


生物技术进展 ›› 2025, Vol. 15 ›› Issue (5): 755-763.DOI: 10.19586/j.2095-2341.2025.0061
李柔柔1,2( ), 赵璞2(
), 赵璞2( ), 郑亚妮1, 杨婧宇1, 马春红2, 王星1(
), 郑亚妮1, 杨婧宇1, 马春红2, 王星1( ), 周硕2(
), 周硕2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-13
接受日期:2025-07-11
出版日期:2025-09-25
发布日期:2025-11-11
通讯作者:
王星,周硕
作者简介:李柔柔 E-mail: 18403203478@163.com;基金资助:
Rourou LI1,2( ), Pu ZHAO2(
), Pu ZHAO2( ), Yani ZHENG1, Jingyu YANG1, Chunhong MA2, Xing WANG1(
), Yani ZHENG1, Jingyu YANG1, Chunhong MA2, Xing WANG1( ), Shuo ZHOU2(
), Shuo ZHOU2( )
)
Received:2025-05-13
Accepted:2025-07-11
Online:2025-09-25
Published:2025-11-11
Contact:
Xing WANG,Shuo ZHOU
摘要:
玉米黄素(zeaxanthin)是一种天然色素,属于类胡萝卜素,具有较强的抗氧化能力,广泛用于预防疾病、饲料添加等方面。综述了玉米黄素的结构和基本化学特性、天然来源、合成调控机制、提取方法(有机溶剂萃取、超临界CO2流体萃取、酶解法)、分析检测方法(色谱法、光谱法),及其在食品着色、抗氧化、视力保健、疾病预防等方面的功能与应用,并对未来的研究方向和应用前景作了展望,以期为玉米黄素在食品加工、医药研发、动物营养领域的具体应用方案及开发新型功能性产品提供参考,对促进营养健康产业的创新发展具有重要价值。
中图分类号:
李柔柔, 赵璞, 郑亚妮, 杨婧宇, 马春红, 王星, 周硕. 玉米黄素的研究进展与展望[J]. 生物技术进展, 2025, 15(5): 755-763.
Rourou LI, Pu ZHAO, Yani ZHENG, Jingyu YANG, Chunhong MA, Xing WANG, Shuo ZHOU. Progress and Future Perspectives in Zeaxanthin Research[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2025, 15(5): 755-763.
| 植物种类 | 玉米黄素含量/(μg·100 g-1) |
|---|---|
| 金盏花 | 1 310 |
| 玉米 | 528 |
| 菠菜 | 331 |
| 羽衣甘蓝 | 266 |
| 大头菜 | 263 |
| 莴苣 | 187 |
| 黄橙 | 74 |
| 西兰花 | 23 |
| 胡萝卜 | 23 |
| 鸡蛋 | 23 |
表 1 各类常见植物或食物中玉米黄素的含量[14-17]
Table 1 Contents of zeaxanthin in various common plants and their derivatives [14-17]
| 植物种类 | 玉米黄素含量/(μg·100 g-1) |
|---|---|
| 金盏花 | 1 310 |
| 玉米 | 528 |
| 菠菜 | 331 |
| 羽衣甘蓝 | 266 |
| 大头菜 | 263 |
| 莴苣 | 187 |
| 黄橙 | 74 |
| 西兰花 | 23 |
| 胡萝卜 | 23 |
| 鸡蛋 | 23 |
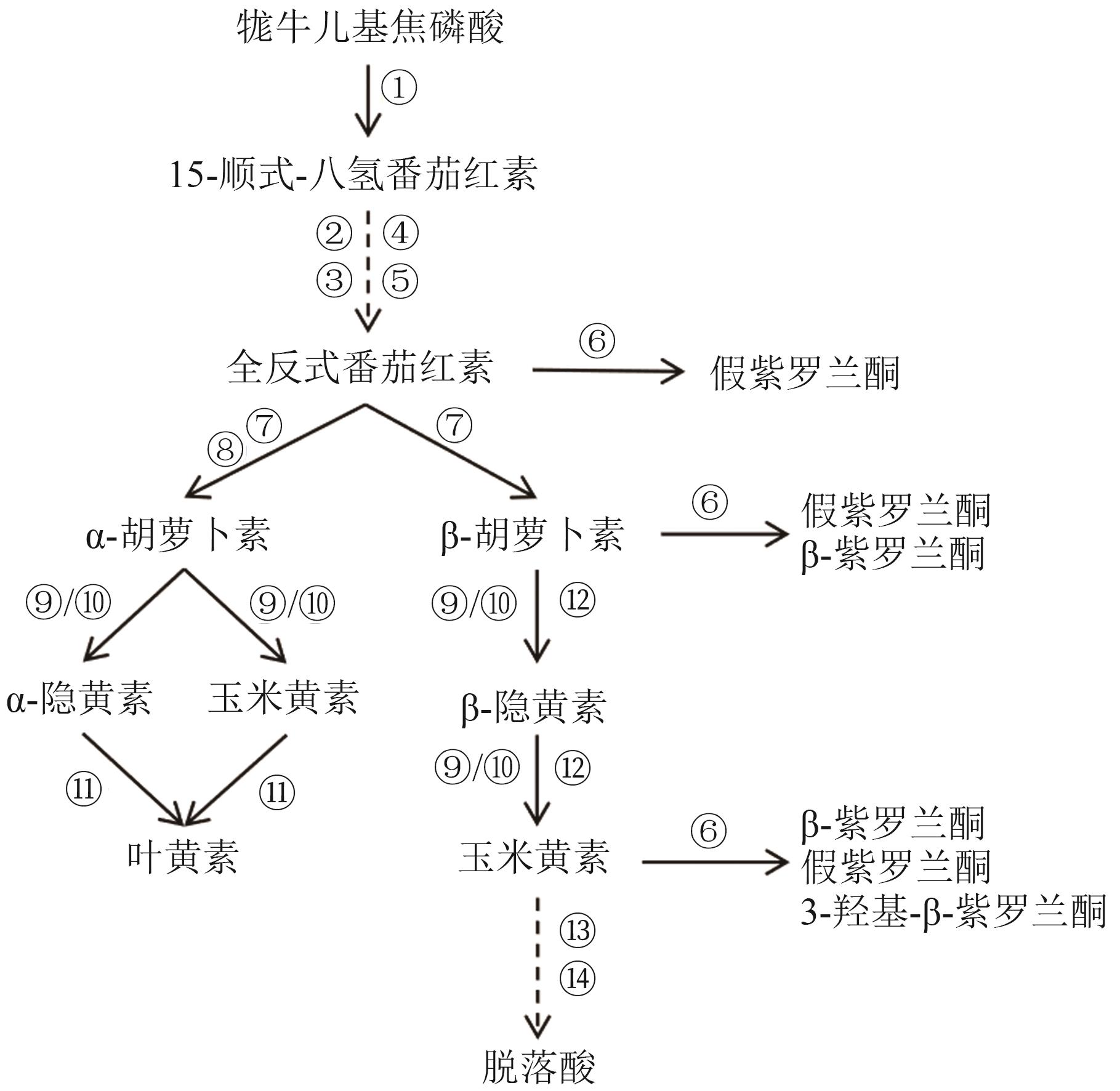
图 2 类胡萝卜素生物合成途径[18-19]注:酶的反应用箭头表示,虚线表示没有显示步骤。①—八氢番茄红素合成酶(phytoene synthase,PSY);②—植物烯去饱和酶(phytoene desaturase,PDS);③—ζ-胡萝卜素去饱和酶(ζ-carotene desaturase,ZDS);④—胡萝卜素异构酶(carotenoid isomerase,CRTISO);⑤—15-顺-ζ-胡萝卜素异构酶(15-cis-ζ-carotene isomerase,Z-ISO);⑥—类胡萝卜素双加氧酶(carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase,CCD1);⑦—番茄红素β环化酶(lycopene β-cyclase,LCYβ);⑧—番茄红素ε环化酶(lycopene ε-cyclase,LCYε);⑨—细胞色素P450型β-羟化酶(cytochrome P450-type β-hydroxylase,CYP97A);⑩—铁氧还蛋白依赖性二铁单加氧酶(ferredoxin-dependent di-iron monooxygenase,HYD);?