Current Biotechnology ›› 2023, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (5): 807-817.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2023.0052
• Articles • Previous Articles
Research on the Mechanism of Jinyinhua Oral Liquid in the Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
Changhu KE1,2( ), Yaqing WU2, Xueru DING1, Huimin HUANG1, Hui YAN1(
), Yaqing WU2, Xueru DING1, Huimin HUANG1, Hui YAN1( )
)
- 1.Sinopharm Dongfeng General Hospital,Hubei University of Medicine,Hubei Shiyan 442008,China
2.School of Pharmacy,Hubei University of Medicine,Hubei Shiyan 442000,China
-
Received:2023-04-17Accepted:2023-06-09Online:2023-09-25Published:2023-10-10 -
Contact:Hui YAN
基于网络药理学和分子对接探讨金银花口服液防治新型冠状病毒感染的作用机制
柯昌虎1,2( ), 吴亚晴2, 丁雪茹1, 黄慧敏1, 严慧1(
), 吴亚晴2, 丁雪茹1, 黄慧敏1, 严慧1( )
)
- 1.湖北医药学院附属国药东风总医院,湖北 十堰 442008
2.湖北医药学院药学院,湖北 十堰 442000
-
通讯作者:严慧 -
作者简介:柯昌虎E-mail: KCHDFZYY@163.com; -
基金资助:湖北省卫生健康委科研项目(WJ2021F054);十堰市科技局科研项目(22Y75);十堰市软科学研究计划项目(2022R020)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Changhu KE, Yaqing WU, Xueru DING, Huimin HUANG, Hui YAN. Research on the Mechanism of Jinyinhua Oral Liquid in the Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(5): 807-817.
柯昌虎, 吴亚晴, 丁雪茹, 黄慧敏, 严慧. 基于网络药理学和分子对接探讨金银花口服液防治新型冠状病毒感染的作用机制[J]. 生物技术进展, 2023, 13(5): 807-817.
share this article
| 分子编码 | 成分名称 | 口服生物利用度/% | 类药性 | 结构式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOL001494 | 亚油酸乙酯 | 42.00 | 0.19 | 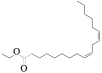 |
| MOL001495 | 亚麻酸乙酯 | 46.10 | 0.20 | 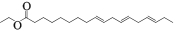 |
| MOL002914 | 圣草酚 | 41.35 | 0.24 | 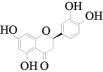 |
| MOL002773 | β-胡萝卜素 | 37.18 | 0.58 | 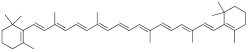 |
| MOL003036 | ZINC03978781 | 43.83 | 0.76 | 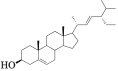 |
| MOL003044 | 金圣草素 | 35.85 | 0.27 | 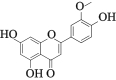 |
| MOL003059 | 隐黄质 | 47.25 | 0.57 | 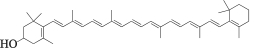 |
| MOL003062 | 玫红黄质 | 31.22 | 0.55 | 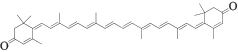 |
| MOL003095 | 伞房花耳草素 | 51.96 | 0.41 | 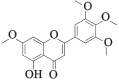 |
| MOL003101 | 7-表断马钱子苷半缩醛内酯 | 46.13 | 0.58 | 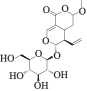 |
