Current Biotechnology ›› 2023, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (3): 375-382.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2023.0009
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
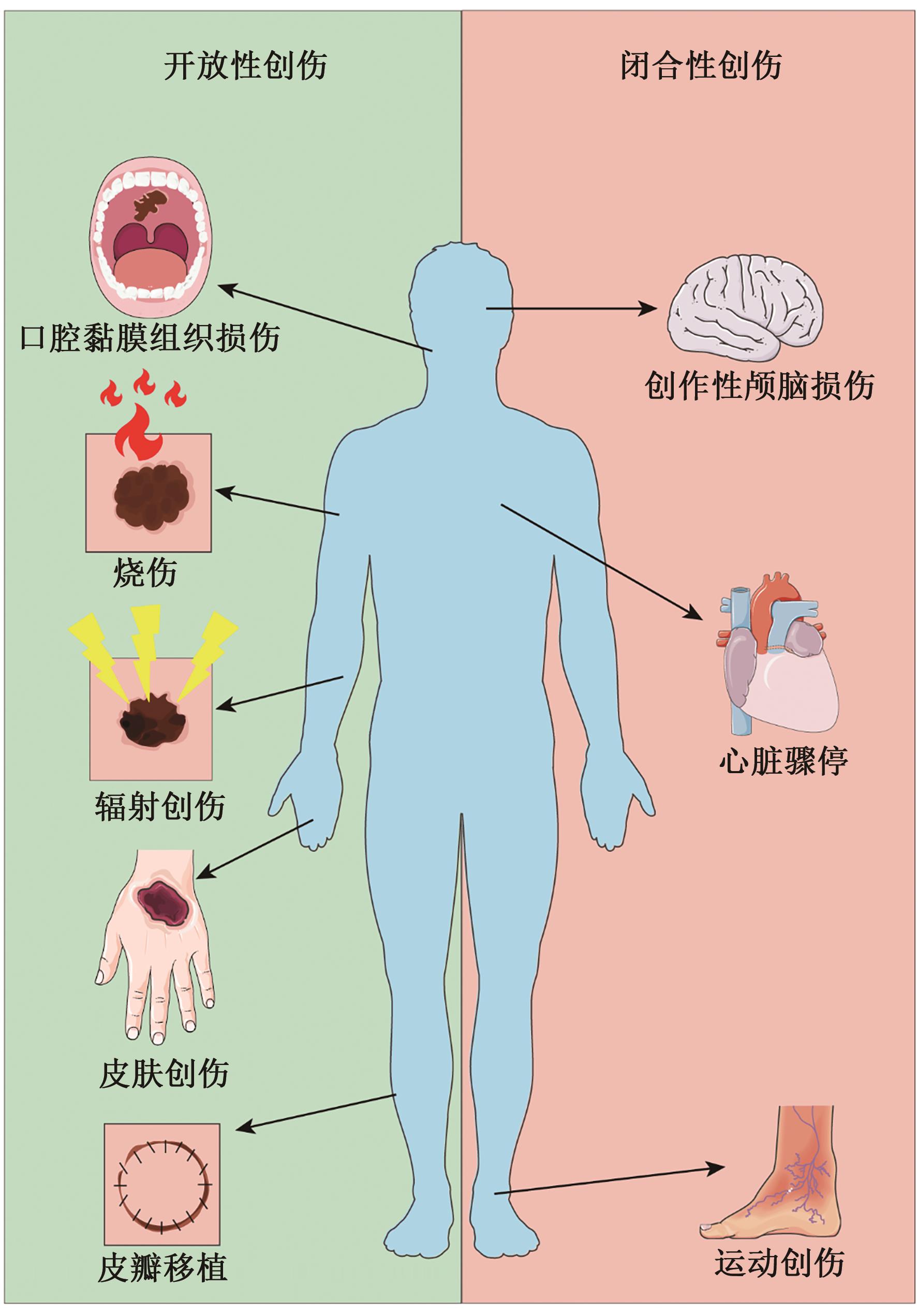
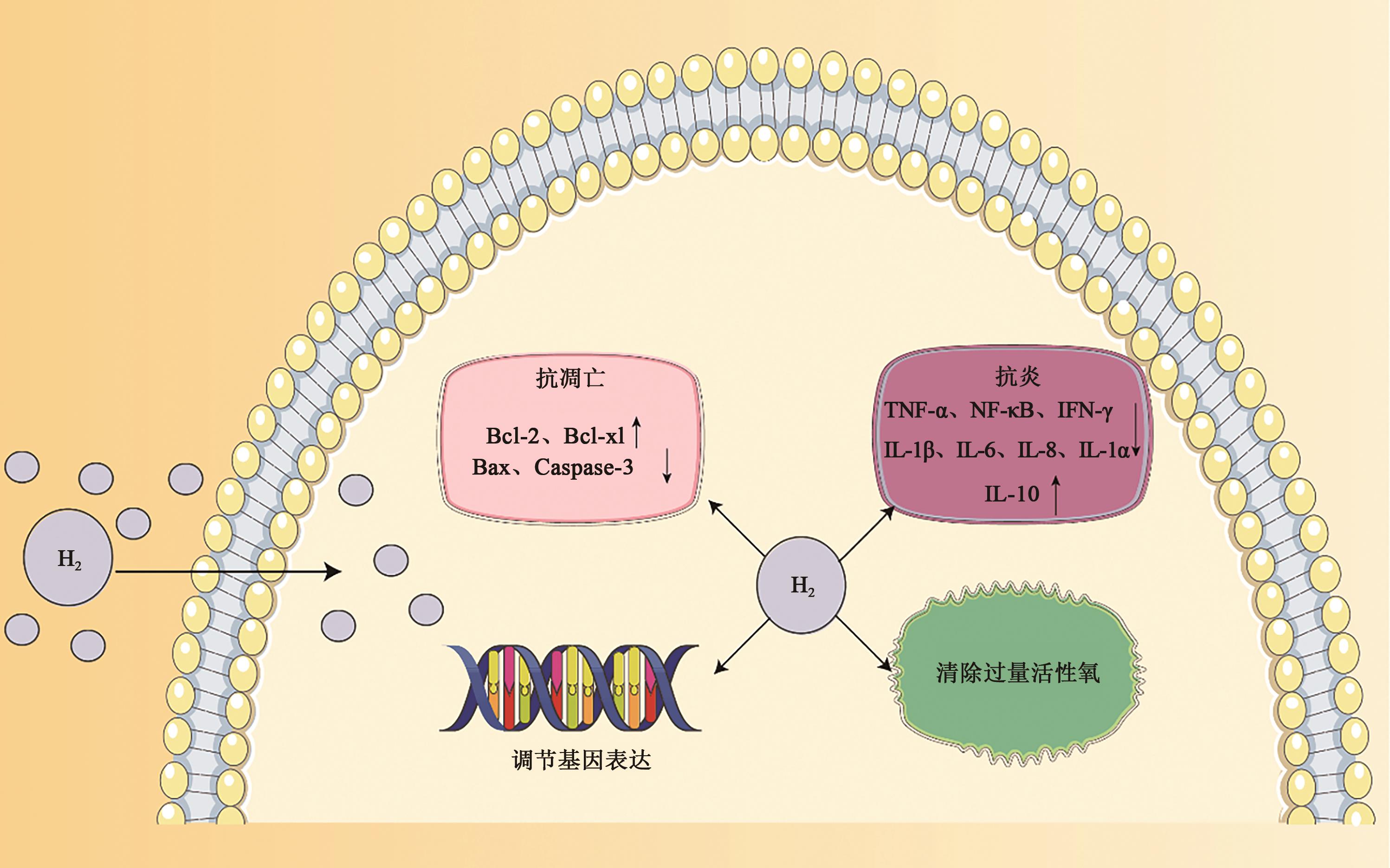
Research Progress on the Application of Hydrogen in Trauma Rescue and Treatment
Zisong CAI( ), Pengxiang ZHAO(
), Pengxiang ZHAO( ), Xujuan ZHANG, Ziyi LIU, Mengyu LIU, Fei XIE, Chen MA
), Xujuan ZHANG, Ziyi LIU, Mengyu LIU, Fei XIE, Chen MA
- Faculty of Environment and Life,Beijing University of Technology,Beijing 100124,China
-
Received:2023-02-06Accepted:2023-03-06Online:2023-05-25Published:2023-06-12 -
Contact:Pengxiang ZHAO
氢气在创伤救治中的应用研究进展
蔡子松( ), 赵鹏翔(
), 赵鹏翔( ), 张旭娟, 刘子怡, 刘梦昱, 谢飞, 马晨
), 张旭娟, 刘子怡, 刘梦昱, 谢飞, 马晨
- 北京工业大学环境与生命学部,北京 100124
-
通讯作者:赵鹏翔 -
作者简介:蔡子松 E-mail:1595075516@qq.com; -
基金资助:军委后勤保障部开放研究重点项目(BHJ17L018)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zisong CAI, Pengxiang ZHAO, Xujuan ZHANG, Ziyi LIU, Mengyu LIU, Fei XIE, Chen MA. Research Progress on the Application of Hydrogen in Trauma Rescue and Treatment[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(3): 375-382.
