Current Biotechnology ›› 2024, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (3): 406-412.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2023.0174
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Research Progress of Fas-mediated Non-apoptotic Signaling in Tumor Cells
- College of Basic Medicine,Inner Mongolia Medical University,Hohhot 010110,China
-
Received:2024-01-02Accepted:2024-03-25Online:2024-05-25Published:2024-06-18 -
Contact:Jianqiang WU
肿瘤细胞中FAS介导的非凋亡信号通路研究进展
- 内蒙古医科大学基础医学院,呼和浩特 010110
-
通讯作者:武建强 -
作者简介:李蓓蓓 E-mail: libeibei960129@163.com; -
基金资助:内蒙古自治区科技厅项目(2019GG037);内蒙古医科大学肿瘤免疫创新人才团队项目(QNLC-2020006)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Beibei LI, Jianqiang WU. Research Progress of Fas-mediated Non-apoptotic Signaling in Tumor Cells[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(3): 406-412.
李蓓蓓, 武建强. 肿瘤细胞中FAS介导的非凋亡信号通路研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(3): 406-412.
share this article
| 1 | SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al.. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA-Cancer J. Clin., 2021, 71(3): 209-249. |
| 2 | QIU H, CAO S, XU R. Cancer incidence, mortality, and burden in China: a time-trend analysis and comparison with the United States and United Kingdom based on the global epidemiological data released in 2020[J]. Cancer Commun., 2021, 41(10): 1037-1048. |
| 3 | NAGATA S, GOLSTEIN P. The Fas death factor[J]. Science, 1995, 267(5203): 1449-1456. |
| 4 | TIMMER T, DE VRIES E G E, DE JONG S. Fas receptor-mediated apoptosis: a clinical application?[J]. J. Pathol., 2002, 196(2): 125-134. |
| 5 | CHINNAIYAN A M, O'ROURKE K, TEWARI M, et al.. FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis[J]. Cell, 1995, 81(4): 505-512. |
| 6 | KISCHKEL F C, HELLBARDT S, BEHRMANN I, et al.. Cytotoxicity-dependent APO-1 (Fas/CD95)-associated proteins form a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) with the receptor[J]. EMBO J., 1995, 14(22): 5579-5588. |