—细胞色素P450型单加氧酶(cytochrome P450-type monooxygenase,CYP97C);?—β-胡萝卜素环羟化酶(β-carotene hydroxylase,BCH);?—玉米黄素环氧化酶(zeaxanthin epoxidase,ZEP);?—9-顺式环氧类胡萝卜素双加氧酶(9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase,NCED)。
Fig. 2 Simplified carotenoid biosynthesis pathway[18-19]
| 提取方法 | 优点 | 缺点 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高效、高纯度 | 萃取率低 | ||
| 有机溶剂萃取法 | 成本较低 | 耗时较长 | [ |
| 溶剂可回收 | 纯度受限 | ||
| 环保、高效 | 成本较高 | ||
| 超临界CO2流体萃取法 | 品质优良 | 设备复杂 | [ |
| 适用广泛 | 条件严苛 | ||
| 高纯、高效 | 酶价高昂 | ||
| 酶解法 | 可去除杂质 | 安全考量 | [ |
| 安全环保 | 产量挑战 |
表 2 常见的玉米黄素提取方法及其优缺点
Table 2 Common zeaxanthin extraction methods and their advantages and disadvantages
| 提取方法 | 优点 | 缺点 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高效、高纯度 | 萃取率低 | ||
| 有机溶剂萃取法 | 成本较低 | 耗时较长 | [ |
| 溶剂可回收 | 纯度受限 | ||
| 环保、高效 | 成本较高 | ||
| 超临界CO2流体萃取法 | 品质优良 | 设备复杂 | [ |
| 适用广泛 | 条件严苛 | ||
| 高纯、高效 | 酶价高昂 | ||
| 酶解法 | 可去除杂质 | 安全考量 | [ |
| 安全环保 | 产量挑战 |
| [1] | PRASANNA B M, PALACIOS-ROJAS N, HOSSAIN F, et al.. Molecular breeding for nutritionally enriched maize: status and prospects[J/OL]. Front. Genet., 2019, 10: 1392[2025-07-10]. . |
| [2] | DEMMIG-ADAMS B, POLUTCHKO S K, ADAMS W W. Structure-function-environment relationship of the isomers zeaxanthin and lutein[J]. Photochem, 2022, 2(2): 308-325. |
| [3] | 董旭丽,张慧,徐公世.玉米黄素及生理功能[J].中国食品添加剂,2006,17(2):83-86. |
| DONG X L, ZHANG H, XU G S. Zeaxanthin and its physiological function[J]. China Food Addit., 2006, 17(2): 83-86. | |
| [4] | 刘美宏.基于AMPK通路玉米黄素调节脂代谢的分子机制研究[D].长春:吉林农业大学,2019. |
| [5] | KARRER P, WEHRLI H, HELFENSTEIN A. Pflanzenfarbstoffe XIX. über zeaxanthin und xanthophyll[J]. Helv. Chim. Acta, 1930, 13(2): 268-273. |
| [6] | ZECHMEISTER L. Cis-trans isomerization and stereochemistry of carotenoids and diphenyl-polyenes[J]. Chem. Rev., 1944, 34(2): 267-344. |
| [7] | MAYER H. Synthesis of optically active carotenoids and related compounds[J/OL]. Pure Appl. Chem., 1979, 10: 101125882[2025-09-30]. . |