| MOL003124 | XYLOSTOSIDINE | 43.17 | 0.64 | 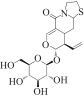 |
| MOL000358 | β-谷甾醇 | 36.91 | 0.75 | 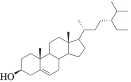 |
| MOL000422 | 山奈酚 | 41.88 | 0.24 | 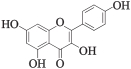 |
| MOL000449 | 豆甾醇 | 43.83 | 0.76 | 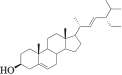 |
| MOL000006 | 木犀草素 | 36.16 | 0.25 | 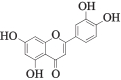 |
| MOL000098 | 槲皮素 | 46.43 | 0.28 | 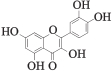 |
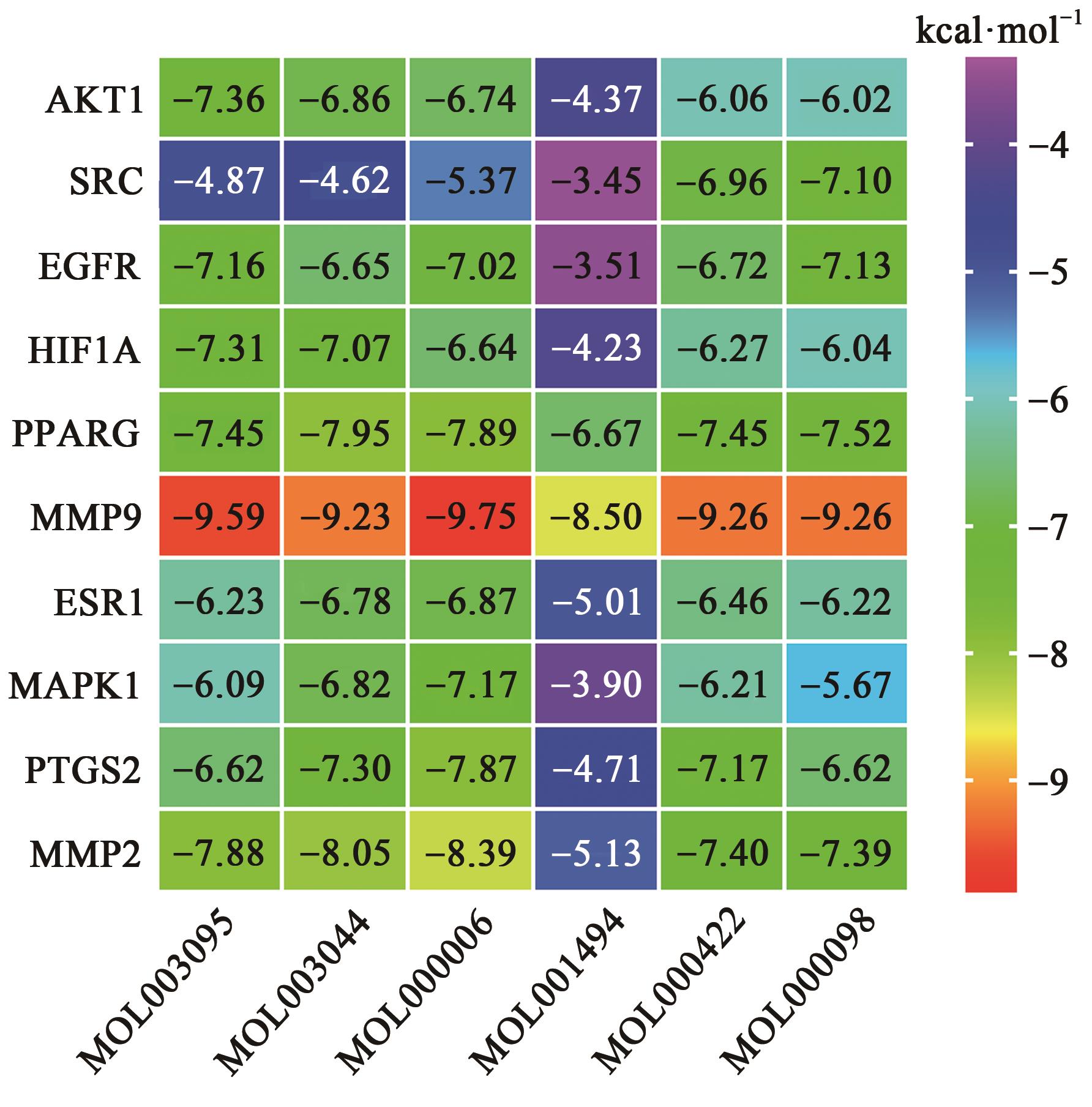
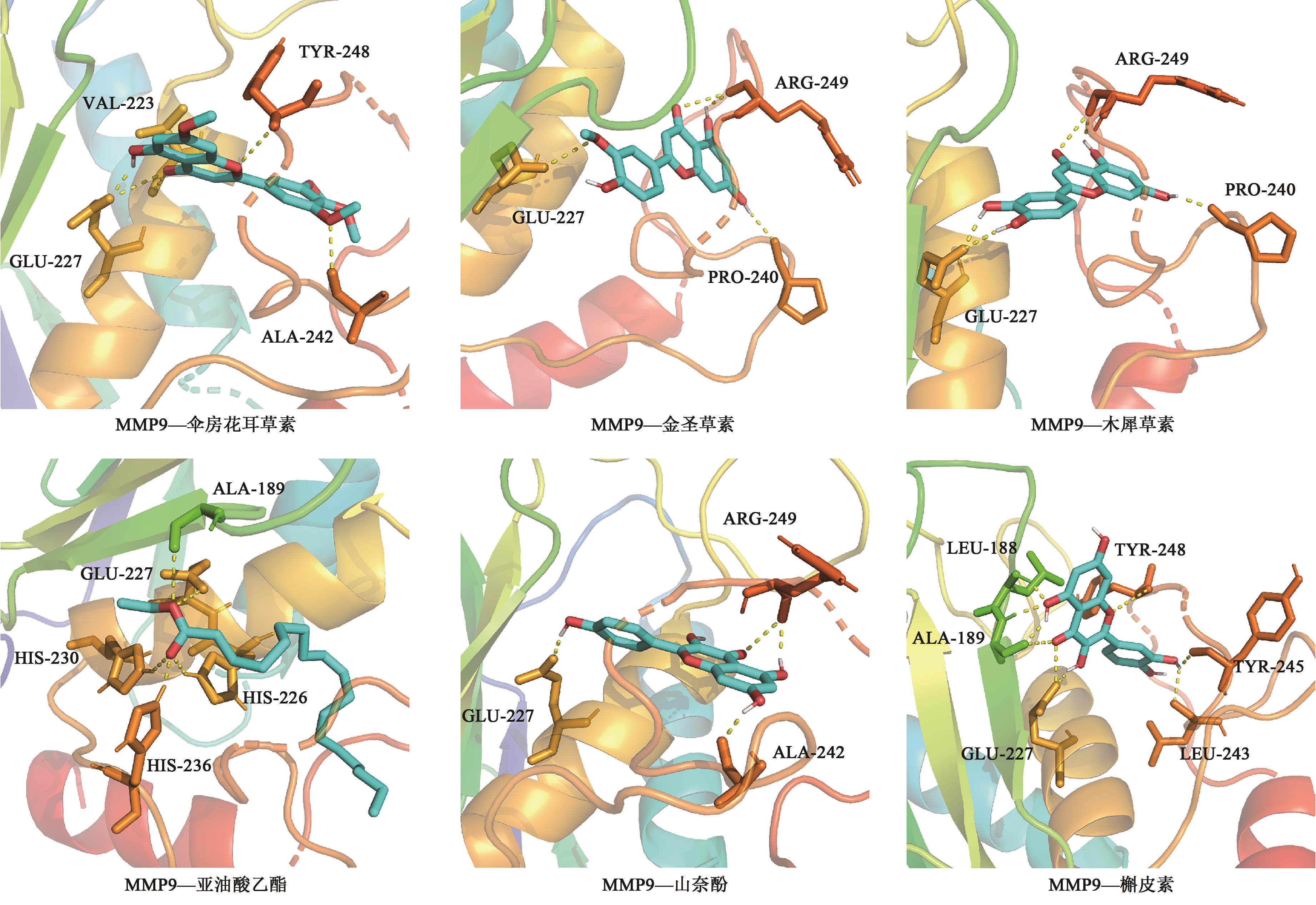
Table 1 Information on active components of Jinyinhua oral liquid
| 分子编码 | 成分名称 | 口服生物利用度/% | 类药性 | 结构式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOL001494 | 亚油酸乙酯 | 42.00 | 0.19 |  |
| MOL001495 | 亚麻酸乙酯 | 46.10 | 0.20 |  |
| MOL002914 | 圣草酚 | 41.35 | 0.24 |  |
| MOL002773 | β-胡萝卜素 | 37.18 | 0.58 |  |
| MOL003036 | ZINC03978781 | 43.83 | 0.76 |  |
| MOL003044 | 金圣草素 | 35.85 | 0.27 |  |
| MOL003059 | 隐黄质 | 47.25 | 0.57 |  |
| MOL003062 | 玫红黄质 | 31.22 | 0.55 |  |
| MOL003095 | 伞房花耳草素 | 51.96 | 0.41 |  |
| MOL003101 | 7-表断马钱子苷半缩醛内酯 | 46.13 | 0.58 |  |
| MOL003124 | XYLOSTOSIDINE | 43.17 | 0.64 |  |
| MOL000358 | β-谷甾醇 | 36.91 | 0.75 |  |
| MOL000422 | 山奈酚 | 41.88 | 0.24 |  |
| MOL000449 | 豆甾醇 | 43.83 | 0.76 |  |
| MOL000006 | 木犀草素 | 36.16 | 0.25 |  |
| MOL000098 | 槲皮素 | 46.43 | 0.28 |  |
| 1 | REHMAN S U, REHMAN S U, YOO H H. COVID-19 challenges and its therapeutics[J/OL]. Biomed. Pharmacother., 2021, 142: 112015[2023-07-25]. . |
| 2 | YANG Y, ISLAM M S, WANG J, et al.. Traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of patients infected with 2019-new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): a review and perspective[J]. Int. J. Biol. Sci., 2020, 16(10): 1708-1717. |
| 3 | AN X, ZHANG Y, DUAN L, et al.. The direct evidence and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of COVID-19[J/OL]. Biomed. Pharmacother., 2021, 137: 111267[2023-07-25]. . |
| 4 | ZHAO H, ZENG S, CHEN L, et al.. Updated pharmacological effects of Lonicerae japonicae flos, with a focus on its potential efficacy on coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19)[J]. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol., 2021, 60: 200-207. |
