Current Biotechnology ›› 2024, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (4): 576-585.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2024.0057
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
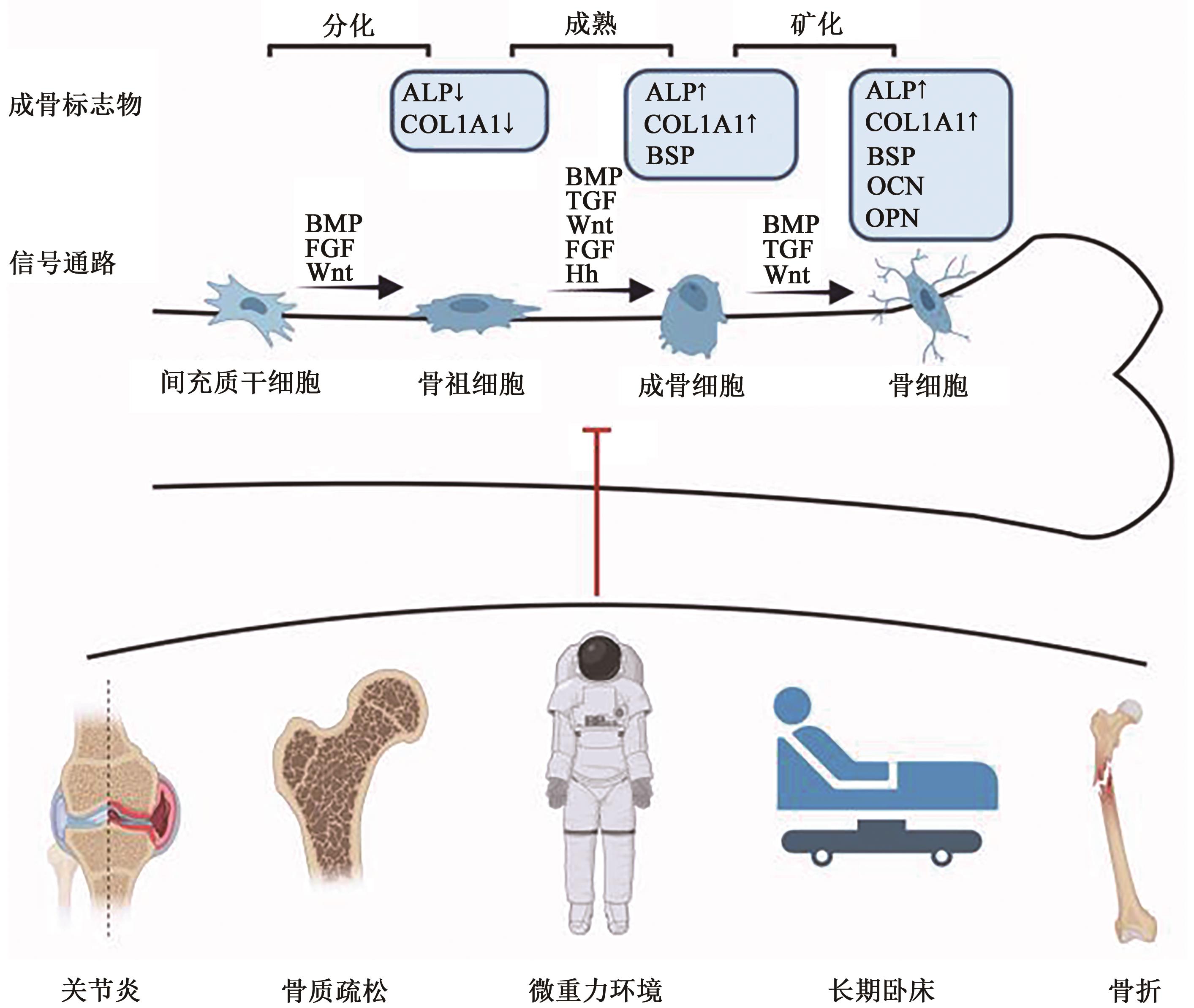
Research Progress of Hydrogen Molecules in Improving Inflammatory and Osteoporotic Bone Loss Related Diseases
Shihao JIANG( ), Xinyue ZHU, Xiaohu WEN, Ziyi LIU, Pengxiang ZHAO(
), Xinyue ZHU, Xiaohu WEN, Ziyi LIU, Pengxiang ZHAO( )
)
- College of Chemistry and Life Sciences,Beijing University of Technology,Beijing 100124,China
-
Received:2024-03-22Accepted:2024-04-22Online:2024-07-25Published:2024-08-07 -
Contact:Pengxiang ZHAO
氢分子在改善炎性和骨质疏松型骨丢失相关疾病中的研究进展
- 北京工业大学化学与生命科学学院,北京 100124
-
通讯作者:赵鹏翔 -
作者简介:姜世豪 E-mail: wsjsh666@163.com; -
基金资助:军委后勤保障部开放研究重点项目(BHJ17L08)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shihao JIANG, Xinyue ZHU, Xiaohu WEN, Ziyi LIU, Pengxiang ZHAO. Research Progress of Hydrogen Molecules in Improving Inflammatory and Osteoporotic Bone Loss Related Diseases[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(4): 576-585.
