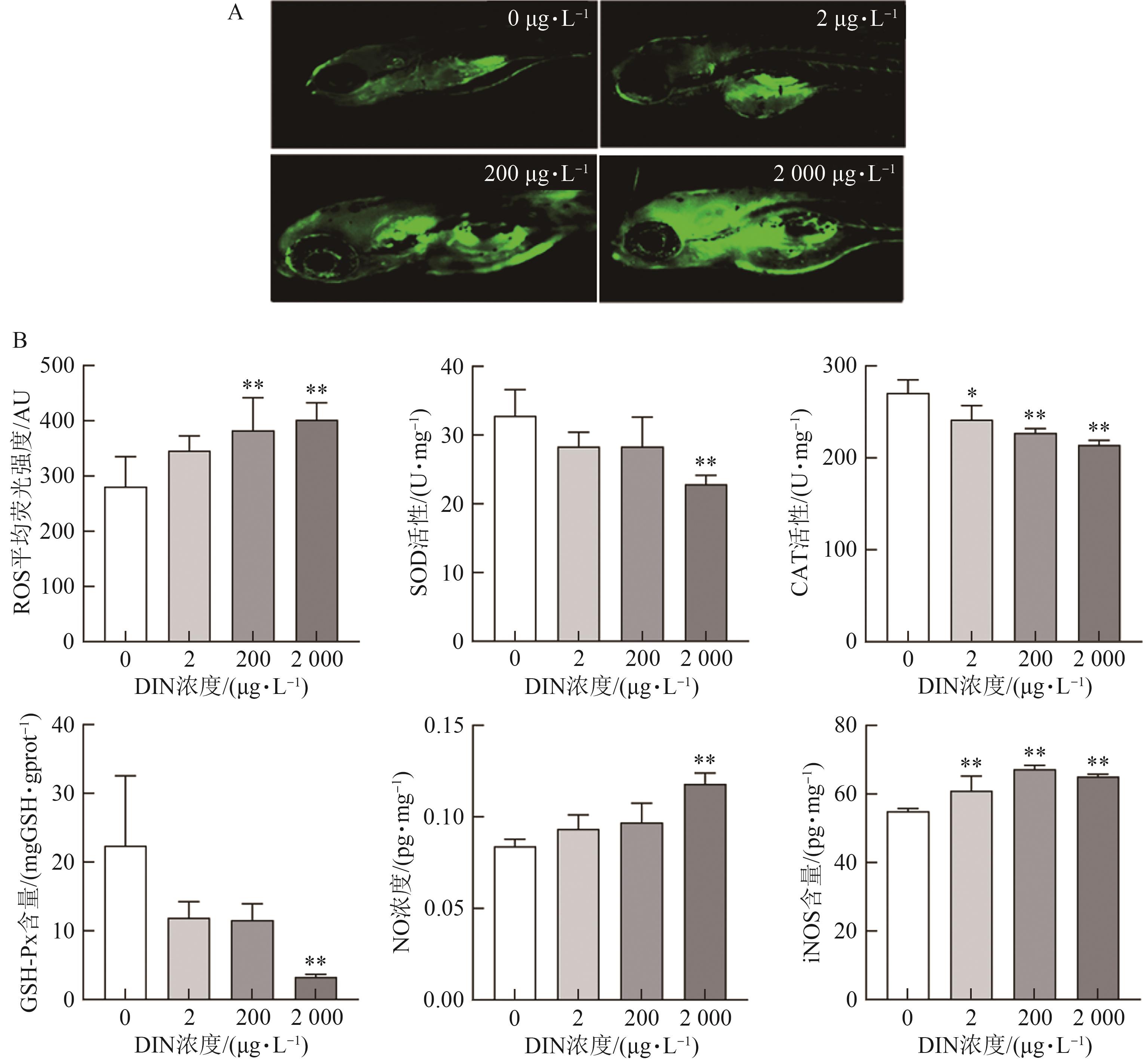
| 22 | WINSTON G W. Oxidants and antioxidants in aquatic animals[J]. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol., 1991, 100(1-2): 173-176. |
| 23 | 陈幕飞, 黄承志, 蒲德永, 等. CdSe/ZnS量子点对斑马鱼胚胎发育的毒性效应[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(2): 719-726. |
| CHEN M F, HUANG C Z, PU D Y, et al.. Toxic effects of CdSe/ZnS QDs to zebrafish embryos[J]. Environ. Sci., 2015, 36(2): 719-726. | |
| 24 | MONTEIRO D A, DE ALMEIDA J A, RANTIN F T, et al.. Oxidative stress biomarkers in the freshwater characid fish, Brycon cephalus, exposed to organophosphorus insecticide Folisuper 600 (methyl parathion)[J]. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol., 2006, 143(2): 141-149. |
| 25 | ZHANG Q, ZHAO M, QIAN H, et al.. Enantioselective damage of diclofop acid mediated by oxidative stress and acetyl-coA carboxylase in nontarget plant Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, 46(15): 8405-8412. |
| 26 | WANG Y Y L, CAI Y, KAZMI S S U H, et al.. Temperature-dependent effects of neonicotinoids on the embryonic development of zebrafish (Danio rerio)[J]. Front. Mar. Sci, 2023, 9: 1101737[2025-04-22]. . |
| 27 | SUZUKI T, YAMAMOTO M. Molecular basis of the Keap1-Nrf2 system[J]. Free. Radic. Biol. Med., 2015, 88: 93-100. |
| 28 | 周俊豪, 刘念, 杨映. 硬骨鱼类Keap1-Nrf2/ARE信号通路研究进展[J]. 水产学杂志, 2022, 35(4): 117-124. |
| ZHOU J H, LIU N, YANG Y. Keap1-Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway and its antioxidant regulation in teleost fish: a review[J]. Chin. J. Fish., 2022, 35(4): 117-124. | |
