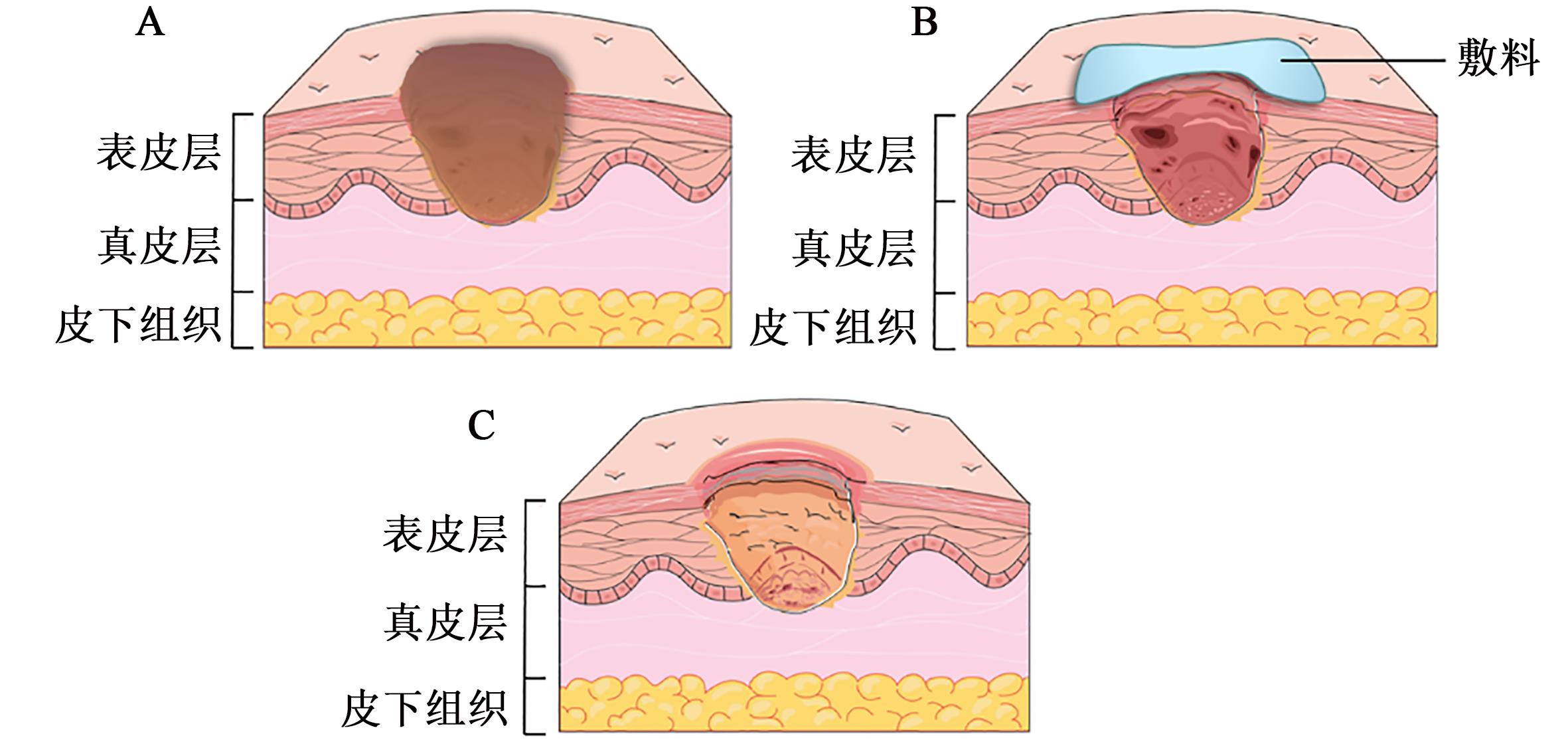
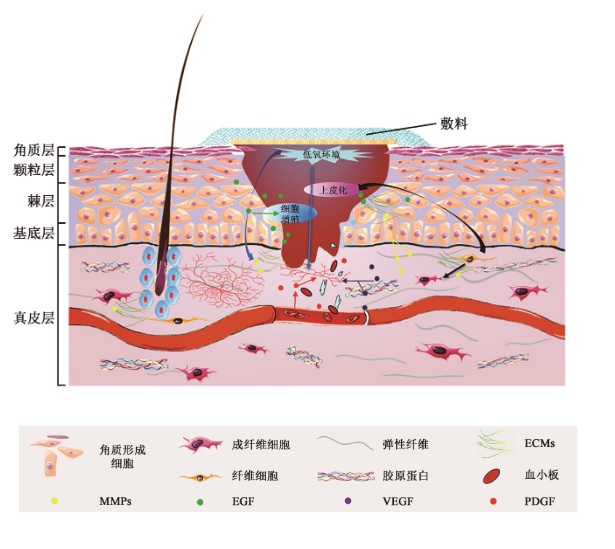
| 1 |
RODRIGUES M, KOSARIC N, BONHAM C A, et al.. Wound healing: a cellular perspective[J]. Physiol. Rev., 2019, 99(1): 665-706.
