Current Biotechnology ›› 2023, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (5): 681-689.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2023.0048
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Research Progress on the Immune Regulation of EBV on the Host
Xujuan ZHANG( ), Pengxiang ZHAO(
), Pengxiang ZHAO( ), Ziyi LIU, Zisong CAI, Mengyu LIU, Fei XIE, Xuemei MA
), Ziyi LIU, Zisong CAI, Mengyu LIU, Fei XIE, Xuemei MA
- Faculty of Environment and Life,Beijing University of Technology,Beijing 100124,China
-
Received:2023-04-12Accepted:2023-07-10Online:2023-09-25Published:2023-10-10 -
Contact:Pengxiang ZHAO
EBV对宿主免疫的调控作用研究进展
张旭娟( ), 赵鹏翔(
), 赵鹏翔( ), 刘子怡, 蔡子松, 刘梦昱, 谢飞, 马雪梅
), 刘子怡, 蔡子松, 刘梦昱, 谢飞, 马雪梅
- 北京工业大学环境与生命学部,北京 100124
-
通讯作者:赵鹏翔 -
作者简介:张旭娟E-mail: 1094191300@qq.com; -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(81602408);北京市科技新星计划项目(20220484218)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xujuan ZHANG, Pengxiang ZHAO, Ziyi LIU, Zisong CAI, Mengyu LIU, Fei XIE, Xuemei MA. Research Progress on the Immune Regulation of EBV on the Host[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(5): 681-689.
张旭娟, 赵鹏翔, 刘子怡, 蔡子松, 刘梦昱, 谢飞, 马雪梅. EBV对宿主免疫的调控作用研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2023, 13(5): 681-689.
share this article
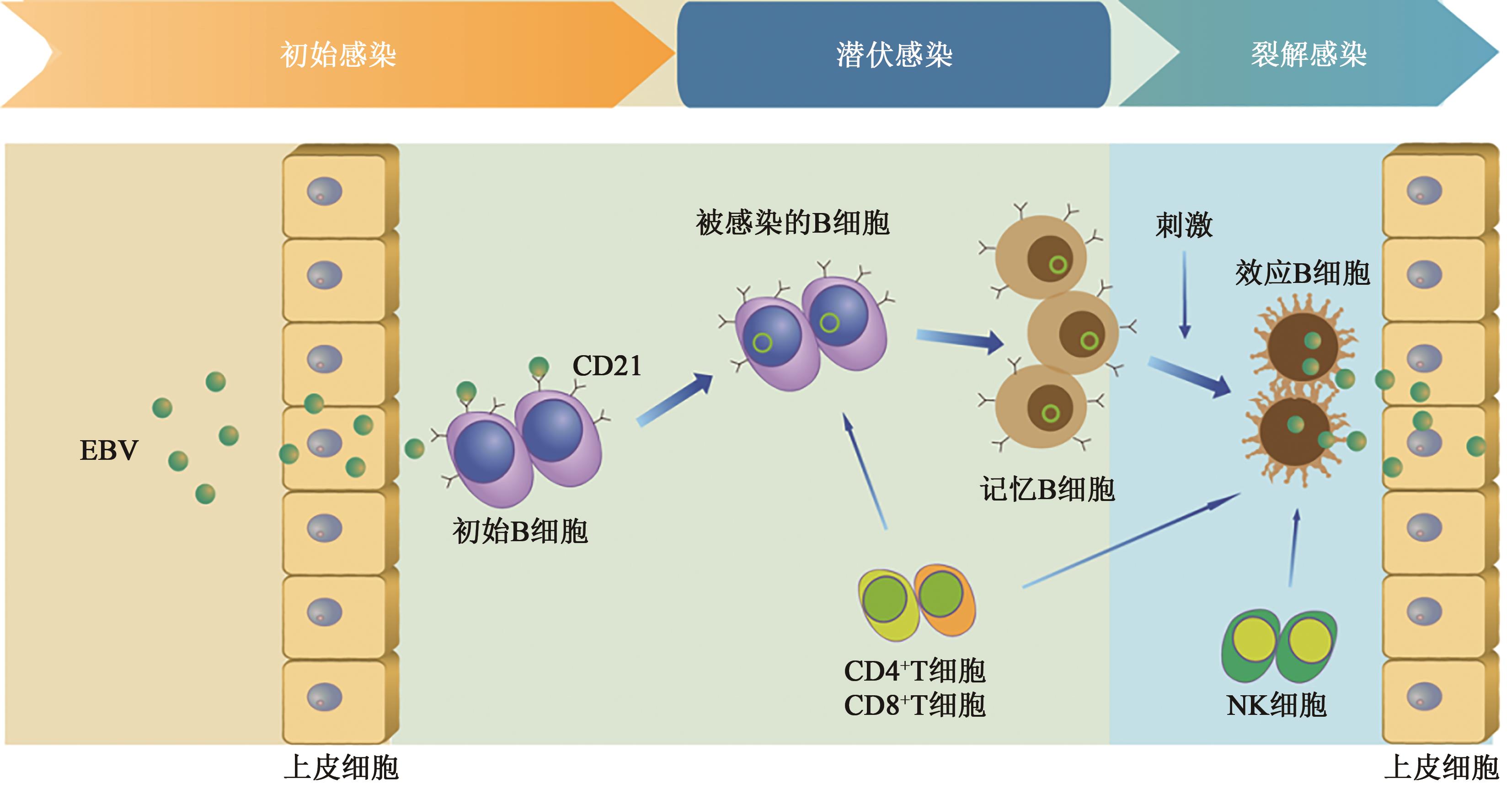
Table 1 Gene expression and associated tumors of the four latent types in the latent state of EBV
Table 2 Host immune regulation by EBV latent gene products
Table 3 Host immune regulation by EBV lytic gene products
| 1 | FARRELL P J. Epstein-barr virus and cancer[J]. Annu. Rev. Pathol., 2019, 14: 29-53. |
| 2 | NOTARTE K I, SENANAYAKE S, MACARANAS I, et al.. microRNA and other non-coding RNAs in epstein-barr virus-associated cancers[J/OL]. Cancers, 2021, 13(15): 3909[2023-07-20]. . |
| 3 | DU Y, ZHANG J Y, GONG L P, et al.. Hypoxia-induced ebv-circLMP2A promotes angiogenesis in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma through the KHSRP/VHL/HIF1α/VEGFA pathway[J]. Cancer Lett., 2022, 526: 259-272. |
| 4 | YUAN L, LI S, CHEN Q, et al.. EBV infection-induced GPX4 promotes chemoresistance and tumor progression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Cell Death Differ., 2022, 29(8): 1513-1527. |
| 5 | HOUEN G, TRIER N H. Epstein-barr virus and systemic autoimmune diseases[J/OL]. Front. Immunol., 2020, 11: 587380[2023-07-20]. . |
| 6 | KAUR B P, SECORD E. Innate immunity[J]. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N Am., 2021, 41(4): 535-541. |
| 7 | VRBA S M, HICKMAN H D. Imaging viral infection in vivo to gain unique perspectives on cellular antiviral immunity[J]. Immunol. Rev., 2022, 306(1): 200-217. |
| 8 | BOUWMAN W, VERHAEGH W, HOLTZER L, et al.. Measurement of cellular immune response to viral infection and vaccination[J/OL]. Front. Immunol., 2020, 11: 575074[2023-07-20]. . |