姜世豪, 朱昕玥, 文小虎, 刘子怡, 赵鹏翔. 氢分子在改善炎性和骨质疏松型骨丢失相关疾病中的研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(4): 576-585.
share this article
| 疾病类型 | 试验类型 | 氢分子介入方式 | 作用机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 类风湿关节炎 | 临床试验 | 饮用富氢水 | 氢气可能通过减轻氧化应激缓解疾病症状 | |
| 注射氢生理盐水 | 氢气可能通过清除羟基自由基破坏NF-κB信号通路中过量活性氧上调的促炎细胞因子——烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸氧化酶-超氧化物和过氧化氢的正反馈循环 | |||
| 动物实验 | 注射氢生理盐水 | 氢气可能通过抑制MAPKs和NF-κB通路的活化和调节TGF-β1表达减缓RA的发展 | ||
| 饮用富氢水 | 氢气可能通过减轻氧化应激来保护骨骼免受RA的影响 | |||
| 吸入氢气 | 氢气通过减轻大鼠体内氧化应激,减少大鼠关节组织破坏,阻止机械痛敏的形成 | |||
| 植入储氢材料 | 氢气通过清除活性氧和炎症,减轻氧化应激并降低炎症细胞因子水平 | |||
| 细胞实验 | 过氧化氢和氢气共处理类风湿关节炎细胞 | 氢气可能通过抑制MAPKs和NF-κB通路的活化和调节TGF-β1表达减缓RA的发展 | ||
| 储氢材料共培养 | 氢气通过清除活性氧和炎症,减轻氧化应激并降低炎症细胞因子水平 | |||
| 骨性关节炎 | 动物实验 | 关节处注射储氢材料 | 局部输送高浓度氢气可减轻组织炎症并防止软骨被破坏 | |
| 腹腔注射氢水 | 富氢水可能通过抗氧化和抗炎作用对骨性关节炎起到保护作用 | |||
| 富氢水能够减轻骨性关节炎中软骨的氧化损伤和炎症反应,减少软骨细胞凋亡 | ||||
| 吸入氢气 | 氢气通过抑制JNK信号通路的激活,减轻人类软骨细胞的凋亡反应和细胞外基质降解 | |||
| 细胞实验 | 储氢材料处理脂多糖刺激的软骨细胞 | 局部输送高浓度氢气可减轻组织炎症并防止软骨被破坏 | ||
| 氢氧氮混合气培养患者软骨细胞 | 氢气通过抑制JNK信号通路的激活,减轻人类软骨细胞中的凋亡反应和细胞外基质降解 | |||
| 银屑病关节炎 | 临床试验 | 滴注氢生理盐水 | 氢气可能通过减少体内自由基缓解银屑病关节炎病变的发展 | |
| 吸入氢气 | ||||
| 饮用富氢水 | ||||
| 痛风性关节炎 | 动物实验 | 氢生理盐水灌胃 | 氢气通过清除自由基、改变体液pH、促进尿酸排出和保护血管内皮细胞中一个或多个环节减轻痛风性关节炎进展 | |
| 创伤性关节炎 | 动物实验 | 注射氢生理盐水 | 未提及 |
Table 1 The mechanism of hydrogen in combating inflammatory bone loss
| 疾病类型 | 试验类型 | 氢分子介入方式 | 作用机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 类风湿关节炎 | 临床试验 | 饮用富氢水 | 氢气可能通过减轻氧化应激缓解疾病症状 | |
| 注射氢生理盐水 | 氢气可能通过清除羟基自由基破坏NF-κB信号通路中过量活性氧上调的促炎细胞因子——烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸氧化酶-超氧化物和过氧化氢的正反馈循环 | |||
| 动物实验 | 注射氢生理盐水 | 氢气可能通过抑制MAPKs和NF-κB通路的活化和调节TGF-β1表达减缓RA的发展 | ||
| 饮用富氢水 | 氢气可能通过减轻氧化应激来保护骨骼免受RA的影响 | |||
| 吸入氢气 | 氢气通过减轻大鼠体内氧化应激,减少大鼠关节组织破坏,阻止机械痛敏的形成 | |||
| 植入储氢材料 | 氢气通过清除活性氧和炎症,减轻氧化应激并降低炎症细胞因子水平 | |||
| 细胞实验 | 过氧化氢和氢气共处理类风湿关节炎细胞 | 氢气可能通过抑制MAPKs和NF-κB通路的活化和调节TGF-β1表达减缓RA的发展 | ||
| 储氢材料共培养 | 氢气通过清除活性氧和炎症,减轻氧化应激并降低炎症细胞因子水平 | |||
| 骨性关节炎 | 动物实验 | 关节处注射储氢材料 | 局部输送高浓度氢气可减轻组织炎症并防止软骨被破坏 | |
| 腹腔注射氢水 | 富氢水可能通过抗氧化和抗炎作用对骨性关节炎起到保护作用 | |||
| 富氢水能够减轻骨性关节炎中软骨的氧化损伤和炎症反应,减少软骨细胞凋亡 | ||||
| 吸入氢气 | 氢气通过抑制JNK信号通路的激活,减轻人类软骨细胞的凋亡反应和细胞外基质降解 | |||
| 细胞实验 | 储氢材料处理脂多糖刺激的软骨细胞 | 局部输送高浓度氢气可减轻组织炎症并防止软骨被破坏 | ||
| 氢氧氮混合气培养患者软骨细胞 | 氢气通过抑制JNK信号通路的激活,减轻人类软骨细胞中的凋亡反应和细胞外基质降解 | |||
| 银屑病关节炎 | 临床试验 | 滴注氢生理盐水 | 氢气可能通过减少体内自由基缓解银屑病关节炎病变的发展 | |
| 吸入氢气 | ||||
| 饮用富氢水 | ||||
| 痛风性关节炎 | 动物实验 | 氢生理盐水灌胃 | 氢气通过清除自由基、改变体液pH、促进尿酸排出和保护血管内皮细胞中一个或多个环节减轻痛风性关节炎进展 | |
| 创伤性关节炎 | 动物实验 | 注射氢生理盐水 | 未提及 |
| 疾病类型 | 实验类型 | 氢分子介入方式 | 作用机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 卵巢切除诱导的骨质疏松症 | 动物实验 | 吸入氢气 | 氢气通过抑制NF-kB激活,减少骨质流失,从而具有潜在的抗骨质疏松症作用 | |
| 饮用富氢水 | 富氢水通过减轻由雌激素减少引起的氧化应激,预防卵巢切除引起的骨质疏松症 | |||
| 泼尼松龙诱导的骨质疏松症 | 动物实验 | 富氢水饲养斑马鱼 | 氢分子通过清除泼尼松龙诱导的活性氧并刺激破骨前细胞中的Nrf2,防止破骨细胞活化 | |
| 糖尿病诱导的骨质疏松症 | 动物实验 | 氢生理盐水灌胃 | 氢气可能通过改善氧化应激水平,减轻对骨骼的负面影响,保护骨骼健康 | |
| 尾悬吊诱导的骨质疏松症 | 动物实验 | 吸入氢气 | 氢分子可能通过减轻氧化应激、恢复成骨细胞分化并抑制破骨细胞分化来改善模拟微重力环境引起的骨丢失 | |
| 细胞实验 | 富氢培养基孵育细胞 |
Table 2 The mechanism of hydrogen in combating osteoporotic bone loss
| 疾病类型 | 实验类型 | 氢分子介入方式 | 作用机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 卵巢切除诱导的骨质疏松症 | 动物实验 | 吸入氢气 | 氢气通过抑制NF-kB激活,减少骨质流失,从而具有潜在的抗骨质疏松症作用 | |