|
| 2 |
马林枭, 鲍济洪, 陈斌. 瘢痕: 评估、防治、早期干预方法的研究与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(20): 3253-3257.
|
| 3 |
宋增丽. 阴证溃疡护场与创面愈合的相关性及中药干预机制研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2019.
|
| 4 |
徐媛, 刘宏伟. 创面修复"TIME"原则及其意义[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(11): 2059-2062.
|
| 5 |
WINTER G D. Formation of the scab and the rate of epithelization of superficial wounds in the skin of the young domestic pig[J]. Nature, 1962, 193: 293-294.
|
| 6 |
HINMAN C D, MAIBACH H. Effect of air exposure and occlusion on experimental human skin wounds[J]. Nature, 1963, 200: 377-378.
|
| 7 |
CASTAÑO O, PÉREZ-AMODIO S, NAVARRO-REQUENA C, et al.. Instructive microenvironments in skin wound healing: biomaterials as signal releasing platforms[J]. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2018, 129: 95-117.
|
| 8 |
KRUSE C R, NUUTILA K, LEE C C Y, et al.. The external microenvironment of healing skin wounds[J]. Wound Repair Regen., 2015, 23(4): 456-464.
|
| 9 |
CUTTING K F. Wound exudate: composition and functions[J]. Br. J. Community Nurs., 2003, 8(S9): 4-9.
|
| 10 |
VOGT P M, ANDREE C, BREUING K, et al.. Dry, moist, and wet skin wound repair[J]. Ann. Plast. Surg., 1995, 34(5): 493-500.
|
| 11 |
JUNKER J P E, KAMEL R A, CATERSON E J, et al.. Clinical impact upon wound healing and inflammation in moist, wet, and dry environments[J]. Adv. Wound Care, 2013, 2(7): 348-356.
|
| 12 |
US Food and Drug Administration. Chronic cutaneous ulcer and burn wounds-developing products for treatment[EB/OL]. (2006-06) [2023-06-23]. .
|
| 13 |
LOKMIC Z, MUSYOKA J, HEWITSON T D, et al.. Hypoxia and hypoxia signaling in tissue repair and fibrosis[J]. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol., 2012, 296: 139-185.
|
| 14 |
梁楚婷, 郭炜骅, 谭理, 等. 低氧诱导因子-1:细胞适应氧供应改变的关键蛋白[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2019, 46(11): 1041-1049.
|
| 15 |
黄翀. 低氧通过CD9调控创面修复主要效应细胞移行与增殖的研究[D]. 重庆: 第三军医大学, 2013.
|
| 16 |
SEMBA H, TAKEDA N, ISAGAWA T, et al.. HIF-1α-PDK1 axis-induced active glycolysis plays an essential role in macrophage migratory capacity[J/OL]. Nat. Commun., 2016, 7: 11635[2016-05-18]. .