| 7 | FUCHS Y, STELLER H. Programmed cell death in animal development and disease[J]. Cell, 2011, 147(4): 742-758. |
| 8 | NAGATA S, TANAKA M. Programmed cell death and the immune system[J]. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2017, 17(5): 333-340. |
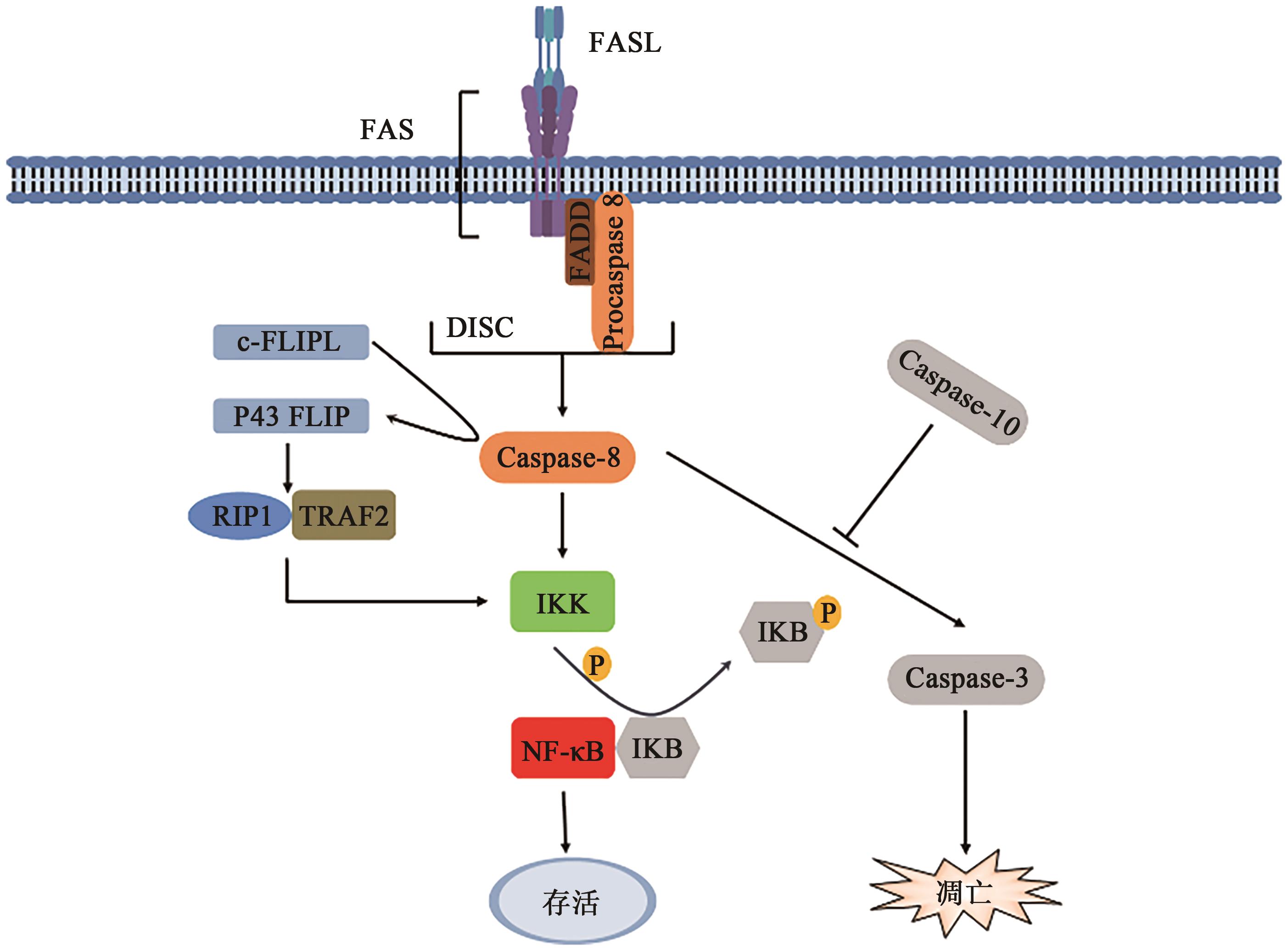
| 9 | CHEN L, MPARK S, TUMANOV A V, et al.. CD95 promotes tumour growth[J]. Nature, 2010, 465(7297): 492-496. |
| 10 | BARNHART B C, LEGEMBRE P, PIETRAS E, et al.. CD95 ligand induces motility and invasiveness of apoptosis-resistant tumor cells[J]. EMBO J., 2004, 23(15): 3175-3185. |
| 11 | HADJI A, CEPPI P, MURMANN A E, et al.. Death induced by CD95 or CD95 ligand elimination[J]. Cell Rep., 2014, 7(1): 208-222. |
| 12 | QUIJANO-RUBIO C, SILGINER M, WELLER M. CD95 gene deletion may reduce clonogenic growth and invasiveness of human glioblastoma cells in a CD95 ligand-independent manner[J/OL]. Cell Death Discov., 2022, 8(1): 341[2024-04-07]. . |
| 13 | QUIJANO-RUBIO C, SILGINER M, WELLER M. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated abrogation of CD95L/CD95 signaling-induced glioma cell growth and immunosuppression increases survival in murine glioma models[J]. J. Neuro Oncol., 2022, 160(2): 299-310. |
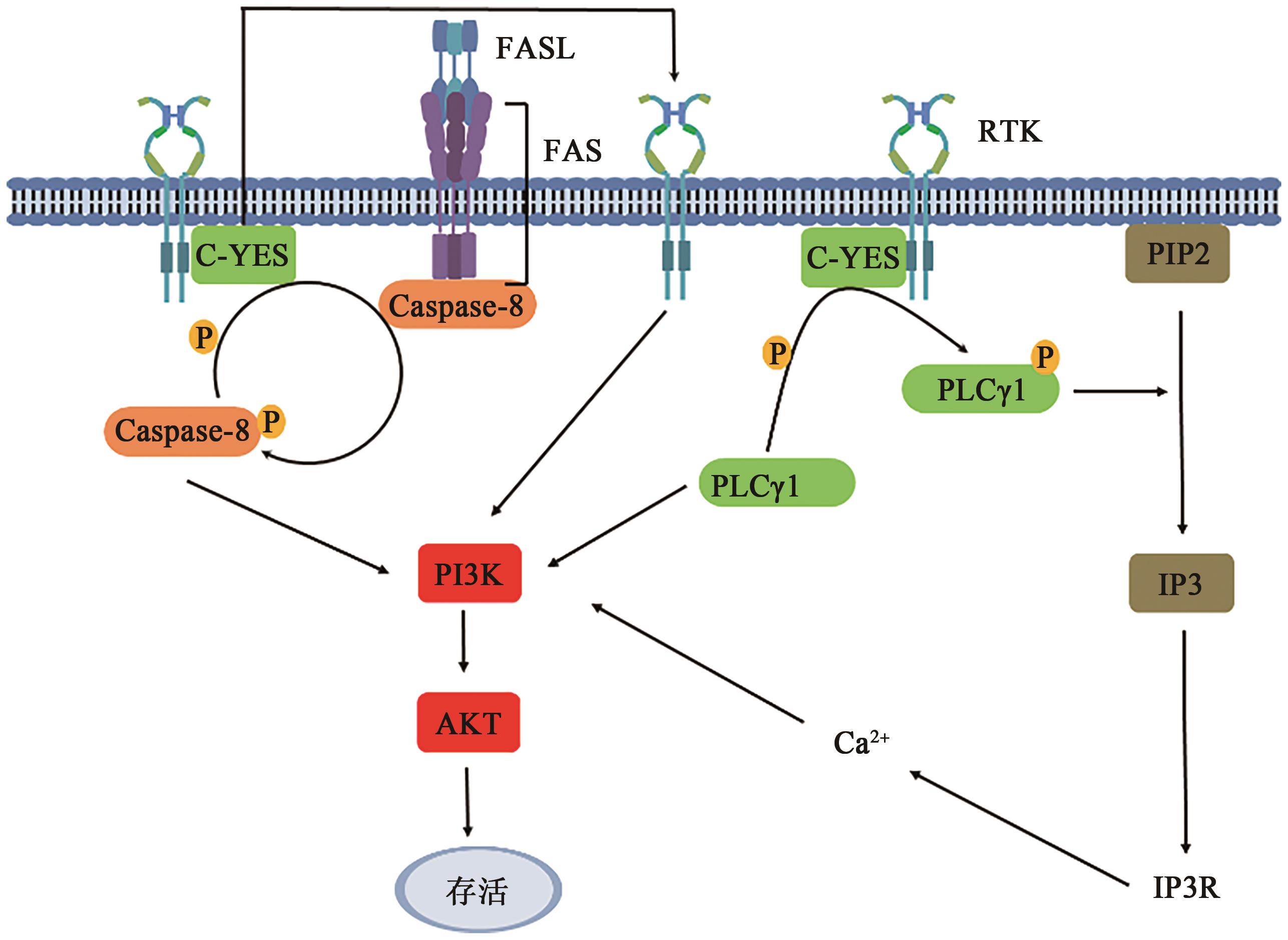
| 14 | CEPPI P, HADJI A, KOHLHAPP F J, et al.. CD95 and CD95L promote and protect cancer stem cells[J/OL]. Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 5238[2024-04-07]. . |
| 15 | QADIR A S, GUÉGAN J P, GINESTIER C, et al.. CD95/Fas protects triple negative breast cancer from anti-tumor activity of NK cells[J/OL]. iScience, 2021, 24(11): 103348[2024-04-07]. . |
| 16 | BALTA G S, MONZEL C, KLEBER S, et al.. 3D cellular architecture modulates tyrosine kinase activity, thereby switching CD95-mediated apoptosis to survival[J]. Cell Rep., 2019, 29(8): 2295-2306. |