| 29 | OSORIO J S, TREVISI E, JI P, et al.. Biomarkers of inflammation, metabolism, and oxidative stress in blood, liver, and milk reveal a better immunometabolic status in peripartal cows supplemented with Smartamine M or MetaSmart[J]. J. Dairy Sci., 2014, 97(12): 7437-7450. |
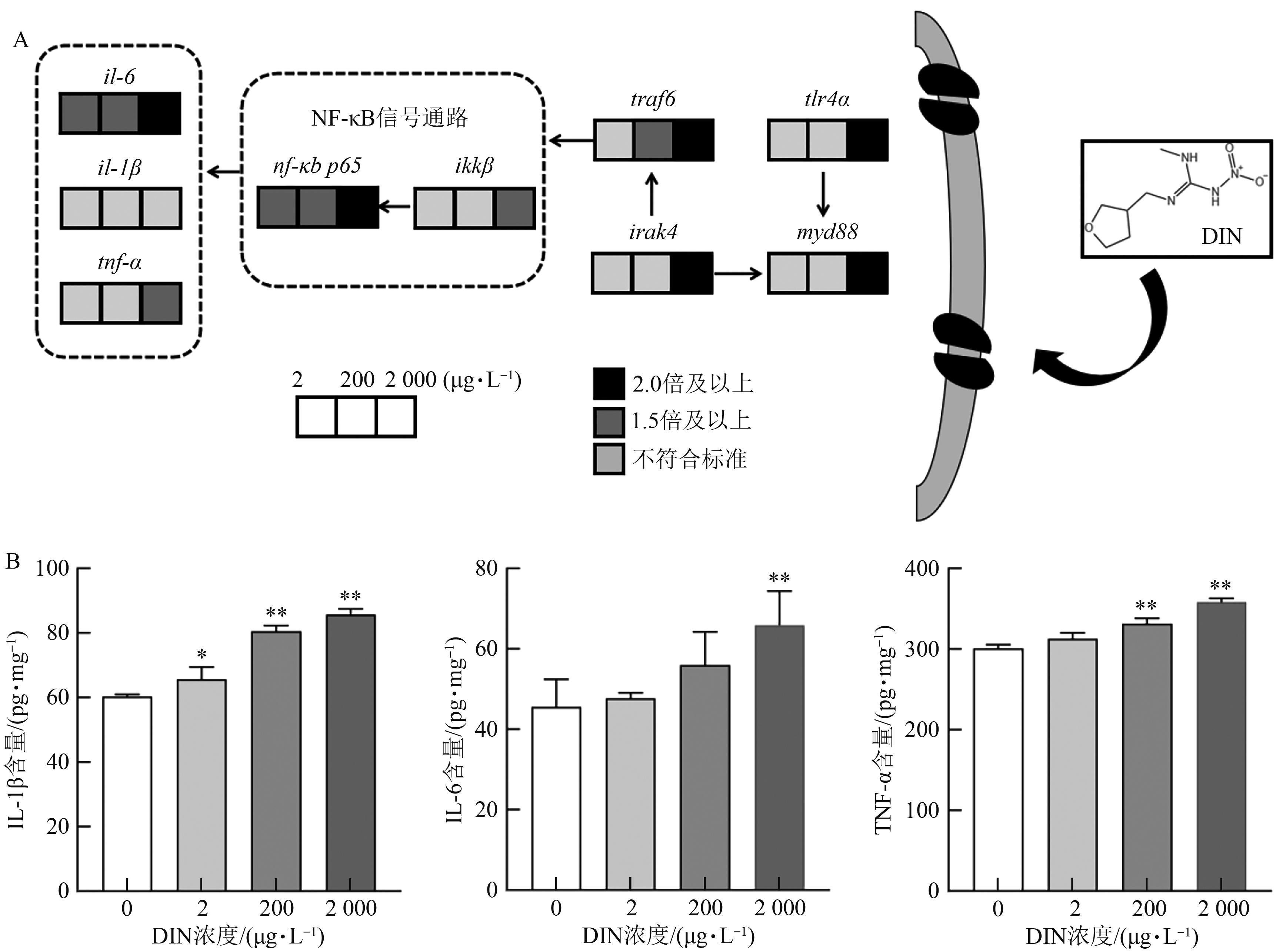
| 30 | STOCKHAMMER O W, ZAKRZEWSKA A, HEGEDÛS Z, et al.. Transcriptome profiling and functional analyses of the zebrafish embryonic innate immune response to Salmonella infection[J]. J. Immunol., 2009, 182(9): 5641-5653. |
| 31 | VAN DER VAART M, VAN SOEST J J, SPAINK H P, et al.. Functional analysis of a zebrafish myd88 mutant identifies key transcriptional components of the innate immune system[J]. Dis. Model. Mech., 2013, 6(3): 841-854. |
| 32 | WU P, LIU X W, FENG L, et al.. (2-Carboxyethyl) dimethylsulfonium bromide supplementation in non-fish meal diets for on-growing grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): beneficial effects on immune function of the immune organs via modulation of NF-κB and TOR signalling pathway[J]. Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2020, 107(Pt A): 309-323. |
| 33 | ZHANG C, PU C, LI S, et al.. Lactobacillus delbrueckii ameliorates Aeromonas hydrophila-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and immunosuppression of Cyprinus carpio Huanghe var NF-κB/Nrf2 signaling pathway[J/OL]. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol., 2024, 285: 110000[2025-03-10]. . |
| 34 | DOU W, ZHANG J, SUN A, et al.. Protective effect of naringenin against experimental colitis via suppression of Toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB signalling[J]. Br. J. Nutr., 2013, 110(4): 599-608. |
| 35 | KHANNA P, CHUA P J, BAY B H, et al.. The JAK/STAT signaling cascade in gastric carcinoma (review)[J]. Int. J. Oncol., 2015, 47(5): 1617-1626. |