|
| 17 |
LI W, LI Y, GUAN S, et al.. Extracellular heat shock protein-90α: linking hypoxia to skin cell motility and wound healing[J]. EMBO J., 2007, 26(5): 1221-1233.
|
| 18 |
陈鑫. 低氧条件下Gαi1通过Akt/mTORC通路调控MAP4影响表皮细胞迁移的机制研究[D]. 重庆: 中国人民解放军陆军军医大学, 2019.
|
| 19 |
周燕, 王俐. 凝血酶与皮肤损伤愈合[J]. 中国麻风皮肤病杂志, 2011, 27(12): 857-859.
|
| 20 |
GRUBER R, JINDRA C, KANDLER B, et al.. Proliferation of dental pulp fibroblasts in response to thrombin involves mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling[J]. Int. Endod. J., 2004, 37(2): 145-150.
|
| 21 |
CUSCHIERI L, DEBOSZ J, MIILLER P, et al.. Autolytic debridement of a large, necrotic, fully occluded foot ulcer using a hydrocolloid dressing in a diabetic patient[J]. Adv. Skin Wound Care, 2013, 26(7): 300-304.
|
| 22 |
WERNER S, GROSE R. Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines[J]. Physiol. Rev., 2003, 83(3): 835-870.
|
| 23 |
GÖKŞEN S, BALABANLı B, COŞKUN-CEVHER Ş. Application of platelet derived growth factor-BB and diabetic wound healing: the relationship with oxidative events[J]. Free Radic. Res., 2017, 51(5): 498-505.
|
| 24 |
XIONG W, CHENG B H, JIA S B, et al.. Involvement of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in platelet-derived growth factor-induced migration of human lens epithelial cells[J]. Curr. Eye Res., 2010, 35(5): 389-401.
|
| 25 |
MELINCOVICI C S, BOŞCA A B, ŞUŞMAN S, et al.. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis[J]. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol., 2018, 59(2): 455-467.
|
| 26 |
王士岩. VEGF信号通路的转录和表观遗传的研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2019.
|
| 27 |
康从民, 王大伟, 吕英涛, 等. 血管内皮生长因子受体-2 所介导信号通路的研究进展[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2009, 36(10): 1267-1274.
|
| 28 |
BRASH J T, DENTI L, RUHRBERG C, et al.. VEGF188 promotes corneal reinnervation after injury[J/OL]. JCI Insight, 2019, 4(21): e130979[2019-11-01]. .
|
| 29 |
GÜÇ E, BRIQUEZ P S, FORETAY D, et al.. Local induction of lymphangiogenesis with engineered fibrin-binding VEGF-C promotes wound healing by increasing immune cell trafficking and matrix remodeling[J]. Biomaterials, 2017, 131: 160-175.
|
| 30 |
LU K J, WANG W, XU X L, et al.. A dual deformable liposomal ointment functionalized with retinoic acid and epidermal growth factor for enhanced burn wound healing therapy[J]. Biomater. Sci., 2019, 7(6): 2372-2382.
|
| 31 |
IŞIKGÖZ TAŞBAKAN M, YILDIRIM ŞIMŞIR I, MERMER S, et al.. Intralesional epidermal growth factor therapy fordiabetic foot ulcers: an evaluation of 15 cases[J]. Turk. J. Med. Sci., 2017, 47(5): 1500-1504.
|
| 32 |
YARDEN Y. The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities[J]. Eur. J. Cancer, 2001, 37 (S4):3-8.
|
| 33 |
蒯仂, 许逊哲, 茹意, 等. Cyr61/CCN1在创面愈合中的研究进展[J]. 临床与病理杂志, 2017, 37(10): 2220-2223.
|
| 34 |
JUN J I, LAU L F. The matricellular protein CCN1 induces fibroblast senescence and restricts fibrosis in cutaneous wound healing[J]. Nat. Cell Biol., 2010, 12(7): 676-685.
|
| 35 |
刘明明, 李爱玲, 修瑞娟. 基质金属蛋白酶的研究进展[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2018, 34(10): 1914-1920.
