Current Biotechnology ›› 2024, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (1): 17-25.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2023.0124
• Special Forum on Development and Technology of Biologics • Previous Articles Next Articles
Overview of Norovirus Vaccine Research
Hongyan JIAO1( ), Guochao LI1, Liang CHANG1, Yanyi LI2, Lili ZHAI1(
), Guochao LI1, Liang CHANG1, Yanyi LI2, Lili ZHAI1( )
)
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Antibody Research & Development,Hebei Engineering Research Center of Antibody Medicine,North China Pharmaceutical Group Corporation New Drug Research and Development Co. ,Ltd. ,Shijiazhuang 052160,China
2.NCPC Genetech Biotechnology Co. ,Ltd. ,Shijiazhuang 050035,China
-
Received:2023-10-13Accepted:2023-11-30Online:2024-01-25Published:2024-02-05 -
Contact:Lili ZHAI
诺如病毒疫苗研究概况
焦红燕1( ), 李国超1, 常亮1, 李岩异2, 翟丽丽1(
), 李国超1, 常亮1, 李岩异2, 翟丽丽1( )
)
- 1.华北制药集团新药研究开发有限责任公司,抗体药物研制国家重点实验室,抗体药物河北省工程研究中心,石家庄 052160
2.华北制药金坦生物技术股份有限公司,石家庄 050035
-
通讯作者:翟丽丽 -
作者简介:焦红燕 E-mail:894808686@qq.com; -
基金资助:河北省重点研发计划项目(21372403D);河北省高层次人才资助项目博士后科研项目择优资助B项目(2021005012)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hongyan JIAO, Guochao LI, Liang CHANG, Yanyi LI, Lili ZHAI. Overview of Norovirus Vaccine Research[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(1): 17-25.
焦红燕, 李国超, 常亮, 李岩异, 翟丽丽. 诺如病毒疫苗研究概况[J]. 生物技术进展, 2024, 14(1): 17-25.
share this article
| 疫苗类型 | 概念 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 灭活疫苗 | 用物理、化学方法杀死病原微生物,但仍保持其免疫原性(能识别结合T/B细胞并使它们活化的能力)的一种生物制剂 | 安全性较高,疫苗稳定,易于保存 | 接种量大,需多次接种;只能引起体液免疫;免疫维持时间较短 |
减毒活疫苗 (活疫苗) | 活疫苗是通过毒力变异或人工选择法(如温度敏感株)而获得的减毒或无毒株,或者是从自然界直接选择出来的弱毒或无毒株经培养后制成的疫苗 | 接种量少,只需接种一次;可诱发体液和细胞免疫;免疫维持时间较长 | 有毒力回升的风险;疫苗不稳定,不易保存 |
| 亚单位疫苗 | 通过化学分解或有控制性的蛋白质水解方法,提取细菌、病毒的特殊蛋白质结构,筛选出具有免疫活性的片段制成的疫苗 | 减少了不良反应和疫苗引起的相关疾病 | 需要联合佐剂使用;不能诱发细胞和黏膜免疫 |
| 重组蛋白疫苗 | 将保护性抗原基因在真核或原核细胞体系中表达,并将其产生的蛋白抗原纯化后制成疫苗 | 安全性高,稳定性好,易放大生产 | 需使用佐剂,生产工艺复杂 |
| 病毒载体疫苗 | 将抗原基因插入病毒载体基因中,进入人体后使之高效表达抗原蛋白,进而诱发免疫保护作用 | 安全性高,可诱发体液和细胞免疫,载体可发挥佐剂作用 | 体内的预存免疫影响免疫效果 |
| RNA疫苗 | 体外合成编码目标抗原的mRNA序列,mRNA进入宿主细胞表达目标抗原从而激活免疫反应 | 安全性高,可快速制备,研发周期短 | 稳定性差,技术难度高,进入细胞效率低 |
| DNA疫苗 | 将含有抗原基因DNA序列的质粒直接引入人体,在宿主细胞内表达目标蛋白,激发机体产生免疫反应 | 生产周期短,可诱发体液和细胞免疫 | 免疫原性差,存在基因组整合突变风险 |
Table 1 Types of vaccines[21]
| 疫苗类型 | 概念 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 灭活疫苗 | 用物理、化学方法杀死病原微生物,但仍保持其免疫原性(能识别结合T/B细胞并使它们活化的能力)的一种生物制剂 | 安全性较高,疫苗稳定,易于保存 | 接种量大,需多次接种;只能引起体液免疫;免疫维持时间较短 |