| 9 | DUAN T, DU Y, XING C, et al.. Toll-like receptor signaling and its role in cell-mediated immunity[J/OL]. Front. Immunol., 2022, 13: 812774[2023-07-20]. . |
| 10 | KAWAI T, AKIRA S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity[J]. Immunity, 2011, 34(5): 637-650. |
| 11 | ZHOU R, LIU L, WANG Y. Viral proteins recognized by different TLRs[J]. J. Med. Virol., 2021, 93(11): 6116-6123. |
| 12 | BUCHER K, RODRÍGUEZ-BOCANEGRA E, WISSINGER B, et al.. Extra-viral DNA in adeno-associated viral vector preparations induces TLR9-dependent innate immune responses in human plasmacytoid dendritic cells[J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2023, 13(1): 1890[2023-07-20]. . |
| 13 | ZHAO H, WU L, YAN G, et al.. Inflammation and tumor progression: signaling pathways and targeted intervention[J/OL]. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther., 2021, 6(1): 263[2023-07-20]. . |
| 14 | NEGISHI H, TANIGUCHI T, YANAI H. The interferon (IFN) class of cytokines and the IFN regulatory factor (IRF) transcription factor family[J/OL]. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol., 2018, 10(11): a028423[2023-07-20]. . |
| 15 | SETTE A, CROTTY S. Adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(4): 861-880. |
| 16 | SCHNEIDER W M, CHEVILLOTTE M D, RICE C M. Interferon-stimulated genes: a complex web of host defenses[J]. Annu. Rev. Immunol., 2014, 32: 513-545. |
| 17 | WOHLFORD E M, BARESEL P C, WILMORE J R, et al.. Changes in tonsil B cell phenotypes and EBV receptor expression in children under 5-years-old[J]. Cytometry B Clin. Cytom., 2018, 94(2): 291-301. |
| 18 | ZUO L L, ZHU M J, DU S J, et al.. The entry of Epstein-Barr virus into B lymphocytes and epithelial cells during infection[J]. Chin. J. Virol., 2014, 30(4): 476-482. |
| 19 | INAGAKI T, SATO Y, ITO J, et al.. Direct evidence of abortive lytic infection-mediated establishment of epstein-barr virus latency during B-cell infection[J/OL]. Front. Microbiol., 2020, 11: 575255[2023-07-20]. . |
| 20 | MURATA T, SUGIMOTO A, INAGAKI T, et al.. Molecular basis of epstein-barr virus latency establishment and lytic reactivation[J/OL]. Viruses, 2021, 13(12): 2344[2023-07-20]. . |
| 21 | LIAO Y, ZHANG J B, LU L X, et al.. Oral microbiota alteration and roles in epstein-barr virus reactivation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J/OL]. Microbiol. Spectr., 2023, 11(1): e0344822 [2023-07-20]. . |
| 22 | BORDE C, QUIGNON F, AMIEL C, et al.. Methyl-qPCR: a new method to investigate Epstein-Barr virus infection in post-transplant lymphoproliferative diseases[J/OL]. Clin. Epigenet., 2022, 14(1): 33[2023-07-20]. . |
| 23 | KO Y H. EBV and human cancer[J/OL]. Exp. Mol. Med., 2015, 47(1): e130[2023-07-20]. . |