| 饮用富氢水 | 富氢水通过减轻由雌激素减少引起的氧化应激,预防卵巢切除引起的骨质疏松症 | |||
| 泼尼松龙诱导的骨质疏松症 | 动物实验 | 富氢水饲养斑马鱼 | 氢分子通过清除泼尼松龙诱导的活性氧并刺激破骨前细胞中的Nrf2,防止破骨细胞活化 | |
| 糖尿病诱导的骨质疏松症 | 动物实验 | 氢生理盐水灌胃 | 氢气可能通过改善氧化应激水平,减轻对骨骼的负面影响,保护骨骼健康 | |
| 尾悬吊诱导的骨质疏松症 | 动物实验 | 吸入氢气 | 氢分子可能通过减轻氧化应激、恢复成骨细胞分化并抑制破骨细胞分化来改善模拟微重力环境引起的骨丢失 | |
| 细胞实验 | 富氢培养基孵育细胞 |
| 调控类型 | 实验类型 | 研究内容 | 作用机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 骨吸收 | 细胞实验 | 氢气处理破骨细胞的分化 | 氢气通过抑制NF-κB激活减少破骨细胞生成 | |
| 动物实验 | 氢气对小鼠BMMCs破骨细胞生成的调节 | 未提及 | ||
| 注射富氢生理盐水对骨髓源干细胞抗老化效应和机制 | 氢气可能通过ROS/p53/p21信号通路减轻细胞老化,实现抗老化效应 | |||
| 骨形成 | 细胞实验 | 氢分子在MSCs扩增中防止细胞老化的发生 | 未提及 | |
| 氢气处理TNF-α诱导下新生大鼠颅骨成骨细胞损伤修复 | 氢气通过减轻氧化应激、保护线粒体功能、抑制炎症以及增强一氧化氮的生物可用性,缓解TNF-α诱导的成骨细胞损伤 | |||
| 氢气对脂多糖剌激后牙周膜细胞成骨能力 | 氢气可能通过保护人牙周膜细胞成骨能力减弱慢性牙周炎骨吸收 | |||
| 动物实验 | 富氢水促进斑马鱼胚胎的骨骼生成 | 氢分子作为抗氧化剂促进胚胎成骨细胞的活化,从而促进胚胎成骨细胞的形成 |
Table 3 The mechanism of hydrogen gas in bone resorption and bone formation
| 调控类型 | 实验类型 | 研究内容 | 作用机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 骨吸收 | 细胞实验 | 氢气处理破骨细胞的分化 | 氢气通过抑制NF-κB激活减少破骨细胞生成 | |
| 动物实验 | 氢气对小鼠BMMCs破骨细胞生成的调节 | 未提及 | ||
| 注射富氢生理盐水对骨髓源干细胞抗老化效应和机制 | 氢气可能通过ROS/p53/p21信号通路减轻细胞老化,实现抗老化效应 | |||
| 骨形成 | 细胞实验 | 氢分子在MSCs扩增中防止细胞老化的发生 | 未提及 | |
| 氢气处理TNF-α诱导下新生大鼠颅骨成骨细胞损伤修复 | 氢气通过减轻氧化应激、保护线粒体功能、抑制炎症以及增强一氧化氮的生物可用性,缓解TNF-α诱导的成骨细胞损伤 | |||
| 氢气对脂多糖剌激后牙周膜细胞成骨能力 | 氢气可能通过保护人牙周膜细胞成骨能力减弱慢性牙周炎骨吸收 | |||
| 动物实验 | 富氢水促进斑马鱼胚胎的骨骼生成 | 氢分子作为抗氧化剂促进胚胎成骨细胞的活化,从而促进胚胎成骨细胞的形成 |
| 1 | ZHOU R, GUO Q, XIAO Y, et al.. Endocrine role of bone in the regulation of energy metabolism[J/OL]. Bone Res., 2021, 9(1): 25[2024-06-13]. . |
| 2 | SALHOTRA A, SHAH H N, LEVI B, et al.. Mechanisms of bone development and repair[J]. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2020, 21(11): 696-711. |
| 3 | 赵鹏翔, 谢飞, 刘梦昱, 等. 氢气生物医学研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2021, 11(4): 503-517. |
| ZHAO P X, XIE F, LIU M Y, et al.. Research progress in hydrogen biomedical science[J]. Curr. Biotechnol., 2021, 11(4): 503-517. | |
| 4 | LU H, WANG W, KANG X, et al.. Hydrogen (H2) alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation via the JNK signaling pathway[J]. J. Inflamm. Res., 2021, 14: 1387-1402. |
| 5 | AMARASEKARA D S, KIM S, RHO J. Regulation of osteoblast differentiation by cytokine networks[J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22(6): 2851[2024-06-13]. . |
| 6 | RUTKOVSKIY A, STENSLØKKEN K O, VAAGE I J. Osteoblast differentiation at a glance[J]. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res., 2016, 22: 95-106. |
| 7 | LIN X, PATIL S, GAO Y G, et al.. The bone extracellular matrix in bone formation and regeneration[J/OL]. Front. Pharmacol., 2020, 11: 757[2024-06-13]. . |
| 8 | LIU Q, LI M, WANG S, et al.. Recent advances of osterix transcription factor in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation[J/OL]. Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 2020, 8: 601224[2024-06-13]. . |
| 9 | BERENDSEN A D, OLSEN B R. Bone development[J]. Bone, 2015, 80: 14-18. |
| 10 | GUASTO A, CORMIER-DAIRE V. Signaling pathways in bone development and their related skeletal dysplasia[J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22(9): 4321[2024-06-13]. . |