减毒活疫苗 (活疫苗) | 活疫苗是通过毒力变异或人工选择法(如温度敏感株)而获得的减毒或无毒株,或者是从自然界直接选择出来的弱毒或无毒株经培养后制成的疫苗 | 接种量少,只需接种一次;可诱发体液和细胞免疫;免疫维持时间较长 | 有毒力回升的风险;疫苗不稳定,不易保存 |
| 亚单位疫苗 | 通过化学分解或有控制性的蛋白质水解方法,提取细菌、病毒的特殊蛋白质结构,筛选出具有免疫活性的片段制成的疫苗 | 减少了不良反应和疫苗引起的相关疾病 | 需要联合佐剂使用;不能诱发细胞和黏膜免疫 |
| 重组蛋白疫苗 | 将保护性抗原基因在真核或原核细胞体系中表达,并将其产生的蛋白抗原纯化后制成疫苗 | 安全性高,稳定性好,易放大生产 | 需使用佐剂,生产工艺复杂 |
| 病毒载体疫苗 | 将抗原基因插入病毒载体基因中,进入人体后使之高效表达抗原蛋白,进而诱发免疫保护作用 | 安全性高,可诱发体液和细胞免疫,载体可发挥佐剂作用 | 体内的预存免疫影响免疫效果 |
| RNA疫苗 | 体外合成编码目标抗原的mRNA序列,mRNA进入宿主细胞表达目标抗原从而激活免疫反应 | 安全性高,可快速制备,研发周期短 | 稳定性差,技术难度高,进入细胞效率低 |
| DNA疫苗 | 将含有抗原基因DNA序列的质粒直接引入人体,在宿主细胞内表达目标蛋白,激发机体产生免疫反应 | 生产周期短,可诱发体液和细胞免疫 | 免疫原性差,存在基因组整合突变风险 |
| 疫苗名称 | 疫苗类型 | 适应人群 | 开发公司 | 阶段 | 临床试验号 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIL-214 | VLP重组蛋白 | 5个月婴儿 | 武田 | Ⅱ/Ⅲ期 | NCT05281094 |
| 四价重组诺如病毒疫苗(毕赤酵母) | VLP重组蛋白 | 6周婴儿、成人、老年人 | 安徽智飞 | Ⅰ/Ⅱ期 | NCT04563533 |
| VXA-NVV-201、VXA-NVV-202 | 腺病毒载体 | 18~49岁;18~80岁 | Vaxart | Ⅰ/Ⅱ期 Ⅱ期 | NCT05212168 NCT05626803 |
重组诺如病毒双价 (GⅠ.1/GⅡ.4)疫苗 (汉逊酵母) | VLP重组蛋白 | 6个月婴儿~59岁成人 6个月婴儿~13岁儿童 | 国药中生 | Ⅱ期 Ⅲ期 | NCT04941261 NCT05916326 |
| 诺如病毒GI.4 / GI.4二价VLP疫苗 | VLP重组蛋白 | 18~40岁 | Icon Genetics GmbH | Ⅰ期 | NCT05508178 |
| 重组六价诺如病毒疫苗(康华生物) | VLP重组蛋白 | 18~59岁 | 成都康华 | Ⅰ期 | NCT05805618 |
| mRNA-1403/ mRNA-1405多价诺如病毒疫苗 | mRNA | 18~80岁 | Moderna | Ⅰ期 | NCT05992935 |
| 四价重组诺如病毒疫苗(汉逊酵母) | VLP重组蛋白 | 6个月婴儿、成人 | 远大赛威 | Ⅰ期 | CXSL2300464 CXSL2300465 |
Table 2 NoV vaccines in clinical research worldwide
| 疫苗名称 | 疫苗类型 | 适应人群 | 开发公司 | 阶段 | 临床试验号 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIL-214 | VLP重组蛋白 | 5个月婴儿 | 武田 | Ⅱ/Ⅲ期 | NCT05281094 |
| 四价重组诺如病毒疫苗(毕赤酵母) | VLP重组蛋白 | 6周婴儿、成人、老年人 | 安徽智飞 | Ⅰ/Ⅱ期 | NCT04563533 |
| VXA-NVV-201、VXA-NVV-202 | 腺病毒载体 | 18~49岁;18~80岁 | Vaxart | Ⅰ/Ⅱ期 Ⅱ期 | NCT05212168 NCT05626803 |
重组诺如病毒双价 (GⅠ.1/GⅡ.4)疫苗 (汉逊酵母) | VLP重组蛋白 | 6个月婴儿~59岁成人 6个月婴儿~13岁儿童 | 国药中生 | Ⅱ期 Ⅲ期 | NCT04941261 NCT05916326 |
| 诺如病毒GI.4 / GI.4二价VLP疫苗 | VLP重组蛋白 | 18~40岁 | Icon Genetics GmbH | Ⅰ期 | NCT05508178 |
| 重组六价诺如病毒疫苗(康华生物) | VLP重组蛋白 | 18~59岁 | 成都康华 | Ⅰ期 | NCT05805618 |
| mRNA-1403/ mRNA-1405多价诺如病毒疫苗 | mRNA | 18~80岁 | Moderna | Ⅰ期 | NCT05992935 |
| 四价重组诺如病毒疫苗(汉逊酵母) | VLP重组蛋白 | 6个月婴儿、成人 | 远大赛威 | Ⅰ期 | CXSL2300464 CXSL2300465 |
| 1 | 王金冬,马亚林,毛彤瑶,等.表达诺如病毒衣壳蛋白的重组腺病毒疫苗的构建及其免疫原性分析[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2022,35(3):257-262. |
| WANG J D, MA Y L, MAO T Y, et al.. Construction and immunogenicity of recombinant adenovirus vaccine expressing capsid protein of norovirus[J]. Chin. J. Biol., 2022, 35(3): 257-262. | |