蔡子松, 赵鹏翔, 张旭娟, 刘子怡, 刘梦昱, 谢飞, 马晨. 氢气在创伤救治中的应用研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2023, 13(3): 375-382.
share this article
| 1 | WHITE A J, GILAD R, MOTIVALA S, et al.. Negative pressure wound therapy in spinal surgery[J/OL]. Bioengineering (Basel), 2022, 9(11): 614[2022-09-29]. . |
| 2 | RODRIGUES M, KOSARIC N, BONHAM C A, et al.. Wound healing: a cellular perspective[J]. Physiol. Rev., 2019, 99(1): 665-706. |
| 3 | CAPIZZI A, WOO J, VERDUZCO-GUTIERREZ M. Traumatic brain injury[J]. Med. Clin. N. Am., 2020, 104(2): 213-238. |
| 4 | BASUKALA S, TAMANG A, BHUSAL U, et al.. Delayed splenic rupture following trivial trauma: a case report and review of literature[J/OL]. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep., 2021, 88: 106481[2021-10-06]. . |
| 5 | NIELSEN J W, SHI J, WHEELER K, et al.. Resource use in pediatric blunt and penetrating trauma[J]. J. Surg. Res., 2016, 202(2): 436-442. |
| 6 | EMING S A, MARTIN P, TOMIC-CANIC M. Wound repair and regeneration: mechanisms, signaling, and translation[J/OL]. Sci. Transl. Med., 2014, 6(265): 265[2014-12-06]. . |
| 7 | LI P, GONG Z, SHULTZ L D, et al.. Mesenchymal stem cells: from regeneration to cancer[J]. Pharmacol. Therapeut., 2019, 200: 42-54. |
| 8 | ARMSTRONG D G, LAVERY L A, DIABETIC F S C. Negative pressure wound therapy after partial diabetic foot amputation: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial[J]. Lancet, 2005, 366(9498): 1704-1710. |
| 9 | 马战军,王天堂.负压封闭引流技术在创面治疗中的新进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2018,26(7):84-88. |
| 10 | ROBSON M C. Growth factors as wound healing agents[J]. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 1991, 2(6): 863-867. |
| 11 | KESSLER L, BILBAULT P, ORTEGA F, et al.. Hyperbaric oxygenation accelerates the healing rate of nonischemic chronic diabetic foot ulcers: a prospective randomized study[J]. Diabetes Care, 2003, 26(8): 2378-2382. |
| 12 | DOLE M, WILSON F R, FIFE W P. Hyperbaric hydrogen therapy: a possible treatment for cancer[J]. Science, 1975, 190(4210): 152-154. |
| 13 | OHSAWA I, ISHIKAWA M, TAKAHASHI K, et al.. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals[J]. Nat. Med., 2007, 13(6): 688-694. |
| 14 | 寻治铭,赵清辉,琚芳迪,等.氢分子在临床应用中的研究进展[J].生物技术进展,2019,9(3):217-222. |
| 15 | LAURENT G, JAFFREZOU J P. Signaling pathways activated by daunorubicin[J]. Blood, 2001, 98(4): 913-924. |
| 16 | 马雪梅,张鑫,谢飞,等.氢气生物学作用的生物酶基础[J].生物技术进展,2020,10(1):15-22. |
| 17 | PENDERS J, KISSNER R, KOPPENOL W H. ONOOH does not react with H2: potential beneficial effects of H2 as an antioxidant by selective reaction with hydroxyl radicals and peroxynitrite[J]. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 2014, 75: 191-194. |
| 18 | JIN Z, ZHAO P, GONG W, et al.. Fe-porphyrin: a redox-related biosensor of hydrogen molecule[J]. Nano Res., 2022,6(2): 1-6. |
| 19 | EMBLEY T M, MARTIN W. Eukaryotic evolution, changes and challenges[J]. Nature, 2006, 440(7084): 623-630. |
| 20 | HORTON J W. Free radicals and lipid peroxidation mediated injury in burn trauma: the role of antioxidant therapy[J]. Toxicology, 2003, 189(1-2): 75-88. |
| 21 | SINGH V, DEVGAN L, BHAT S, et al.. The pathogenesis of burn wound conversion[J]. Ann. Plast Surg., 2007, 59(1): 109-115. |
| 22 | GUO S X, JIN Y Y, FANG Q, et al.. Beneficial effects of hydrogen-rich saline on early burn-wound progression in rats[J/OL]. PLoS ONE, 2015, 10(4): e0124897[2015-04-13]. . |
| 23 | 潘宇红,黄璇,丁羚涛,等.严重烧伤患者促炎和抗炎细胞因子的变化及其意义[J].国际检验医学杂志,2013,34(19):10-13. |
| 24 | 张余,廖毅.氢在治疗烧伤中的研究进展[J].西南军医,2015,17(2):189-191. |