|
| 36 |
陈端凯. 湿润暴露疗法/湿润烧伤膏通过PTEN/AKT信号通路影响慢性难愈合创面中MMP-2和MMP-9表达[D]. 广西右江: 右江民族医学院, 2020.
|
| 37 |
KESKIN E S, KESKIN E R, ÖZTÜRK M B, et al.. The effect of MMP-1 on wound healing and scar formation[J]. Aesthetic Plast. Surg., 2021, 45(6): 2973-2979.
|
| 38 |
STOICA A E, CHIRCOV C, GRUMEZESCU A M. Hydrogel dressings for the treatment of burn wounds: an up-to-date overview[J/OL]. Materials, 2020, 13(12): 2853[2020-06-25]. .
|
| 39 |
YERGOZ F, HASTAR N, CIMENCI C E, et al.. Heparin mimetic peptide nanofiber gel promotes regeneration of full thickness burn injury[J]. Biomaterials, 2017, 134: 117-127.
|
| 40 |
GORSE G J, MESSNER R L. Improved pressure sore healing with hydrocolloid dressings[J]. Arch. Dermatol., 1987, 123(6): 766-771.
|
| 41 |
赵天宇.藻酸盐敷料对促进糖尿病足溃疡愈合效果的研究[J].世界最新医学信息文摘, 2018, 18(31):74-74.
|
| 42 |
黄英, 韩薇, 温丽. 湿性愈合疗法在Ⅲ~Ⅳ期重症压疮中的应用[J]. 现代临床护理, 2017, 16(8): 46-48.
|
| 43 |
王立琴. 湿性愈合理论在高位截瘫多处压疮患者护理中的应用探索[J]. 实用临床护理学电子杂志, 2020, 5(21): 4+15.
|
| 44 |
LOH M L, GOH B K L, KONG Y, et al.. Combination therapy of oxidised regenerated cellulose/collagen/silver dressings with negative pressure wound therapy for coverage of exposed critical structures in complex lower-extremity wounds[J]. Int. Wound J., 2020, 17(5): 1356-1365.
|
| 45 |
YOUNIS I. Role of oxygen in wound healing[J]. J. Wound Care, 2020, 29(S5b): 4-10.
|
| 46 |
KAUFMAN H, GUREVICH M, TAMIR E, et al.. Topical oxygen therapy stimulates healing in difficult, chronic wounds: a tertiary centre experience[J]. J. Wound Care, 2018, 27(7): 426-433.
|
| 47 |
HISAMUDDIN N A R, WAN MOHD ZAHIRUDDIN W N, MOHD YAZID B, et al.. Use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) in chronic diabetic wound-a randomised trial[J]. Med. J. Malaysia, 2019, 74(5): 418-424.
|
| 48 |
KRANKE P, BENNETT M H, MARTYN-ST J M, et al.. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for chronic wounds[J/OL]. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev., 2015,6: CD004123[2015-06-24]. .
|
| 49 |
SIM P, SONG Y, YANG G N, et al.. In vitro wound healing properties of novel acidic treatment regimen in enhancing metabolic activity and migration of skin cells[J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23(13): 7188[2022-06-28]. .
|
| 50 |
SIM P, STRUDWICK X L, SONG Y, et al.. Influence of acidic pH on wound healing in vivo: A novel perspective for wound treatment[J/OL]. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23(21): 13655[2022-11-07]. .
|
| 51 |
KIM J K, XU Y, XU X, et al.. A novel binding site in collagen type Ⅲ for integrins alpha1beta1 and alpha2beta1[J]. J. Biol. Chem., 2005, 280(37): 32512-32520.
|
 ), Xujuan ZHANG, Zisong CAI, Chen MA, Mengyu LIU, Pengxiang ZHAO(
), Xujuan ZHANG, Zisong CAI, Chen MA, Mengyu LIU, Pengxiang ZHAO( )
)
 ), 张旭娟, 蔡子松, 马晨, 刘梦昱, 赵鹏翔(
), 张旭娟, 蔡子松, 马晨, 刘梦昱, 赵鹏翔( )
)