| 2 | AHMED S M, HALL A J, ROBINSON A E, et al.. Global prevalence of norovirus in cases of gastroenteritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Infect. Dis., 2014, 14(8): 725-730. |
| 3 | BARTSCH S M, LOPMAN B A, OZAWA S, et al.. Global economic burden of norovirus gastroenteritis[J/OL]. PLoS ONE, 2016, 11(4): e0151219[2023-12-07]. . |
| 4 | 刘宇阳,陈勇.诺如病毒疫苗的研究进展[J].微生物学免疫学进展,2020,48(4):46. |
| LIU Y Y, CHEN Y. Research progress of norovirus vaccine[J]. Prog. Microbiol. Immunol., 2020, 48(4): 46. | |
| 5 | 侯亚楠,李启明.诺如病毒及其疫苗研究进展[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志,2019,39(8):628-632. |
| HOU Y N, LI Q M. Progress in norovirus research and vaccine development[J]. Chin. J. Microbiol. Immunol., 2019, 39(8): 628-632. | |
| 6 | LUCERO Y, MATSON D O, ASHKENAZI S, et al.. Norovirus: facts and reflections from past, present, and future[J/OL]. Viruses, 2021, 13(12): 2399[2023-11-30]. . |
| 7 | 刘晖,周东明,谢迪,等.六价诺如病毒VLPs疫苗及其制备方法:CN115677838A[P].2023-02-03. |
| LIU H, ZHOU D M, XIE D, et al.. Hexavalent norovirus VLPs vaccine and its preparation method:CN115677838A[P].2023-02-03. | |
| 8 | ZHAO B, HU L, SONG Y, et al.. Norovirus protease structure and antivirals development[J/OL]. Viruses, 2021, 13(10): 2069[2023-11-30]. . |
| 9 | CAMPILLAY-VÉLIZ C P, CARVAJAL J J, AVELLANEDA A M, et al.. Human norovirus proteins: implications in the replicative cycle, pathogenesis, and the host immune response[J/OL]. Front. Immunol., 2020, 11: 961[2023-11-30]. . |
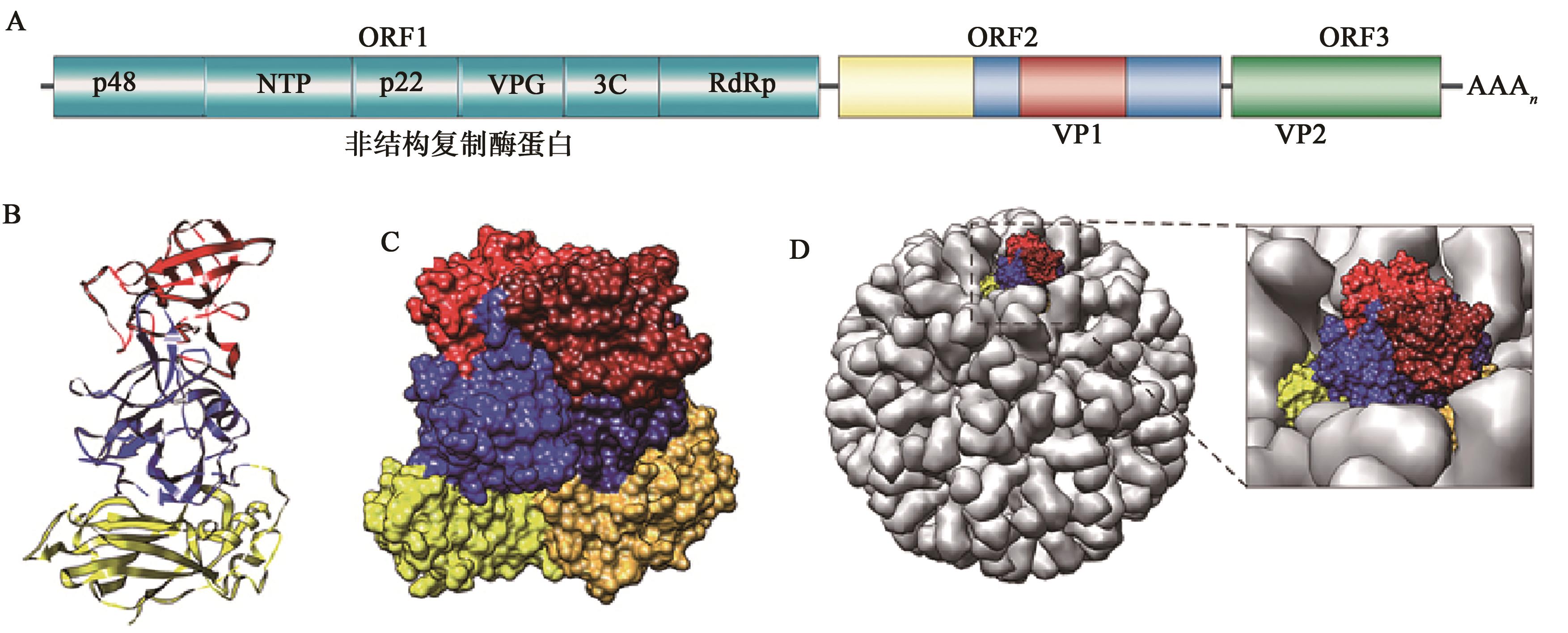
| 10 | VONGPUNSAWAD S, VENKATARAM P V, ESTES M K. Norwalk virus minor capsid protein VP2 associates within the VP1 shell domain[J]. J. Virol., 2013, 87(9): 4818-4825. |
| 11 | OPERARIO D J, PLATTS-MILLS J A, NADAN S, et al.. Etiology of severe acute watery diarrhea in children in the global rotavirus surveillance network using quantitative polymerase chain reaction[J]. J. Infect. Dis., 2017, 216(2): 220-227. |
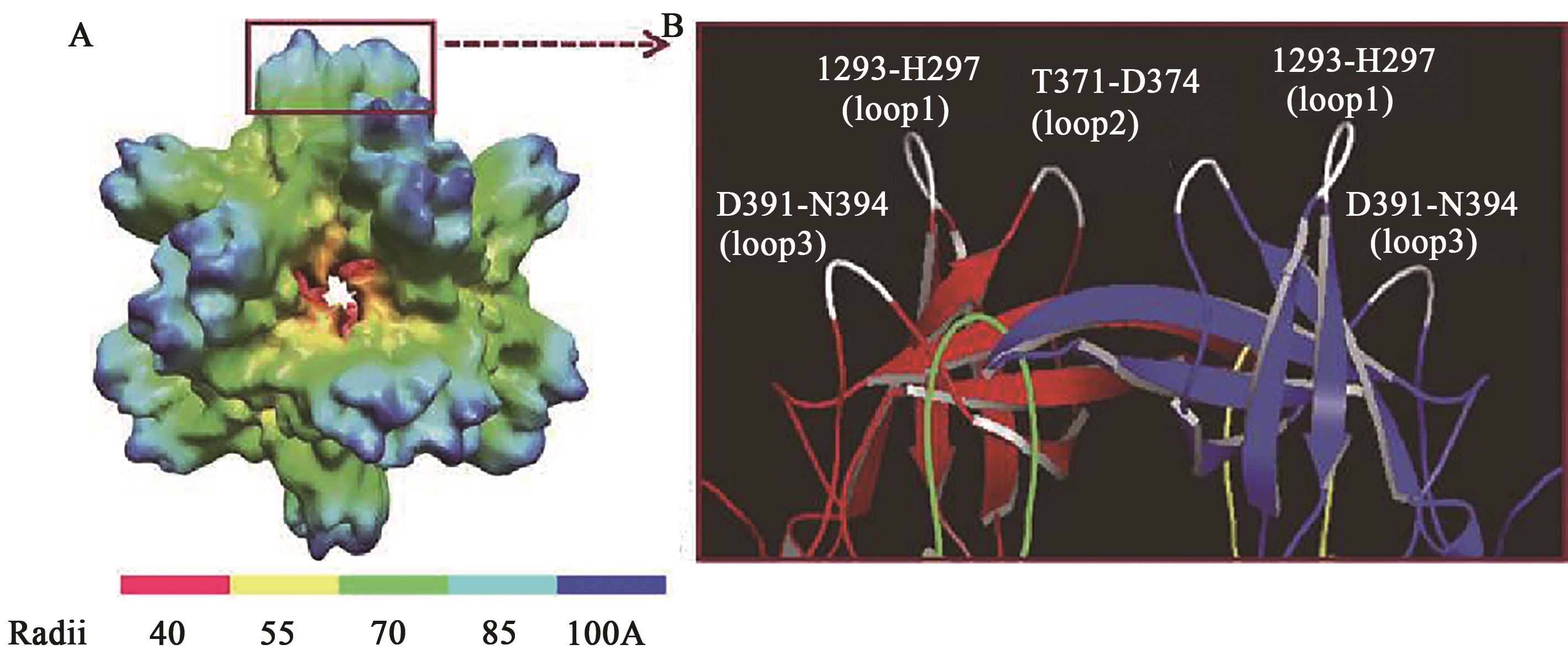
| 12 | TAN M, HEGDE R S, JIANG X. The P domain of norovirus capsid protein forms dimer and binds to histo-blood group antigen receptors[J]. J. Virol., 2004, 78(12): 6233-6242. |
| 13 | ALLEN D J, GRAY J J, GALLIMORE C I, et al.. Analysis of amino acid variation in the P2 domain of the GII-4 norovirus VP1 protein reveals putative variant-specific epitopes[J/OL]. PLoS ONE, 2008, 3(1): e1485[2023-12-07]. . |