| 5 | 胡芬, 郭爱华,黄 鹿, 等. 不同剂量金银花口服液联合西医常规疗法治疗新型冠状病毒感染普通型187例多中心临床观察[J]. 中医杂志, 2021, 62(6): 510-515. |
| 6 | ZHOU L K, ZHOU Z, JIANG X M, et al.. Absorbed plant MIR2911 in honeysuckle decoction inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication and accelerates the negative conversion of infected patients[J/OL]. Cell Discov., 2020, 6(1): 54[2023-07-25]. . |
| 7 | DU X Q, SHI L P, CAO W F, et al.. Add-on effect of honeysuckle in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J/OL]. Front. Pharmacol., 2021, 12: 708636[2023-07-25]. . |
| 8 | YEH Y C, DOAN L H, HUANG Z Y, et al.. Honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica) and Huangqi (Astragalus membranaceus) suppress SARS-CoV-2 entry and COVID-19 related cytokine storm in vitro [J/OL]. Front. Pharmacol., 2021, 12: 765553[2023-07-25]. . |
| 9 | LEE Y R, CHANG C M, YEH Y C, et al.. Honeysuckle aqueous extracts induced let-7a suppress EV71 replication and pathogenesis in vitro and in vivo and is predicted to inhibit SARS-CoV-2[J/OL]. Viruses, 2021, 13(2): 308[2023-07-25]. . |
| 10 | 董峰, 皇甫秉欣, 徐佳, 等. 基于网络药理学探究薏苡仁干预脂肪性肝病的机制[J]. 生物技术进展, 2023, 13(2): 264-272. |
| 11 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 新型冠状病毒感染诊疗方案(试行第八版 修订版)[J]. 中华临床感染病杂志, 2021, 14(2): 81-88. |
| 12 | REN J L, ZHANG A H, WANG X J. Traditional Chinese medicine for COVID-19 treatment[J/OL]. Pharmacol. Res., 2020, 155: 104743[2023-07-25]. . |
| 13 | 高新生, 张又莉, 韩立虎. 金银花口服液治疗普通型新型冠状病毒感染1例临床观察[J]. 中国药业, 2020, 29(7): 58-59. |
| 14 | 张又莉, 雷亮, 徐勇, 等. 金银花口服液治疗新型冠状病毒感染80例临床疗效分析[J]. 中国药业, 2020, 29(9): 23-26. |
| 15 | KHAN SHAWAN M MALI, HALDER S K, HASAN M A. Luteolin and abyssinone Ⅱ as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2: an in silico molecular modeling approach in battling the COVID-19 outbreak[J/OL]. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent., 2021, 45(1): 27[2023-07-25]. . |
| 16 | 王利华, 孙成宏, 邸琨,等. 黄酮类单体抗奥密克戎毒株药理活性研究[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2023, 41(1): 18-20+261. |
| 17 | RABHA D J, SINGH T U, RUNGSUNG S, et al.. Kaempferol attenuates acute lung injury in caecal ligation and puncture model of sepsis in mice[J]. Exp. Lung Res., 2018, 44(2): 63-78. |