| 36 | ARUMUGGAM N, BHOWMICK N A, VASANTHA RUPASINGHE H P. A review: phytochemicals targeting JAK/STAT signaling and IDO expression in cancer[J]. Phytother. Res., 2015, 29(6): 805-817. |
| 37 | TRACEY K J. The inflammatory reflex[J]. Nature, 2002, 420(6917): 853-859. |
| 38 | ANDERSSON J. The inflammatory reflex: introduction[J]. J. Intern. Med., 2005, 257(2): 122-125. |
| 39 | 刘旺. 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚对斑马鱼的免疫毒性效应及其作用机制研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2021. |
| 40 | 姚一琳. 斑马鱼肠道微细结构及肠粘膜屏障的研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学,2010. |
| [1] | Xuejiao CHEN, Ping YU, Di ZHAO, Jia SONG, Xiangbo MIN. Study on the Anti-inflammatory Effect of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HCS03-001 Based on Zebrafish Model and Network Pharmacology [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(2): 295-303. |
| [2] | Xin ZHAO, Xinyu LI, Minghao LI, Shiyi ZHOU, Yaqi DENG, Zhiyuan ZHENG, Wei ZOU. Application of Caenorhabditis elegans Model in the Study of Memory and Forgetting Behavior [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(6): 837-843. |
| [3] | Ali WANG, Jiangdong LIU. Research Progress on the CRISPR/Cas System in Zebrafish [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(4): 485-491. |
| [4] | Qianting YANG, Xiaoying TIAN, Junfang ZHANG, Bingshe HAN. Effect of tp53 Knockout on High Temperature Tolerance and Swimming Capacity in Zebrafish [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(4): 580-587. |
| [5] | Maolan XIONG, Siyan WEI, Juntao LUO, Bingshe HAN, Junfang ZHANG. The Effects of hdac11 Knockout of Zebrafish on Lipid Metabolism [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(4): 588-595. |