| 14 | YAO L, LI F, WANG L, et al.. Function of VP2 protein in the stability of the secondary structure of virus-like particles of genogroup Ⅱ norovirus at different pH levels: function of VP2 protein in the stability of NoV VLPs[J]. J. Microbiol., 2014, 52(11): 970-975. |
| 15 | DONALDSON E F, LINDESMITH L C, LOBUE A D, et al.. Viral shape-shifting: norovirus evasion of the human immune system[J]. Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2010, 8(3): 231-241. |
| 16 | CHHABRA P, GRAAF M D, PARRA G I, et al.. Updated classification of norovirus genogroups and genotypes[J]. J. Gen. Virol., 2019, 100(10): 1393-1406. |
| 17 | DE GRAAF M, VAN BEEK J, KOOPMANS M P G. Human norovirus transmission and evolution in a changing world[J]. Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2016, 14(7): 421-433. |
| 18 | 熊佩.诺如病毒四价疫苗的免疫学评价和GⅡ.4型诺如病毒阻断抗体表位的鉴定[D].上海:中国科学院大学(中国科学院上海巴斯德研究所),2019. |
| XIONG P. Immunological evaluation of Norovirus tetravalent vaccine and identification of GⅡ.4 Norovirus blocking antibody epitopes[D]. Shanghai: University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Chinese Academy of Sciences Shanghai Pasteur Institute), 2019. | |
| 19 | ZHENG D P, ANDO T, FANKHAUSER R L, et al.. Norovirus classification and proposed strain nomenclature[J]. Virology, 2006, 346(2): 312-323. |
| 20 | 杨洁.现代疫苗的发展、分类、影响因素及问题探讨[J].现代养生,2019,19(22):61-62. |
| YANG J. Development, classification, influencing factors and problems of modern vaccines[J]. Health Prot. Promot., 2019, 19(22): 61-62. | |
| 21 | 王传林,李明,吕新军.人用疫苗的分类及生产工艺[J].中华预防医学杂志,2020,54(9):1017-1025. |
| WANG C Y, LI M, LV X J. Classification and production process of human vaccine[J]. Chin. Prev. Med., 2020, 54(9): 1017-1025. | |
| 22 | 曹颖雯,罗奕熔,梁耀民,等.人诺如病毒体外培养体系研究进展[J].现代预防医学,2020,47(22):4151-4154. |
| CAO Y W, LUO Y R, LIANG Y M, et al.. Research progress of human norovirus culture system in vitro[J]. Mod. Prev. Med., 2020, 47(22): 4151-4154. | |
| 23 | JONES M K, WATANABE M, ZHU S, et al.. Enteric bacteria promote human and mouse norovirus infection of B cells[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6210): 755-759. |
| 24 | ETTAYEBI K, CRAWFORD S E, MURAKAMI K, et al.. Replication of human noroviruses in stem cell-derived human enteroids[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6306): 1387-1393. |
| 25 | 周弘璐,汪萱怡.诺如病毒在研疫苗及挑战[J].中国新药杂志,2019,28(21):2607-2611. |
| ZHOU H L, WANG X Y. Norovirus vaccines under development and challenges[J]. Chin. J. N. Drugs, 2019, 28(21): 2607-2611. | |