| 11 | COURY F, PEYRUCHAUD O, MACHUCA-GAYET I. Osteoimmunology of bone loss in inflammatory rheumatic diseases[J/OL]. Front. Immunol., 2019, 10: 679[2024-06-13]. . |
| 12 | 马小涵, 黄丽晶, 汪飞, 等. 生物制品治疗类风湿关节炎评价新视角[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(1): 55-59. |
| MA X H, HUANG L J, WANG F, et al.. A new perspective to evaluate the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with biological products[J]. Curr. Biotechnol., 2024, 14(1): 55-59. | |
| 13 | REDLICH K, SMOLEN J S. Inflammatory bone loss: pathogenesis and therapeutic intervention[J]. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., 2012, 11(3): 234-250. |
| 14 | MOTTA F, BARONE E, SICA A, et al.. Inflammaging and osteoarthritis[J]. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol., 2023, 64(2): 222-238. |
| 15 | ZHOU M, LI S, PATHAK J L. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and osteocytes[J]. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep., 2019, 17(3): 97-104. |
| 16 | 姚佳炜, 邱波. 骨关节炎滑膜病变的体液标志物研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2022, 12(3): 373-378. |
| YAO J W, QIU B. Research progress of body fluid markers of osteoarthritis synovial lesions[J]. Curr. Biotechnol., 2022, 12(3): 373-378. | |
| 17 | DIMITROULAS T, NIKAS S N, TRONTZAS P, et al.. Biologic therapies and systemic bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Autoimmun. Rev., 2013, 12(10): 958-966. |
| 18 | LORENTZON M, CUMMINGS S R. Osteoporosis: the evolution of a diagnosis[J]. J. Intern. Med., 2015, 277(6): 650-661. |
| 19 | YCHIN K, NG B N, ROSTAM M K I, et al.. A mini review on osteoporosis: from biology to pharmacological management of bone loss[J/OL]. J. Clin. Med., 2022, 11(21): 6434[2024-06-13]. . |
| 20 | BRENT M B. Pharmaceutical treatment of bone loss: from animal models and drug development to future treatment strategies[J/OL]. Pharmacol. Ther., 2023, 244: 108383[2024-06-03]. . |
| 21 | EASTELL R, O'NEILL T W, HOFBAUER L C, et al.. Postmenopausal osteoporosis[J/OL]. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers, 2016, 2: 16069[2024-06-13]. . |
| 22 | VILACA T, EASTELL R, SCHINI M. Osteoporosis in men[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endo., 2022, 10(4): 273-283. |
| 23 | EBELING P R, NGUYEN H H, ALEKSOVA J, et al.. Secondary osteoporosis[J]. Endocr. Rev., 2022, 43(2): 240-313. |
| 24 | BUCKLEY L, HUMPHREY M B. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis[J]. New Engl. J. Med., 2018, 379(26): 2547-2556. |
| 25 | HARDY R S, ZHOU H, SEIBEL M J, et al.. Glucocorticoids and bone: consequences of endogenous and exogenous excess and replacement therapy[J]. Endocr. Rev., 2018, 39(5): 519-548. |
| 26 | CHEN M, FU W, XU H, et al.. Pathogenic mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev., 2023, 70: 54-66. |
| 27 | GRIMM D, GROSSE J, WEHLAND M, et al.. The impact of microgravity on bone in humans[J]. Bone, 2016, 87: 44-56. |
| 28 | FOURNIER R, HARRISON R E. Strategies for studying bone loss in microgravity[J/OL]. Reach, 2020, 17: 100036[2024-06-13]. . |