| 24 | ZHENG X, WANG R, ZHANG X, et al.. A deep learning model and human-machine fusion for prediction of EBV-associated gastric cancer from histopathology[J/OL]. Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(1): 2790[2023-07-20]. . |
| 25 | THORLEY-LAWSON D A. EBV persistence: introducing the virus[J]. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol., 2015, 390(Pt 1): 151-209. |
| 26 | KUTZ H, REISBACH G, SCHULTHEISS U, et al.. The C-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway is critical for cell transformation by the latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus[J]. Virology, 2008, 371(2): 246-256. |
| 27 | ZHANG J, DAS S C, KOTALIK C, et al.. The latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus establishes an antiviral state via induction of interferon-stimulated genes[J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2004, 279(44): 46335-46342. |
| 28 | HUYE L E, NING S, KELLIHER M, et al.. Interferon regulatory factor 7 is activated by a viral oncoprotein through RIP-dependent ubiquitination[J]. Mol. Cell. Biol., 2007, 27(8): 2910-2918. |
| 29 | FATHALLAH I, PARROCHE P, GRUFFAT H, et al.. EBV latent membrane protein 1 is a negative regulator of TLR9[J]. J. Immunol., 2010, 185(11): 6439-6447. |
| 30 | STEWART S, DAWSON C W, TAKADA K, et al.. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP2A regulates viral and cellular gene expression by modulation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor pathway[J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2004, 101(44): 15730-15735. |
| 31 | FISH K, COMOGLIO F, SHAFFER A L, et al.. Rewiring of B cell receptor signaling by Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A[J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2020, 117(42): 26318-26327. |
| 32 | SHAH K M, STEWART S E, WEI W, et al.. The EBV-encoded latent membrane proteins, LMP2A and LMP2B, limit the actions of interferon by targeting interferon receptors for degradation[J]. Oncogene, 2009, 28(44): 3903-3914. |
| 33 | MANCAO C, HAMMERSCHMIDT W. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A is a B-cell receptor mimic and essential for B-cell survival[J]. Blood, 2007, 110(10): 3715-3721. |
| 34 | VALENTINE R, DAWSON C W, HU C, et al.. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 inhibits the canonical NF-kappa B pathway in carcinoma cells by inhibiting IKK phosphorylation[J/OL]. Mol. Cancer, 2010, 9: 1[2023-07-20]. . |
| 35 | WESTHOFF SMITH D, CHAKRAVORTY A, HAYES M, et al.. The epstein-barr virus oncogene EBNA1 suppresses natural killer cell responses and apoptosis early after infection of peripheral B cells[J/OL]. mBio, 2021, 12(6): e0224321[2023-07-20]. . |
| 36 | KIS L L, TAKAHARA M, NAGY N, et al.. IL-10 can induce the expression of EBV-encoded latent membrane protein-1 (LMP-1) in the absence of EBNA-2 in B lymphocytes and in Burkitt lymphoma and NK lymphoma-derived cell lines[J]. Blood, 2006, 107(7): 2928-2935. |