| 17 | LE GALLO M, POISSONNIER A, BLANCO P, et al.. CD95/fas, non-apoptotic signaling pathways, and kinases[J/OL]. Front. Immunol., 2017, 8: 1216[2024-04-07]. . |
| 18 | CHAKRABANDHU K, HUAULT S, DURIVAULT J, et al.. An evolution-guided analysis reveals a multi-signaling regulation of fas by tyrosine phosphorylation and its implication in human cancers[J/OL]. PLoS Biol., 2016, 14(3): e1002401[2024-04-07]. . |
| 19 | LAVRIK I N, GOLKS A, RIESS D, et al.. Analysis of CD95 threshold signaling: triggering of CD95 (FAS/APO-1) at low concentrations primarily results in survival signaling[J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2007, 282(18): 13664-13671. |
| 20 | LEGEMBRE P, BARNHART B C, ZHENG L, et al.. Induction of apoptosis and activation of NF-κB by CD95 require different signalling thresholds[J]. EMBO Rep., 2004, 5(11): 1084-1089. |
| 21 | YU H, LIN L, ZHANG Z, et al.. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study[J/OL]. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther., 2020, 5(1): 209[2024-04-07]. . |
| 22 | NEUMANN L, PFORR C, BEAUDOUIN J, et al.. Dynamics within the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex decide life and death of cells[J/OL]. Mol. Syst. Biol., 2010, 6: 352[2024-04-07]. . |
| 23 | BUCHBINDER J H, PISCHEL D, SUNDMACHER K, et al.. Quantitative single cell analysis uncovers the life/death decision in CD95 network[J/OL]. PLoS Comput. Biol., 2018, 14(9): e1006368[2024-04-07]. . |
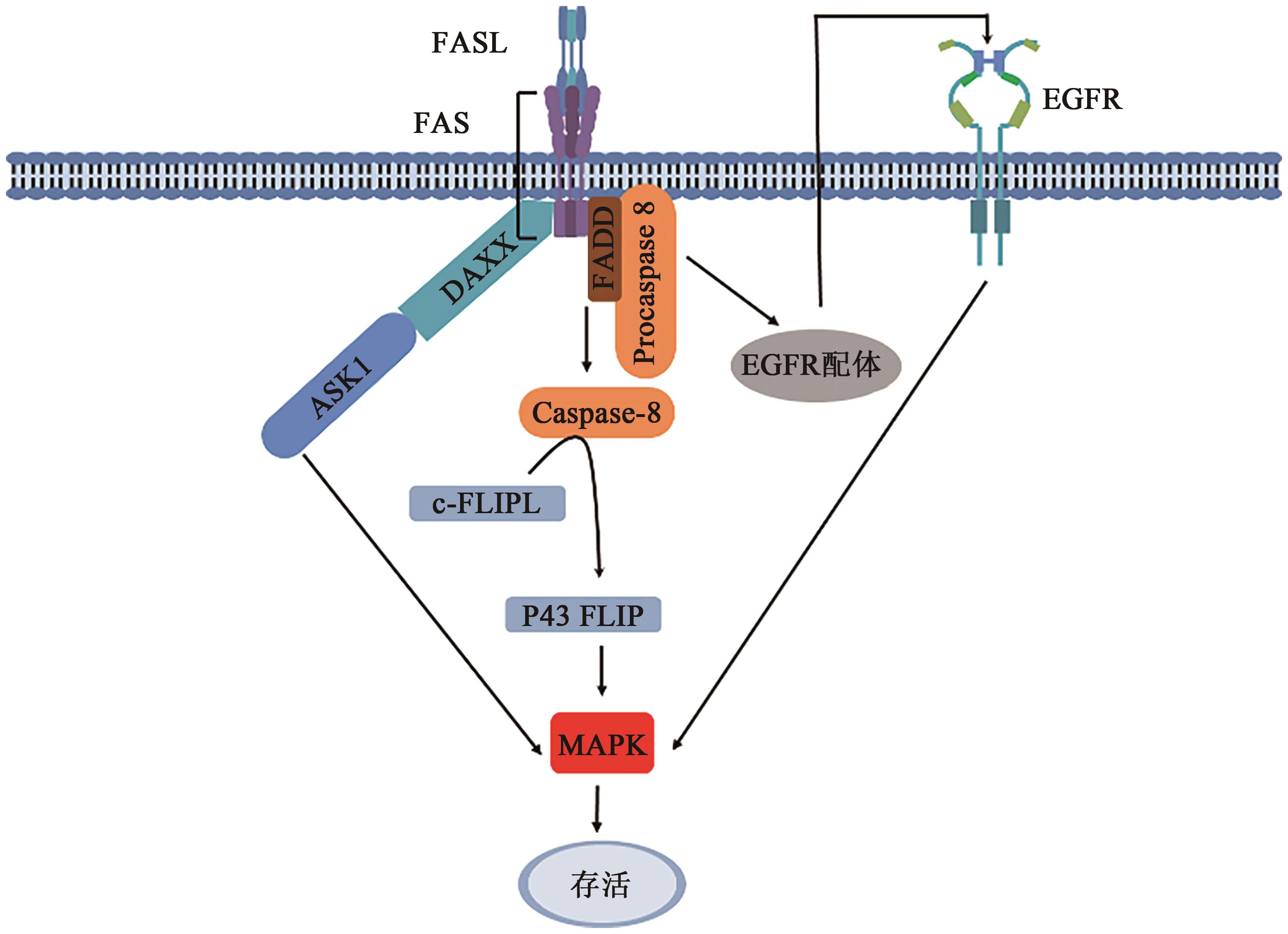
| 24 | KREUZ S, SIEGMUND D, RUMPF J J, et al.. NF-κB activation by Fas is mediated through FADD, caspase-8, and RIP and is inhibited by FLIP[J]. J. Cell Biol., 2004, 166(3): 369-380. |
| 25 | KARIN M, BEN-NERIAH Y. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-κB activity[J]. Annu. Rev. Immunol., 2000, 18: 621-663. |
| 26 | HORN S, HUGHES M A, SCHILLING R, et al.. Caspase-10 negatively regulates caspase-8-mediated cell death, switching the response to CD95L in favor of NF-κB activation and cell survival[J]. Cell Rep., 2017, 19(4): 785-797. |