| 29 | COULOMBE J C, SENWAR B, FERGUSON V L. Spaceflight-induced bone tissue changes that affect bone quality and increase fracture risk[J]. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep., 2020, 18(1): 1-12. |
| 30 | RIGGS B L, KHOSLA S, MELTON L J. A unitary model for involutional osteoporosis: estrogen deficiency causes both type I and type Ⅱ osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and contributes to bone loss in aging men[J]. J. Bone Miner. Res., 1998, 13(5): 763-773. |
| 31 | VICO L, VAN RIETBERGEN B, VILAYPHIOU N, et al.. Cortical and trabecular bone microstructure did not recover at weight-bearing skeletal sites and progressively deteriorated at non-weight-bearing sites during the year following international space station missions[J]. J. Bone Miner. Res., 2017, 32(10): 2010-2021. |
| 32 | EIMORI K, ENDO N, UCHIYAMA S, et al.. Disrupted bone metabolism in long-term bedridden patients[J/OL]. PLoS ONE, 2016, 11(6): e0156991[2024-06-13]. . |
| 33 | LEMS W F, DREINHÖFER K E, BISCHOFF-FERRARI H, et al.. EULAR/EFORT recommendations for management of patients older than 50 years with a fragility fracture and prevention of subsequent fractures[J]. Ann. Rheum. Dis., 2017, 76(5): 802-810. |
| 34 | ZHENG X Q, HUANG J, LIN J L, et al.. Pathophysiological mechanism of acute bone loss after fracture[J]. J. Adv. Res., 2023, 49: 63-80. |
| 35 | OSIPOV B, EMAMI A J, CHRISTIANSEN B A. Systemic bone loss after fracture[J]. Clin. Rev. Bone Miner. Metab., 2018, 16(4): 116-130. |
| 36 | ZHU S, EHNERT S, ROUSS M, et al.. From the clinical problem to the basic research-co-culture models of osteoblasts and osteoclasts[J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2018, 19(8): 2284[2024-06-13]. . |
| 37 | HAN Y, YOU X, XING W, et al.. Paracrine and endocrine actions of bone-the functions of secretory proteins from osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts[J/OL]. Bone Res., 2018, 6: 16[2024-06-13]. . |
| 38 | LOI F, CÓRDOVA L A, PAJARINEN J, et al.. Inflammation, fracture and bone repair[J]. Bone, 2016, 86: 119-130. |
| 39 | WANG S H, WU C C, LI W T, et al.. Outcomes of distal femoral fractures treated with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis versus open reduction internal fixation with combined locking plate and interfragmentary screws[J]. Int. J. Surg. Lond. Engl., 2019, 65: 107-112. |
| 40 | CHEN J H, LIU C, YOU L, et al.. Boning up on Wolff's Law: mechanical regulation of the cells that make and maintain bone[J]. J. Biomech., 2010, 43(1): 108-118. |
| 41 | XIAO Z, QUARLES L D. Physiological mechanisms and therapeutic potential of bone mechanosensing[J]. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord., 2015, 16(2): 115-129. |
| 42 | ROLVIEN T, AMLING M. Disuse osteoporosis: clinical and mechanistic insights[J]. Calcif. Tissue Int., 2022, 110(5): 592-604. |
| 43 | EMAMI A J, TOUPADAKIS C A, TELEK S M, et al.. Age dependence of systemic bone loss and recovery following femur fracture in mice[J]. J. Bone Miner. Res., 2019, 34(1): 157-170. |
| 44 | CERONI D, MARTIN X, DELHUMEAU C, et al.. Effects of cast-mediated immobilization on bone mineral mass at various sites in adolescents with lower-extremity fracture[J]. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am., 2012, 94(3): 208-216. |