| 18 | KHAN A, HENG W, WANG Y, et al.. In silico and in vitro evaluation of kaempferol as a potential inhibitor of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (3CLpro)[J]. Phytother. Res., 2021, 35(6): 2841-2845. |
| 19 | HUANG K, ZHANG P, ZHANG Z, et al.. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) in the treatment of COVID-19 and other viral infections: efficacies and mechanisms[J/OL]. Pharmacol. Ther., 2021, 225: 107843[2023-07-25]. . |
| 20 | SAEEDI-BOROUJENI A, M-RMAHMOUDIAN-SANI. Anti-inflammatory potential of quercetin in COVID-19 treatment[J/OL]. J. Inflamm., 2021, 18(1): 3[2023-07-25]. . |
| 21 | PAN B, FANG S, ZHANG J, et al.. Chinese herbal compounds against SARS-CoV-2: puerarin and quercetin impair the binding of viral S-protein to ACE2 receptor[J]. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J., 2020, 18: 3518-3527. |
| 22 | ZALPOOR H, BAKHTIYARI M, LIAGHAT M, et al.. Quercetin potential effects against SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19-associated cancer progression by inhibiting mTOR and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α)[J]. Phytother. Res., 2022, 36(7): 2679-2682. |
| 23 | APPELBERG S, GUPTA S, SVENSSON AKUSJÄRVI S, et al.. Dysregulation in Akt/mTOR/HIF-1 signaling identified by proteo-transcriptomics of SARS-CoV-2 infected cells[J]. Emerg. Microbes Infect., 2020, 9(1): 1748-1760. |
| 24 | DÜLGER S U, MUTLU N, CEYLAN İ, et al.. The relationship between lung fibrosis, the epidermal growth factor receptor, and disease outcomes in COVID-19 pneumonia: a postmortem evaluation[J]. Clin. Exp. Med., 2022: 1-8. |
| 25 | SEREBROVSKA Z O, CHONG E Y, SEREBROVSKA T V, et al.. Hypoxia, HIF-1α, and COVID-19: from pathogenic factors to potential therapeutic targets[J]. Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 2020, 41(12): 1539-1546. |
| 26 | VALLÉE A, LECARPENTIER Y, VALLÉE J N. Interplay of opposing effects of the WNT/β-catenin pathway and PPARγ and implications for SARS-CoV2 treatment[J/OL]. Front. Immunol., 2021, 12: 666693[2023-07-25]. . |
| 27 | AVILA-MESQUITA C D, COUTO A E S, CAMPOS L C B, et al.. MMP-2 and MMP-9 levels in plasma are altered and associated with mortality in COVID-19 patients[J/OL]. Biomed. Pharmacother., 2021, 142: 112067[2023-07-25]. . |