| 27 | MATSUDA I, MATSUO K, MATSUSHITA Y, et al.. The C-terminal domain of the long form of cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (c-FLIPL) inhibits the interaction of the caspase 8 prodomain with the receptor-interacting protein 1 (RIP1) death domain and regulates caspase 8-dependent nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) activation[J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2014, 289(7): 3876-3887. |
| 28 | RISSO V, LAFONT E, LE GALLO M. Therapeutic approaches targeting CD95L/CD95 signaling in cancer and autoimmune diseases[J/OL]. Cell Death Dis., 2022, 13(3): 248[2024-04-07]. . |
| 29 | FRUMAN D A, CHIU H, HOPKINS B D, et al.. The PI3K pathway in human disease[J]. Cell, 2017, 170(4): 605-635. |
| 30 | FOUQUÉ A, LEGEMBRE P. Study of the CD95-mediated non-apoptotic signaling pathway: PI3K[J]. Methods Mol. Biol., 2017, 1557: 103-110. |
| 31 | TAUZIN S, CHAIGNE-DELALANDE B, SELVA E, et al.. The naturally processed CD95L elicits a c-yes/calcium/PI3K-driven cell migration pathway[J/OL]. PLoS Biol., 2011, 9(6): e1001090[2024-04-07]. . |
| 32 | KLEBER S, SANCHO-MARTINEZ I, WIESTLER B, et al.. Yes and PI3K bind CD95 to signal invasion of glioblastoma[J]. Cancer Cell, 2008, 13(3): 235-248. |
| 33 | CURSI S, RUFINI A, STAGNI V, et al.. Src kinase phosphorylates Caspase-8 on Tyr380: a novel mechanism of apoptosis suppression[J]. EMBO J., 2006, 25(9): 1895-1905. |
| 34 | FINLAY D, HOWES A, VUORI K. Critical role for caspase-8 in epidermal growth factor signaling[J]. Cancer Res., 2009, 69(12): 5023-5029. |
| 35 | MOTZ G T, SANTORO S P, WANG L P, et al.. Tumor endothelium FasL establishes a selective immune barrier promoting tolerance in tumors[J]. Nat. Med., 2014, 20(6): 607-615. |
| 36 | STELLER E J, RITSMA L, RAATS D A, et al.. The death receptor CD95 activates the cofilin pathway to stimulate tumour cell invasion[J]. EMBO Rep., 2011, 12(9): 931-937. |