| 26 | PARK B J, JUNG S T, CHOI C S, et al.. Pathogenesis of human norovirus genogroup Ⅱ genotype 4 in post-weaning gnotobiotic pigs[J]. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2018, 28(12): 2133-2140. |
| 27 | SOUZA M, AZEVEDO M S, JUNG K, et al.. Pathogenesis and immune responses in gnotobiotic calves after infection with the genogroup Ⅱ.4-HS66 strain of human norovirus[J]. J. Virol., 2008, 82(4): 1777-1786. |
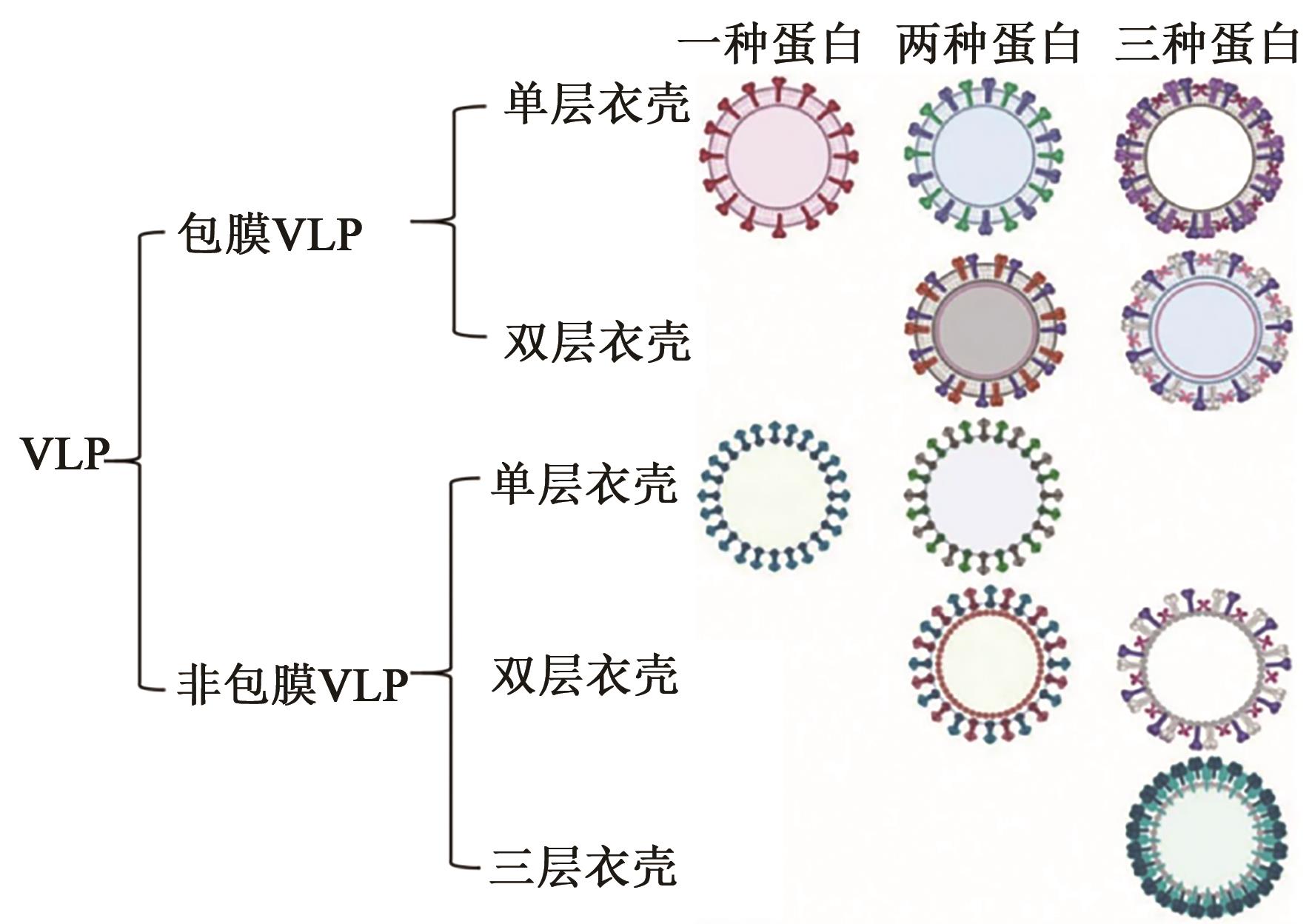
| 28 | FUENMAYOR J, GÒDIA F, CERVERA L. Production of virus-like particles for vaccines[J]. N. Biotechnol., 2017, 39(Pt B): 174-180. |
| 29 | NOORAEI S, BAHRULOLUM H, HOSEINI Z S, et al.. Virus-like particles: preparation, immunogenicity and their roles as nanovaccines and drug nanocarriers[J/OL]. J. Nanobiotechnol., 2021, 19(1): 59[2023-12-07]. . |
| 30 | JEONG H, SEONG B L. Exploiting virus-like particles as innovative vaccines against emerging viral infections[J]. J. Microbiol., 2017, 55(3): 220-230. |
| 31 | LEE Y T, KO E J, LEE Y, et al.. Intranasal vaccination with M2e5x virus-like particles induces humoral and cellular immune responses conferring cross-protection against heterosubtypic influenza viruses[J/OL]. PLoS ONE, 2018, 13(1): e0190868[2023-12-07]. . |
| 32 | MOHSEN M O, GOMES A C, VOGEL M, et al.. Interaction of viral capsid-derived virus-like particles (VLPs) with the innate immune system[J/OL]. Vaccines, 2018, 6(3): 37[2023-11-30]. . |
| 33 | ROLDÃO A, MELLADO M C M, CASTILHO L R, et al.. Virus-like particles in vaccine development[J]. Expert Rev. Vaccines, 2010, 9(10): 1149-1176. |
| 34 | WU X, CHEN P, LIN H, et al.. Hepatitis E virus: current epidemiology and vaccine[J]. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother., 2016, 12(10): 2603-2610. |
| 35 | ZHU F C, ZHANG J, ZHANG X F, et al.. Efficacy and safety of a recombinant hepatitis E vaccine in healthy adults: a large-scale, randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Lond. Engl., 2010, 376(9744): 895-902. |
| 36 | 马苏达 T, 舍伍德 J, 门德尔曼 P,等.诺如病毒疫苗配制品及方法:CN113453711A[P].2021-09-28. |
| MASUDA T, SHERWOOD J, MENDELMAN P, et al.. Norovirus vaccine formulations and methods: CN113453711A[P]. 2021-09-28. | |
| 37 | BERNSTEIN D I, ATMAR R L, LYON G M, et al.. Norovirus vaccine against experimental human GII.4 virus illness: a challenge study in healthy adults[J]. J. Infect. Dis., 2015, 211(6): 870-878. |