| 28 | LI F, BOON A C M, MICHELSON A P, et al.. Estrogen hormone is an essential sex factor inhibiting inflammation and immune response in COVID-19[J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2022, 12(1): 9462[2023-07-25]. . |
| 29 | ZHANG Q, WU X, YANG J. miR-194-5p protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via MAPK1/PTEN/AKT pathway[J/OL]. Ann. Transl. Med., 2021, 9(8): 654[2023-07-25]. . |
| 30 | WING P A C, KEELEY T P, ZHUANG X, et al.. Hypoxic and pharmacological activation of HIF inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection of lung epithelial cells[J/OL]. Cell Rep., 2021, 35(3): 109020[2023-07-25]. . |
| 31 | TIAN M, LIU W, LI X, et al.. HIF-1α promotes SARS-CoV-2 infection and aggravates inflammatory responses to COVID-19[J/OL]. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther., 2021, 6(1): 308[2023-07-25]. . |
| 32 | AL-QAHTANI A A, PANTAZI I, ALHAMLAN F S, et al.. SARS-CoV-2 modulates inflammatory responses of alveolar epithelial type Ⅱ cells via PI3K/AKT pathway[J/OL]. Front. Immunol., 2022, 13: 1020624[2023-07-25]. . |
| 33 | LI F, LI J, WANG P H, et al.. SARS-CoV-2 spike promotes inflammation and apoptosis through autophagy by ROS-suppressed PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling[J/OL]. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis., 2021, 1867(12): 166260[2023-07-25]. . |
| 34 | ABEL T, MOODLEY J, KHALIQ O P, et al.. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2: molecular mechanism and therapeutic potential in preeclampsia comorbidity with human immunodeficiency virus and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infections[J/OL]. Cell. Signal., 2022, 23(22): 13752[2023-07-25]. . |
| 35 | ZENG F M, LI Y W, DENG Z H, et al.. SARS-CoV-2 spike spurs intestinal inflammation via VEGF production in enterocytes[J/OL]. EMBO Mol. Med., 2022, 14(5): e14844[2023-07-25]. . |
| 36 | YAMAMOTO K, TAKAGI Y, ANDO K, et al.. Rap1 small GTPase regulates vascular endothelial-cadherin-mediated endothelial cell-cell junctions and vascular permeability[J]. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 2021, 44(10): 1371-1379. |