| 37 | GUO Y J, PAN W W, LIU S B, et al.. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis[J]. Exp. Ther. Med., 2020, 19(3): 1997-2007. |
| 38 | ZHANG Y, JIN T, DOU Z, et al.. The dual role of the CD95 and CD95L signaling pathway in glioblastoma[J/OL]. Front. Immunol., 2022, 13: 1029737[2024-04-07]. . |
| 39 | CHANG H Y, NISHITOH H, YANG X, et al.. Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) by the adapter protein Daxx[J]. Science, 1998, 281(5384): 1860-1863. |
| 40 | KOENIG A, BUSKIEWICZ I A, FORTNER K A, et al.. The c-FLIPL cleavage product p43FLIP promotes activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), and caspase-8 and T cell survival[J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2014, 289(2): 1183-1191. |
| 41 | FARLEY S M, PURDY D E, RYABININA O P, et al.. Fas ligand-induced proinflammatory transcriptional responses in reconstructed human epidermis. Recruitment of the epidermal growth factor receptor and activation of MAP kinases[J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2008, 283(2): 919-928. |
| 42 | O'DONNELL M A, PEREZ-JIMENEZ E, OBERST A, et al.. Caspase 8 inhibits programmed necrosis by processing CYLD[J]. Nat. Cell Biol., 2011, 13(12): 1437-1442. |
| 43 | ZHU G, HERLYN M, YANG X. TRIM15 and CYLD regulate ERK activation via lysine-63-linked polyubiquitination[J]. Nat. Cell Biol., 2021, 23(9): 978-991. |
| 44 | XU S, TANG L, LI X, et al.. Immunotherapy for glioma: current management and future application[J]. Cancer Lett., 2020, 476: 1-12. |
| 45 | TUETTENBERG J, SEIZ M, MDEBATIN K, et al.. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety and tolerability of APG101, a CD95-Fc fusion protein, in healthy volunteers and two glioma patients[J]. Int. Immunopharmacol., 2012, 13(1): 93-100. |