| 45 | KAZAKIA G J, TJONG W, NIRODY J A, et al.. The influence of disuse on bone microstructure and mechanics assessed by HR-pQCT[J]. Bone, 2014, 63: 132-140. |
| 46 | JACOBS C A, OLSEN Z M, MARCHAND L S, et al.. The inflamma-type: a patient phenotype characterized by a dysregulated inflammatory response after lower extremity articular fracture[J]. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 72(1): 9-11. |
| 47 | ISHIBASHI T, SATO B, RIKITAKE M, et al.. Consumption of water containing a high concentration of molecular hydrogen reduces oxidative stress and disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: an open-label pilot study[J/OL]. Med. Gas Res., 2012, 2(1): 27[2024-06-13]. . |
| 48 | ISHIBASHI T, SATO B, SHIBATA S, et al.. Therapeutic efficacy of infused molecular hydrogen in saline on rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study[J]. Int. Immunopharmacol., 2014, 21(2): 468-473. |
| 49 | MENG J, YU P, JIANG H, et al.. Molecular hydrogen decelerates rheumatoid arthritis progression through inhibition of oxidative stress[J]. Am. J. Transl. Res., 2016, 8(10): 4472-4477. |
| 50 | TERASAKI Y, TERASAKI M, KANAZAWA S, et al.. Effect of H2 treatment in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease[J]. J. Cell. Mol. Med., 2019, 23(10): 7043-7053. |
| 51 | XU C, WANG S, WANG H, et al.. Magnesium-based micromotors as hydrogen generators for precise rheumatoid arthritis therapy[J]. Nano Lett., 2021, 21(5): 1982-1991. |
| 52 | 李号令, 周亚兰, 周书转, 等. 氢气对单关节炎大鼠的保护作用[J]. 第二军医大学学报, 2019, 40(11): 1258-1262. |
| LI H L, ZHOU Y L, ZHOU S Z, et al.. Protective effects of hydrogen on monoarthritis rats[J]. Acad. J. Second. Mil. Med. Univ., 2019, 40(11): 1258-1262. | |
| 53 | MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR A J, CICUTTINI F M, et al.. Osteoarthritis[J/OL]. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers, 2016, 2: 16072[2024-06-13]. . |
| 54 | WAN W L, LIN Y J, SHIH P C, et al.. An in situ depot for continuous evolution of gaseous H2 mediated by a magnesium passivation/activation cycle for treating osteoarthritis[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(31): 9875-9879. |
| 55 | CHENG S, PENG L, XU B, et al.. Protective effects of hydrogen-rich water against cartilage damage in a rat model of osteoarthritis by inhibiting oxidative stress, matrix catabolism, and apoptosis[J/OL]. Med. Sci. Monit., 2020, 26: e920211[2024-06-13]. . |
| 56 | 徐百超. 富氢水对兔骨性关节炎模型关节软骨的作用研究[J]. 家庭医药·就医选药, 2018(12): 12-13. |
| XU B C. Effect of hydrogen-rich water on articular cartilage of rabbit osteoarthritis model[J]. Home Med., 2018(12): 12-13. | |
| 57 | ISHIBASHI T, ICHIKAWA M, SATO B, et al.. Improvement of psoriasis-associated arthritis and skin lesions by treatment with molecular hydrogen: a report of three cases[J]. Mol. Med. Rep., 2015, 12(2): 2757-2764. |
| 58 | 招友, 樊彦伟, 马广斌, 等. 富氢生理盐水对大鼠痛风性关节炎的保护作用[J]. 广东医学, 2017, 38(5): 672-674. |
| ZHAO Y, FAN Y W, MA G B, et al.. Study on the effect of hydrogen rich saline on gout arthritis in rats[J]. Guangdong Med. J., 2017, 38(5): 672-674. | |