| [1] | Xi KANG, Ziyu LIN, Yishu YANG, Jintao LI, Minglian WANG. Variation Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron RdRp and Construction of its Active Reaction System [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(6): 1042-1054. |
| [2] | Xuejiao CHEN, Ping YU, Di ZHAO, Jia SONG, Xiangbo MIN. Study on the Anti-inflammatory Effect of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HCS03-001 Based on Zebrafish Model and Network Pharmacology [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(2): 295-303. |
| [3] | Fanglin SU, Xin LUO, Sainan TANG, Leyun HUANG, Wei HU, Shilong LU, Longjiao RAN, Shaowei XIANG. The Mechanism Research of Tangshenbao Compound in Treating Diabetic Nephropathy Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(1): 160-171. |
| [4] | Yuemaierabola ANWAIER, Lili SUN, Yeerkenbieke BUERLAN, Wenjia GUO. Advances on the Role of Piezo1 in Cancer [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(5): 712-717. |
| [5] | Dan YU, Yunlong MA, Fang WAN, Jianqiang WU. Advances on Research and Application of mRNA Vaccines [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(4): 492-498. |
| [6] | Feng DONG, Bingxin HUANGFU, Jia XU, Wentao XU. Mechanism Exploring of Coix Seed Intervention in Fatty Liver Disease Based on Network Pharmacology [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(2): 264-272. |
| [7] | Minyi KAU, Xiao XU, Yiwen GAO, Ying CHEN, Zhengfei MA, Linxi YUAN. Narrative Review on the Roles of Selenium Against COVID-19 [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(1): 72-76. |
| [8] | Min YU, Min WANG, Yanhuan WEI, Yiyi LIU. Analysis of Potential Key Molecular Biomarkers and Immune Infiltration Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 Virus Infection [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2022, 12(5): 760-768. |
| [9] | Yiqi YANG, Zhigao ZHANG, Xiaolong YOU, Jing ZHANG, Guanfeng LIN, Yingsong WU. Development and Application of Monoclonal Antibody-based Drug [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2022, 12(3): 358-365. |
| [10] | SUN Jing1, LIU Dan2*, HUI Wenqi2. Study on Design of Colchicine Inhibitors of Tubulin for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on Computer Simulation [J]. Curr. Biotech., 2019, 9(1): 84-88. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||