| 38 | LINDESMITH L C, FERRIS M T, MULLAN C W, et al.. Broad blockade antibody responses in human volunteers after immunization with a multivalent norovirus VLP candidate vaccine: immunological analyses from a phase I clinical trial[J/OL]. PLoS Med., 2015, 12(3): e1001807[2023-12-07]. . |
| 39 | 程博.诺如病毒四价疫苗获批进入临床研究[J].高科技与产业化,2019(7):71. |
| CHENG B. Norovirus tetravalent vaccine approved for clinical research[J]. High Tech. Industrialization, 2019(7): 71. | |
| 40 | KIM S H, CHEN S, JIANG X, et al.. Newcastle disease virus vector producing human norovirus-like particles induces serum, cellular, and mucosal immune responses in mice[J]. J. Virol., 2014, 88(17): 9718-9727. |
| 41 | KIM L, MARTINEZ C J, HODGSON K A, et al.. Systemic and mucosal immune responses following oral adenoviral delivery of influenza vaccine to the human intestine by radio controlled capsule[J/OL]. Sci. Rep., 2016, 6: 37295[2023-12-07]. . |
| 42 | KIM L, LIEBOWITZ D, LIN K, et al.. Safety and immunogenicity of an oral tablet norovirus vaccine, a phase I randomized, placebo-controlled trial[J/OL]. JCI Insight, 2018, 3(13): 121077[2023-12-07]. . |
| 43 | JOHNSON P C, MATHEWSON J J, DUPONT H L, et al.. Multiple-challenge study of host susceptibility to Norwalk gastroenteritis in US adults[J]. J. Infect. Dis., 1990, 161(1): 18-21. |
| 44 | HARRINGTON P R, YOUNT B, JOHNSTON R E, et al.. Systemic, mucosal, and heterotypic immune induction in mice inoculated with Venezuelan equine encephalitis replicons expressing norwalk virus-like particles[J]. J. Virol., 2002, 76(2): 730-742. |
| 45 | MA Y, LI J. Vesicular stomatitis virus as a vector to deliver virus-like particles of human norovirus: a new vaccine candidate against an important noncultivable virus[J]. J. Virol., 2011, 85(6): 2942-2952. |
| 46 | LICHTY B D, POWER A T, STOJDL D F, et al.. Vesicular stomatitis virus: re-inventing the bullet[J]. Trends Mol. Med., 2004, 10(5): 210-216. |
| 47 | BUKREYEV A, COLLINS P L. Newcastle disease virus as a vaccine vector for humans[J]. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther., 2008, 10(1): 46-55. |
| 48 | KARIKÓ K, BUCKSTEIN M, NI H, et al.. Suppression of RNA recognition by toll-like receptors: the impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA[J]. Immunity, 2005, 23(2): 165-175. |
| 49 | TAN M, FANG P, CHACHIYO T, et al.. Noroviral P particle: structure, function and applications in virus-host interaction[J]. Virology, 2008, 382(1): 115-123. |
| 50 | TAN M, HUANG P, XIA M, et al.. Norovirus P particle, a novel platform for vaccine development and antibody production[J]. J. Virol., 2011, 85(2): 753-764. |