| 59 | 马广斌, 黄永吉, 严冬雪. 氢气饱和等渗盐水腹腔注射治疗兔创伤性关节炎的实验研究[J]. 医学研究生学报, 2014, 27(8): 810-813. |
| MA G B, HUANG Y J, YAN D X. Experimental research on intraperitoneal injection of saturated hydrogen saline for treating traumatic arthritis in rabbits[J]. J. Med. Postgrad., 2014, 27(8): 810-813. | |
| 60 | WU G, PAN L, SUN J, et al.. Hydrogen gas protects against ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by inhibiting NF-κB activation[J]. Menopause, 2019, 26(7): 785-792. |
| 61 | GUO J D, LI L, SHI Y M, et al.. Hydrogen water consumption prevents osteopenia in ovariectomized rats[J]. Br. J. Pharmacol., 2013, 168(6): 1412-1420. |
| 62 | CARNOVALI M, BANFI G, MARIOTTI M. Molecular hydrogen prevents osteoclast activation in a glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis zebrafish scale model[J/OL]. Antioxidants, 2023, 12(2): 345[2024-06-13]. . |
| 63 | GUO J, DONG W, JIN L, et al.. Hydrogen-rich saline prevents bone loss in diabetic rats induced by streptozotocin[J]. Int. Orthop., 2017, 41(10): 2119-2128. |
| 64 | SUN Y, SHUANG F, CHEN D M, et al.. Treatment of hydrogen molecule abates oxidative stress and alleviates bone loss induced by modeled microgravity in rats[J]. Osteoporos. Int. 2013, 24(3): 969-978. |
| 65 | LIU Y, WANG D L, HUANG Y C, et al.. Hydrogen inhibits the osteoclastogenesis of mouse bone marrow mononuclear cells[J/OL]. Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2020, 110: 110640[2024-06-13]. . |
| 66 | ZHANG W, HUANG C, SUN A, et al.. Hydrogen alleviates cellular senescence via regulation of ROS/p53/p21 pathway in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vivo [J]. Biomed. Pharmacother., 2018, 106: 1126-1134. |
| 67 | KAWASAKI H, GUAN J, TAMAMA K. Hydrogen gas treatment prolongs replicative lifespan of bone marrow multipotential stromal cells in vitro while preserving differentiation and paracrine potentials[J]. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2010, 397(3): 608-613. |
| 68 | CARNOVALI M, MARIOTTI M, BANFI G. Molecular hydrogen enhances osteogenesis in Danio rerio embryos[J]. J. Fish Biol., 2021, 98(5): 1471-1474. |
| 69 | CAI W W, ZHANG M H, YU Y S, et al.. Treatment with hydrogen molecule alleviates TNFα-induced cell injury in osteoblast[J]. Mol. Cell. Biochem., 2013, 373(1-2): 1-9. |
| 70 | 刘红卫, 袁昌青, 于新波, 等. 氢气减弱脂多糖对人牙周膜细胞成骨能力的抑制[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2015, 31(6): 797-800. |
| LIU H W, YUAN C Q, YU X B, et al.. Hydrogen attenuates the inhibition of P.g-LPS on osteogenic capacity of Huma periodental ligament cells[J]. J. Pract. Stomatol., 2015, 31(6): 797-800. |
| [1] | Yifei CAI, Yezi MA, Meijuan XIA, Cuicui LIU, Hongtao WANG, Jiaxi ZHOU. Analysis of Molecular Characteristics of Megakaryocytes Between Embryonic Aorta-gonad-mesonephros and Adult Bone Marrow [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(4): 702-710. |
| [2] | HanXiao MA. Development of qPCR Standard Curves for Monitoring Population Dynamics in a Dual-bacterial Fermentative Hydrogen Production System [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(2): 325-332. |