| 46 | WICK W, FRICKE H, JUNGE K, et al.. A phase Ⅱ, randomized, study of weekly APG101+reirradiation versus reirradiation in progressive glioblastoma[J]. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20(24): 6304-6313. |
| 47 | WEI K C, HSU P W, TSAI H C, et al.. Safety and tolerability of asunercept plus standard radiotherapy/temozolomide in Asian patients with newly-diagnosed glioblastoma: a phase I study[J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2021, 11(1): 24067[2024-04-07]. . |
| 48 | BLAES J, THOMÉ C M, NPFENNING P, et al.. Inhibition of CD95/CD95L (FAS/FASLG) signaling with APG101 prevents invasion and enhances radiation therapy for glioblastoma[J]. Mol. Cancer Res., 2018, 16(5): 767-776. |
| [1] | Lulu ZHAO, Tian HONG, Yiran HAO, Erning CHEN, Jingwen LI, Meihong DU. Research Progress of Immunomagnetic Separation Technology in Detection of Circulating Tumor Cell [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(4): 606-614. |
| [2] | Lina ZHU, Zhiling SONG. Autophagy and Apoptosis: Interactions and Their Role in Disease [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(4): 622-626. |
| [3] | Xiaoyi ZHAI, Haiyue ZHANG, Wenjia GUO, Xiaogang DONG. Research Progress of Cancer-associated Fibroblasts in Breast Cancer [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(4): 636-644. |
| [4] | Lixin XIONG, Yujie WANG, Zhongle LI, Enming ZHONG, Shouyang YU, Yuxin JIANG, Hongshu SUI, Ronghua LIN. Research Progress on Neurodevelopmental Toxicity in Offspring of PFASs Exposure [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(4): 661-667. |
| [5] | Xiaoya LIU, Shuomin ZHANG, Peng ZHENG, Rui MA, Chaojun ZHANG. Role and Mechanisms of DBNDD1 in Colorectal Cancer Development [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(4): 726-734. |
| [6] | Geyemuri WU, Jianqiang WU. Anti-tumor Effects of Gentian Violet [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(2): 226-233. |
| [7] | Xu ZHU, Yingnan ZHANG, Jinfa MA, Lihong SHI. The Role of Ptbp1 in T Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Mice [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(2): 341-348. |