| 25 | FANG Y, FU X J, GU C, et al.. Hydrogen-rich saline protects against acute lung injury induced by extensive burn in rat model[J]. J. Burn. Care Res., 2011, 32(3): 82-91. |
| 26 | GUO S X, FANG Q, YOU C G, et al.. Effects of hydrogen-rich saline on early acute kidney injury in severely burned rats by suppressing oxidative stress induced apoptosis and inflammation[J]. J. Transl. Med., 2015, 13: 1-15. |
| 27 | 骆宁王.富氢水浸浴治疗烧伤患者面部色素沉着疗效观察[J].中国临床实用医学,2014(3):7-10. |
| 28 | GRANGER D N, KVIETYS P R. Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: the evolution of a concept[J]. Redox Biol., 2015, 6: 524-551. |
| 29 | ZHAO L, WANG Y B, QIN S R, et al.. Protective effect of hydrogen-rich saline on ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat skin flap[J]. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B, 2013, 14(5): 382-391. |
| 30 | LIU Y Q, LIU Y F, MA X M, et al.. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates skin ischemia/reperfusion induced apoptosis via regulating Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and ASK-1/JNK pathway[J]. J. Plast Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg., 2015, 68(7): 147-156. |
| 31 | HAO Y, DONG X, LIU H, et al.. Preconditioning with one-time hydrogen gas does not attenuate skin flap ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat models[J]. J. Plast Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg., 2019, 72(10): 1661-1668. |
| 32 | SUN B K, SIPRASHVILI Z, KHAVARI P A. Advances in skin grafting and treatment of cutaneous wounds[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6212): 941-945. |
| 33 | 王婷.富氢水促进犬皮肤创面愈合的效果评价[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2020. |
| 34 | FERGUSON M W, O'KANE S. Scar-free healing: from embryonic mechanisms to adult therapeutic intervention[J]. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond B Biol. Sci., 2004, 359(1445): 839-850. |
| 35 | MCQUESTION M. Evidence-based skin care management in radiation therapy: clinical update[J]. Semin. Oncol. Nurs., 2011, 27(2): 1-17. |
| 36 | KIM J H, KOLOZSVARY A J, JENROW K A, et al.. Mechanisms of radiation-induced skin injury and implications for future clinical trials[J]. Int. J. Radiat. Biol., 2013, 89(5): 311-318. |
| 37 | WATANABE S, FUJITA M, ISHIHARA M, et al.. Protective effect of inhalation of hydrogen gas on radiation-induced dermatitis and skin injury in rats[J]. J. Radiat. Res., 2014, 55(6): 1107-1113. |
| 38 | ZHOU P, LIN B, WANG P, et al.. The healing effect of hydrogen-rich water on acute radiation-induced skin injury in rats[J]. J. Radiat. Res., 2019, 60(1): 17-22. |
| 39 | QIAN L, SHEN J, CHUAI Y, et al.. Hydrogen as a new class of radioprotective agent[J]. Int. J. Biol. Sci., 2013, 9(9): 887-894. |
| 40 | POLIMENI G, XIROPAIDIS A V, WIKESJO U M. Biology and principles of periodontal wound healing/regeneration[J]. Periodontology, 2000, 2006, 41(1): 30-47. |
| 41 | LI X, NOBUHIKO M. Hydrogen-rich water achieves cytoprotection from oxidative stress injury in human gingival fibroblasts in culture or 3D-tissue equivalents, and wound-healing promotion, together with ROS-scavenging and relief from glutathione diminishment[J]. Hum. Cell, 2017, 30(2): 72-87. |
| 42 | TAMAKI N, ORIHUELA-CAMPOS R C, FUKUI M, et al.. Hydrogen-rich water intake accelerates oral palatal wound healing via activation of the Nrf2/antioxidant defense pathways in a rat model[J/OL]. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev., 2016, 2016: 5679040[2016-12-21]. . |
| 43 | 琚芳迪,谢飞,郭大志,等.吸氢对大鼠颅脑损伤引起的急性炎症反应的抑制作用[J].生物技术进展,2020,10(5): 541-549. |