| 37 | KANDA K, KEMPKES B, BORNKAMM G W, et al.. The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2), a protein required for B lymphocyte immortalization, induces the synthesis of type I interferon in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines[J]. Biol. Chem., 1999, 380(2): 213-221. |
| 38 | KANDA K, DECKER T, AMAN P, et al.. The EBNA2-related resistance towards alpha interferon (IFN-alpha) in Burkitt's lymphoma cells effects induction of IFN-induced genes but not the activation of transcription factor ISGF-3[J]. Mol. Cell. Biol., 1992, 12(11): 4930-4936. |
| 39 | PAGÈS F, GALON J, KARASCHUK G, et al.. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 induces interleukin-18 receptor expression in B cells[J]. Blood, 2005, 105(4): 1632-1639. |
| 40 | MUROMOTO R, IKEDA O, OKABE K, et al.. Epstein-Barr virus-derived EBNA2 regulates STAT3 activation[J]. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2009, 378(3): 439-443. |
| 41 | BOUVET M, VOIGT S, TAGAWA T, et al.. Multiple viral microRNAs regulate interferon release and signaling early during infection with epstein-barr virus[J]. mBio, 2021, 12(2): e03440-20[2023-07-20]. . |
| 42 | LI Z, DUAN Y, CHENG S, et al.. EBV-encoded RNA via TLR3 induces inflammation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(27): 24291-24303. |
| 43 | HANEKLAUS M, GERLIC M, KUROWSKA-STOLARSKA M, et al.. Cutting edge: miR-223 and EBV miR-BART15 regulate the NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-1β production[J]. J. Immunol., 2012, 189(8): 3795-3799. |
| 44 | HUANG W T, LIN C W. EBV-encoded miR-BART20-5p and miR-BART8 inhibit the IFN-γ-STAT1 pathway associated with disease progression in nasal NK-cell lymphoma[J]. Am. J. Pathol., 2014, 184(4): 1185-1197. |
| 45 | ZENG M, CHEN Y, JIA X, et al.. The anti-apoptotic role of EBV-LMP1 in lymphoma cells[J]. Cancer Manag. Res., 2020, 12: 8801-8811. |
| 46 | VOIGT S, STERZ K R, GIEHLER F, et al.. A central role of IKK2 and TPL2 in JNK activation and viral B-cell transformation[J/OL]. Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1): 685[2023-07-20]. . |
| 47 | KAYKAS A, WORRINGER K, SUGDEN B. LMP-1's transmembrane domains encode multiple functions required for LMP-1's efficient signaling[J]. J. Virol., 2002, 76(22): 11551-11560. |
| 48 | LEE J, SUGDEN B. A membrane leucine heptad contributes to trafficking, signaling, and transformation by latent membrane protein 1[J]. J. Virol., 2007, 81(17): 9121-9130. |
| 49 | YASUI T, LUFTIG M, SONI V, et al.. Latent infection membrane protein transmembrane FWLY is critical for intermolecular interaction, raft localization, and signaling[J]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2004, 101(1): 278-283. |
| 50 | NING S, PAGANO J S, BARBER G N. IRF7: activation, regulation, modification and function[J]. Genes Immun., 2011, 12(6): 399-414. |