| [8] | Kaijing SUN, Xinze LIU, Xin JIN, Xue YANG, Qi WANG, Yu LI, Changbao CHEN, Xilin WAN. Research Progress on Antitumor Active Constituents and Their Mechanism of Action of Traditional Chinese Medicine Sanghuangporus baumii [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(6): 929-936. |
| [9] | Hui SONG, Wengang CAO, Xiaowen XIAO, Jun DU. Development and Application of Fast NGS Sequencing Method for Plasmid DNA [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(4): 594-600. |
| [10] | Yan ZENG, Hengcheng ZHU, Kang YANG. The Mechanism of DNASE1L3 in Renal Cell Carcinoma [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(3): 486-491. |
| [11] | Yeerkenbieke BUERLAN, Wenjia GUO, Xiaogang DONG. Advances on the Function of POSTN in Tumor Microenvironment [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(2): 205-210. |
| [12] | Lili SUN, Yuemaierabola ANWAIER, Fuzhong LIU, Yeerkenbieke BUERLAN, Ye DILINAER, Wenjia GUO. Construction of Prognostic Prediction Model of Breast Cancer Based on Tumor-associated Fibroblast Genes and Analysis of Immune Infiltration [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(2): 312-322. |
| [13] | Pengxiao ZHANG, Nian HU. The Research Progress on Action Mechanism of Melanoma Immunotherapy [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(6): 900-906. |
| [14] | Yuemaierabola ANWAIER, Lili SUN, Yeerkenbieke BUERLAN, Wenjia GUO. Advances on the Role of Piezo1 in Cancer [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(5): 712-717. |
| [15] | Wenbo MA, Yiqun PAN, Qun WANG, Zhuang MA, Minglian WANG, Yishu YANG. Preliminary Study on the Application of Graphene-coated Iron Nitride Magnetic Beads to Capture Lung Cancer Circulating Tumor Cells [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(4): 628-636. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||