| 44 | CORNELIUS C, CRUPI R, CALABRESE V, et al.. Traumatic brain injury: oxidative stress and neuroprotection[J]. Antioxid. Redox Sign., 2013, 19(8): 836-853. |
| 45 | ZHAO Q H, XIE F, GUO D Z, et al.. Hydrogen inhalation inhibits microglia activation and neuroinflammation in a rat model of traumatic brain injury[J/OL]. Brain Res., 2020, 1748: 147053[2020-08-16]. . |
| 46 | HWANG I K, PARK J H, LEE T K, et al.. CD74-immunoreactive activated M1 microglia are shown late in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 region following transient cerebral ischemia[J]. Mol. Med. Rep., 2017, 15(6): 4148-4154. |
| 47 | TIAN R, HOU Z, HAO S, et al.. Hydrogen-rich water attenuates brain damage and inflammation after traumatic brain injury in rats[J]. Brain Res., 2016, 1637: 1-13. |
| 48 | HOU Z, LUO W, SUN X, et al.. Hydrogen-rich saline protects against oxidative damage and cognitive deficits after mild traumatic brain injury[J]. Brain Res. Bull., 2012, 88(6): 560-565. |
| 49 | SHAO C, ROBERTS K N, MARKESBERY W R, et al.. Oxidative stress in head trauma in aging[J]. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 2006, 41(1): 77-85. |
| 50 | YUAN J, WANG D, LIU Y, et al.. Hydrogen-rich water attenuates oxidative stress in rats with traumatic brain injury via Nrf2 pathway[J]. J. Surg. Res., 2018, 228: 238-246. |
| 51 | WANG L, ZHAO C, WU S, et al.. Hydrogen gas treatment improves the neurological outcome after traumatic brain injury via increasing miR-21 expression[J]. Shock, 2018, 50(3): 308-315. |
| 52 | OSTOJIC S M, VUKOMANOVIC B, CALLEJA-GONZALEZ J, et al.. Effectiveness of oral and topical hydrogen for sports-related soft tissue injuries[J]. Postgrad. Med., 2014, 126(5): 187-195. |
| 53 | WATSON J, ROUND A, HAMILTON W. Raised inflammatory markers[J]. Brithish Med. J., 2012, 344(31): 54-60. |
| 54 | 东人.氢饱和生理盐水在创伤性脊髓损伤中抗炎效应的实验研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2015. |
| 55 | HARRIS T, MASUD S, LAMOND A, et al.. Traumatic cardiac arrest: a unique approach[J]. Eur. J. Emerg. Med., 2015, 22(2): 72-78. |
| 56 | 王兴磊,张蜀.肾上腺素在创伤性心博骤停患者中的价值[J].重庆医学,2021,50(13):2314-2318. |
| 57 | MOULAERT V R, VERBUNT J A, VAN HEUGTEN C M, et al.. Cognitive impairments in survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a systematic review[J]. Resuscitation, 2009, 80(3): 297-305. |
| 58 | TAMURA T, HAYASHIDA K, SANO M, et al.. Efficacy of inhaled hydrogen on neurological outcome following brain ischemia during post-cardiac arrest care (HYBRID Ⅱ trial): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial[J]. Trials, 2017, 18(1): 1-9. |
| 59 | HAYASHIDA K, SANO M, KAMIMURA N, et al.. H2 gas improves functional outcome after cardiac arrest to an extent comparable to therapeutic hypothermia in a rat model[J/OL]. J. Am. Heart Assoc., 2012, 1(5): e003459[2012-10-16]. . |
| 60 | HUO T T, ZENG Y, LIU X N, et al.. Hydrogen-rich saline improves survival and neurological outcome after cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation in rats[J]. Anesth. Analg., 2014, 119(2): 368-380. |
| 61 | CHEN H, GUO Y, ZHANG Z, et al.. Symbiotic algae-bacteria dressing for producing hydrogen to accelerate diabetic wound healing[J]. Nano Lett., 2022, 22(1): 229-237. |
| 62 | YANG F, CHEN Z, CHEN S A, et al.. Skin ulcers infected with conditional pathogenic strains treated with local hydrogen water packing in two pemphigus vulgaris patients: case reports with follow-up for 2 months[J/OL]. Dermatol. Ther., 2019, 32(5): e13027[2019-07-19]. . |
| 63 | 常银涛.高压氧联合氢水用于胸部战创伤后严重肺损伤治疗的基础研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2017. |