| 51 | TAN M, JIANG X. The p domain of norovirus capsid protein forms a subviral particle that binds to histo-blood group antigen receptors[J]. J. Virol., 2005, 79(22): 14017-14030. |
| 52 | 吴佳颖,许红梅.与P颗粒相关的诺如病毒疫苗研究进展[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2021,21(105):146-147+150. |
| WU J Y, XU H M. Research progress on norovirus vaccines related to P particles[J]. Digest World Latest Med. Inf., 2021, 21(105): 146-147+150. | |
| 53 | TAN M, FANG P A, XIA M, et al.. Terminal modifications of norovirus P domain resulted in a new type of subviral particles, the small P particles[J]. Virology, 2011, 410(2): 345-352. |
| 54 | CAO S, LOU Z, TAN M, et al.. Structural basis for the recognition of blood group trisaccharides by norovirus[J]. J. Virol., 2007, 81(11): 5949-5957. |
| 55 | XIA M, TAN M, WEI C, et al.. A candidate dual vaccine against influenza and noroviruses[J]. Vaccine, 2011, 29(44): 7670-7677. |
| 56 | WANG L, CAO D, WEI C, et al.. A dual vaccine candidate against norovirus and hepatitis E virus[J]. Vaccine, 2014, 32(4): 445-452. |
| 57 | XIA M, WEI C, WANG L, et al.. A trivalent vaccine candidate against hepatitis E virus, norovirus, and astrovirus[J]. Vaccine, 2016, 34(7): 905-913. |
| 58 | YU Y, FU L, SHI Y, et al.. Elicitation of HIV-1 neutralizing antibodies by presentation of 4E10 and 10E8 epitopes on Norovirus P particles[J]. Immunol. Lett., 2015, 168(2): 271-278. |
| 59 | 付璐.基于诺如病毒P颗粒的Aβ免疫疗法对阿尔茨海默症的治疗效果研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2017. |
| FU L. Study on the effect of norovirus P particle-based Aβ immunotherapy of Alzheimer's disease[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017. | |
| 60 | 孙瑶.以诺如病毒P颗粒为载体的pTau31表位疫苗对阿尔茨海默症的治疗研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2020. |
| SUN Y. Study on theimmunotherapeutic effect of a norovirus P particle-based pTau31 epitope vaccine for Alzheimer's disease[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020. |
| [1] | Xiaojing GAO, Zhulan ZHANG, Xianju LIN, Guanrong QIU, Yaoming WEN, Jianhui FAN, Hongxiang HUANG. Optimization of Fermentation Culture Conditions for Cyclosporine A Using Response Surface Method [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(3): 518-525. |
| [2] | Zhaohui CUI, Ling GUO, Xudong SHEN, Yi LIN, Lili ZHAI. Immunogenicity Formation Mechanism and Control Strategy of Biopharmaceuticals [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(2): 212-219. |