| [3] | Shangshang WANG, Zhenya XUE, Haiyan XING, Xue YANG, Min WANG, Qing RAO. Influence of Different Lodging Sites on the Stemness of Leukemia Cells in a Mouse Leukemia Model [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(2): 349-354. |
| [4] | Jianhong YANG, Boyan LIU, Jun CHEN, Zhihui QIU, Baoqiang LI, Shucun QIN, Yandong NIU, Lei HE. Effects of Pre-treatment of Nanobubble Hydrogen Water on the Mouse Psoriasis Induction by Imiquimod [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(4): 676-684. |
| [5] | Jiaqi SUN, Jia GUO, Chuang ZHANG, Qing LIU, Ziyu WANG, Hanchao XIA, Buxuan QIAN, Fangfang ZHAO, Qi WANG, Jianfeng LIU, Xiangguo LIU. Research Progress of Phosphite Dehydrogenase in Genetically Engineered Microorganisms and Plants [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(2): 173-181. |
| [6] | Xingyu LIU, Guoli ZHAO, Xuejing LI. Application Progress of Hydrogen in Medical Field [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(1): 102-110. |
| [7] | Jianhong YANG, Jun CHEN, Xuefei LI, Lijun LIU, Lili CHEN, Xinsuo DUAN, Shucun QIN, Lei HE. The Potential and Prospect of Molecular Hydrogen in the Treatment of Skin Diseases [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(6): 875-881. |
| [8] | Junkai ZHU, Lingzhi GE, Chao ZHANG, Can CAO, Jiahui WU, Zhen MU. Inhibitory Effect of Hydrogen Molecule on Imiquimod-induced Psoriasis-like Dermatitis in Mice [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(6): 945-953. |
| [9] | Jun LI, Yifei SONG, Yang YI, Chen MA, Ziyi ZHANG⁃HUANG, Linlin DU, Junyu LI, Fei XIE, Xuemei MA. Research Progress on Heme Protein Targets of Gas Signaling Molecules [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(4): 499-508. |
| [10] | Chen MA, Yifei SONG, Yang YI, Ziyi LIU, Fei XIE, Xuemei MA. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Hydrogen and Mitochondria [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(3): 366-374. |
| [11] | Zisong CAI, Pengxiang ZHAO, Xujuan ZHANG, Ziyi LIU, Mengyu LIU, Fei XIE, Chen MA. Research Progress on the Application of Hydrogen in Trauma Rescue and Treatment [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(3): 375-382. |
| [12] | Jingyi ZHANG, Xue JIANG, Siyu MA, Zhichao FENG, Yang YI, Chen MA, Yifei SONG, Fei XIE. Research Progress on the Protective Effects of Hydrogen Gas on Traumatic Brain Injury [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(2): 234-239. |
| [13] | Zijia LIU, Xue JIANG, Yang YI, Meng WANG, Cheng MA, Yifei SONG, Fei XIE. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Hydrogen and Intestinal Flora [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2022, 12(6): 847-852. |
| [14] | Yifei SONG, Fei XIE, Chen MA, Xuemei MA. Research Progress on Hydrogenase Activity in Higher Plants [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2022, 12(4): 481-489. |
| [15] | Geru TAO, Shucun QIN. Molecular Mechanism of Hydrogen Biomedicine in Relieving Free Radical Oxidative Stress [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2022, 12(4): 490-496. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||