| 51 | YIN Y, MANOURY B, FAHRAEUS R. Self-inhibition of synthesis and antigen presentation by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1[J]. Science, 2003, 301(5638): 1371-1374. |
| 52 | WOOD V H J, O'NEIL J D, WEI W, et al.. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 regulates cellular gene transcription and modulates the STAT1 and TGF beta signaling pathways[J]. Oncogene, 2007, 26(28): 4135-4147. |
| 53 | ZVEJNIECE L, KOZIREVA S, RUDEVICA Z, et al.. Expression of the chemokine receptor CCR1 in Burkitt lymphoma cell lines is linked to the CD10-negative cell phenotype and co-expression of the EBV latent genes EBNA2, LMP1, and LMP2[J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23(7): 3434[2023-07-20]. . |
| 54 | LI Y, LONG X, HUANG L, et al.. Epstein-barr virus BZLF1-mediated downregulation of proinflammatory factors is essential for optimal lytic viral replication[J]. J. Virol., 2016, 90(2): 887-903. |
| 55 | MORRISON T E, MAUSER A, WONG A, et al.. Inhibition of IFN-gamma signaling by an Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early protein[J]. Immunity, 2001, 15(5): 787-799. |
| 56 | HAHN A M, HUYE L E, NING S, et al.. Interferon regulatory factor 7 is negatively regulated by the Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early gene, BZLF-1[J]. J. Virol., 2005, 79(15): 10040-10052. |
| 57 | BENTZ G L, LIU R, HAHN A M, et al.. Epstein-Barr virus BRLF1 inhibits transcription of IRF3 and IRF7 and suppresses induction of interferon-beta[J]. Virology, 2010, 402(1): 121-128. |
| 58 | MORRISON T E, KENNEY S C. BZLF1, an Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early protein, induces p65 nuclear translocation while inhibiting p65 transcriptional function[J]. Virology, 2004, 328(2): 219-232. |
| 59 | GUTSCH D E, HOLLEY-GUTHRIE E A, ZHANG Q, et al.. The bZIP transactivator of epstein-barr virus, BZLF1, functionally and physically interacts with the p65 subunit of NF-kappa B[J]. Mol. Cell. Biol., 1994, 14(3): 1939-1948. |
| 60 | WANG J T, CHANG L S, CHEN C J, et al.. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 negatively regulates IFN regulatory factor 3 transactivation through phosphorylation at its linker region[J]. Innate Immun., 2014, 20(1): 78-87. |
| 61 | WANG J T, LDOONG S, TENG S C, et al.. Epstein-Barr virus BGLF4 kinase suppresses the interferon regulatory factor 3 signaling pathway[J]. J. Virol., 2009, 83(4): 1856-1869. |
| 62 | CHANG L S, WANG J T, LDOONG S, et al.. Epstein-barr virus BGLF4 kinase downregulates NF-κB transactivation through phosphorylation of coactivator UXT[J]. J. Virol., 2012, 86(22): 12176-12186. |
| 63 | WU L, FOSSUM E, JOO C H, et al.. Epstein-Barr virus LF2: an antagonist to type I interferon[J]. J. Virol., 2009, 83(2): 1140-1146. |