| [1] | HanXiao MA. Development of qPCR Standard Curves for Monitoring Population Dynamics in a Dual-bacterial Fermentative Hydrogen Production System [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(2): 325-332. |
| [2] | Shihao JIANG, Xinyue ZHU, Xiaohu WEN, Ziyi LIU, Pengxiang ZHAO. Research Progress of Hydrogen Molecules in Improving Inflammatory and Osteoporotic Bone Loss Related Diseases [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(4): 576-585. |
| [3] | Jianhong YANG, Boyan LIU, Jun CHEN, Zhihui QIU, Baoqiang LI, Shucun QIN, Yandong NIU, Lei HE. Effects of Pre-treatment of Nanobubble Hydrogen Water on the Mouse Psoriasis Induction by Imiquimod [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(4): 676-684. |
| [4] | Jiaqi SUN, Jia GUO, Chuang ZHANG, Qing LIU, Ziyu WANG, Hanchao XIA, Buxuan QIAN, Fangfang ZHAO, Qi WANG, Jianfeng LIU, Xiangguo LIU. Research Progress of Phosphite Dehydrogenase in Genetically Engineered Microorganisms and Plants [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(2): 173-181. |
| [5] | Xingyu LIU, Guoli ZHAO, Xuejing LI. Application Progress of Hydrogen in Medical Field [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(1): 102-110. |
| [6] | Jianhong YANG, Jun CHEN, Xuefei LI, Lijun LIU, Lili CHEN, Xinsuo DUAN, Shucun QIN, Lei HE. The Potential and Prospect of Molecular Hydrogen in the Treatment of Skin Diseases [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(6): 875-881. |
| [7] | Junkai ZHU, Lingzhi GE, Chao ZHANG, Can CAO, Jiahui WU, Zhen MU. Inhibitory Effect of Hydrogen Molecule on Imiquimod-induced Psoriasis-like Dermatitis in Mice [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(6): 945-953. |
| [8] | Jun LI, Yifei SONG, Yang YI, Chen MA, Ziyi ZHANG⁃HUANG, Linlin DU, Junyu LI, Fei XIE, Xuemei MA. Research Progress on Heme Protein Targets of Gas Signaling Molecules [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(4): 499-508. |
| [9] | Chen MA, Yifei SONG, Yang YI, Ziyi LIU, Fei XIE, Xuemei MA. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Hydrogen and Mitochondria [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(3): 366-374. |
| [10] | Jingyi ZHANG, Xue JIANG, Siyu MA, Zhichao FENG, Yang YI, Chen MA, Yifei SONG, Fei XIE. Research Progress on the Protective Effects of Hydrogen Gas on Traumatic Brain Injury [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(2): 234-239. |
| [11] | Zijia LIU, Xue JIANG, Yang YI, Meng WANG, Cheng MA, Yifei SONG, Fei XIE. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Hydrogen and Intestinal Flora [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2022, 12(6): 847-852. |
| [12] | Yifei SONG, Fei XIE, Chen MA, Xuemei MA. Research Progress on Hydrogenase Activity in Higher Plants [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2022, 12(4): 481-489. |
| [13] | Geru TAO, Shucun QIN. Molecular Mechanism of Hydrogen Biomedicine in Relieving Free Radical Oxidative Stress [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2022, 12(4): 490-496. |
| [14] | Kaiyao HOU, Erfei ZHANG, Lina ZHENG, Hongguang CHEN, Keliang XIE. The Effect of Hydrogen-rich Saline on Mitochondrial Autophagy of Myocardial Cells in Sepsis-induced Mice [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2022, 12(4): 497-502. |
| [15] | Jun CHEN, Shucun QIN, Lei HE. Inhibiting Effect of Hydrogen-rich Saline on Psoriasis in Imiquimod-induced Mouse Models [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2022, 12(4): 503-509. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||