| [3] | Jin WANG, Jing BAI, Jing ZHAO, Jian TIAN, Wei ZHANG, Yuan WANG, Haomeng YANG, Meishan SHI, Beibei ZHANG, Xinxin XU, Huoqing HUANG. Intelligent Mining of Novel GH45 Cellulases and its Efficient Expression in Trichoderma reesei [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(2): 287-295. |
| [4] | Xiaoqi WU, Wenjing GONG, Guoyu LI, Ang LI, Jihua WANG, Di CUI. Knowledge Gaps and Chanllenges in Microbial Fermentation of Traditional Chinese Medicine: From Strain Selection to Quality Control [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(2): 201-211. |
| [5] | Shuanghui ZHOU. Microbial Contamination and Antibiotic Resistance Characteristics in Raw Milk from Pastures in Northern Fujian Province [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(1): 127-134. |
| [6] | Ping YU, Di ZHAO, Xuejiao CHEN, Jia SONG, Haitao WANG, Xiangbo MIN. Study on Relieving Hyperuricemia and Gout Function by Limosilactobacillus reuteri HCS02-001 [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(3): 473-479. |
| [7] | Ting XU, Jiahao SHEN, Kang ZHAO, Lu HUANG, Enhui DONG, Kexin ZENG, Xinwei BIAN, Minghui JI, Qin XU. Bacterial Signature for Prediction of Disease Type Based on Abundance of Ruminococcus [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2024, 14(2): 323-330. |
| [8] | Pengxiao ZHANG, Nian HU. The Research Progress on Action Mechanism of Melanoma Immunotherapy [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(6): 900-906. |
| [9] | Pingcheng DUAN, Kai ZHENG, Yuhong ZHANG, Guoli ZHANG, Guoqing SUN. Evaluation of the Anti-disease Effect of Antagonistic Bacterium BJB01 Against Verticillium wilt [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(6): 913-918. |
| [10] | Xujuan ZHANG, Pengxiang ZHAO, Ziyi LIU, Zisong CAI, Mengyu LIU, Fei XIE, Xuemei MA. Research Progress on the Immune Regulation of EBV on the Host [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(5): 681-689. |
| [11] | Jiasheng BAO, Bingzhen PAN, Qiwu QIAO, Huizhi LIU, Suhua PAN. Advances in Yeast Bioactive Substances and Their Cosmetic Efficacy [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(3): 345-352. |
| [12] | Yuxuan GAO, Jingchen JIN, Yajuan GAO, Wentian ZHANG, Chenchen LI, Yongsheng JIN. Application of Heterotrophic Nitrification Aerobic Denitrifying Bacteria in the Landfill Leachate Treatment [J]. Current Biotechnology, 2022, 12(4): 630-637. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||