| 64 | VAN GENT M, BRAEM S G, JONG A D, et al.. Epstein-Barr virus large tegument protein BPLF1 contributes to innate immune evasion through interference with toll-like receptor signaling[J/OL]. PLoS Pathog., 2014, 10(2): e1003960[2023-07-20]. . |
| 65 | ARIZA M E, RIVAILLER P, GLASER R, et al.. Epstein-Barr virus encoded dUTPase containing exosomes modulate innate and adaptive immune responses in human dendritic cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells[J/OL]. PLoS ONE, 2013, 8(7): e69827[2023-07-20]. . |
| 66 | WALDMAN W J, WILLIAMS M V, LEMESHOW S, et al.. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded dUTPase enhances proinflammatory cytokine production by macrophages in contact with endothelial cells: evidence for depression-induced atherosclerotic risk[J]. Brain Behav. Immun., 2008, 22(2): 215-223. |
| 67 | HAGEMEIER S R, BARLOW E A, KLEMAN A A, et al.. The Epstein-Barr virus BRRF1 protein, Na, induces lytic infection in a TRAF2- and p53-dependent manner[J]. J. Virol., 2011, 85(9): 4318-4329. |
| 68 | ADAMSON A L, DARR D, HOLLEY-GUTHRIE E, et al.. Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early proteins BZLF1 and BRLF1 activate the ATF2 transcription factor by increasing the levels of phosphorylated p38 and C-Jun N-terminal kinases[J]. J. Virol., 2000, 74(3): 1224-1233. |
| 69 | ZUO J, THOMAS W A, HAIGH T A, et al.. Epstein-Barr virus evades CD4+ T cell responses in lytic cycle through BZLF1-mediated downregulation of CD74 and the cooperation of vBcl-2[J/OL]. PLoS Pathog., 2011, 7(12): e1002455[2023-07-20]. . |
| 70 | QUINN L L, ZUO J, ABBOTT R J, et al.. Cooperation between Epstein-Barr virus immune evasion proteins spreads protection from CD8+ T cell recognition across all three phases of the lytic cycle[J/OL]. PLoS Pathog., 2014, 10(8): e1004322[2023-07-20]. . |
| 71 | BOWLING B L, ADAMSON A L. Functional interactions between the Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 protein and the promyelocytic leukemia protein[J]. Virus Res., 2006, 117(2): 244-253. |
| 72 | VAN GENT M, GRIFFIN B D, BERKHOFF E G, et al.. EBV lytic-phase protein BGLF5 contributes to TLR9 downregulation during productive infection[J]. J. Immunol., 2011, 186(3): 1694-1702. |
| 73 | ZUO J, THOMAS W, VAN LEEUWEN D, et al.. The DNase of gammaherpesviruses impairs recognition by virus-specific CD8+ T cells through an additional host shutoff function[J]. J. Virol., 2008, 82(5): 2385-2393. |
| 74 | SAITO S, MURATA T, KANDA T, et al.. Epstein-Barr virus deubiquitinase downregulates TRAF6-mediated NF-κB signaling during productive replication[J]. J. Virol., 2013, 87(7): 4060-4070. |
| [1] | Xiaoya LIU, Shuomin ZHANG, Peng ZHENG, Rui MA, Chaojun ZHANG. Role and Mechanisms of DBNDD1 in Colorectal Cancer Development [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(4): 726-734. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||