| [6] | Wei ZHANG, Hongfang WANG, Baohua XU. Overview of the Main Molecular Mechanisms of Biological Aging [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(2): 228-233. |
| [7] | Guizhen GAO, Yungu ZHAI, Lubin ZHANG, Jinmei CHANG, Haihua LUO, Xiaoming WU. Advances on Germplasm Identification and Variety Breeding to Saline-alkali Stress of Rapeseed [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2022, 12(5): 647-654. |
| [8] | Geru TAO, Shucun QIN. Molecular Mechanism of Hydrogen Biomedicine in Relieving Free Radical Oxidative Stress [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2022, 12(4): 490-496. |
| [9] | LIAO Taotao1, TANG Junjie1, SHI Xiaoxiang1, ZHANG Weijie2, MAO Guanghua1*, WU Xiangyang1*. Study on the Immunotoxicity of Short-term Exposure of Decabromodiphenyl Ether (BDE-209) in Adult Mice [J]. Curr. Biotech., 2021, 11(2): 204-213. |
| [10] | XIE Yadong, XIE Mingxu, LI Jie, WANG Anran, YANG Peilong, RAN Chao, ZHOU Zhigang*. Establishment of a Germ-free Zebrafish Model for Spring Viraemia of Carp Virus Infection [J]. Curr. Biotech., 2019, 9(4): 369-374. |
| [11] | YAO Mawulikplimi Adzavon, ZHAO Pengxiang*, ZHANG Xujuan, WANG Limin, MA Xuemei. Research Progress on Molecular Mechanism of Microphage Migration Inhibotry Factor [J]. Curr. Biotech., 2018, 8(5): 389-396. |
| [12] | LU Chengyao§, ZHANG Zhen§, DING Qianwen, LI Jie, LIU Yu, RAN Chao, ZHANG Hongling, ZHANG Jinxiong, ZHOU Zhigang*. Effect of Exogenous Insulin on Blood Glucose and its Transport in Zebrafish [J]. Curr. Biotech., 2018, 8(5): 426-434. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||