| [8] | BARTLETT L, KLYNE W, MOSE W P, et al.. Optical rotatory dispersion of carotenoids[J]. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1969, 18(19): 2527-2544. |
| [9] | HLUBUCEK J R, HORA J, RUSSELL S W, et al.. Carotenoids and related compounds. Part XXIX. Stereochemistry and synthesis of the allenic end group. Absolute configuration of zeaxanthin[J]. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans., 1974, 5(23): 848-852. |
| [10] | 邱涛涛,黄明发,陈颜虹,等.玉米黄素提取及应用研究进展[J].中国调味品,2008,33(11):18-23. |
| QIU T T, HUANG M F, CHEN Y H, et al.. Progress of research on utilization and extracting of zeaxanthin[J]. China Condiment, 2008, 33(11): 18-23. | |
| [11] | 申晓慧.系列玉米胚乳成分性状突变体的获得与表征[D].太原:山西大学,2020. |
| [12] | SAINI R K, PRASAD P, LOKESH V, et al.. Carotenoids: dietary sources, extraction, encapsulation, bioavailability, and health benefits-a review of recent advancements[J/OL]. Antioxidants, 2022, 11(4): 795[2025-07-10]. . |
| [13] | 张冠华,刁倩楠.类胡萝卜素研究进展[J].现代农业,2021(4):46-49. |
| ZHANG G H, DIAO Q N. Research progress of carotenoids[J]. Mod. Agric., 2021(4): 46-49. | |
| [14] | 王超跃.以玉米黄粉为原料制备玉米蛋白和玉米黄素的研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2016. |
| [15] | SAJILATA M G, SINGHAL R S, KAMAT M Y. The carotenoid pigment zeaxanthin: a review[J]. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf., 2008, 7(1): 29-49. |
| [16] | PENG Y, MA C, LI Y, et al.. Quantification of zeaxanthin dipalmitate and total carotenoids in Lycium fruits (Fructus lycii)[J]. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr., 2005, 60(4): 161-164. |
| [17] | LIU H, ZHANG Y, ZHENG B, et al.. Microwave-assisted hydrolysis of lutein and zeaxanthin esters in marigold (Tagetes erecta L.)[J]. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr., 2011, 62(8): 851-856. |
| [18] | SILVA MESSIAS R, GALLI V, DOS ANJOS E SILVA S D, et al.. Carotenoid biosynthetic and catabolic pathways: gene expression and carotenoid content in grains of maize landraces[J]. Nutrients, 2014, 6(2): 546-563. |
| [19] | 刘宇华.基于转录组学与靶向代谢组学解析辣椒果实颜色的形成[D].长沙:湖南大学,2020. |
| [20] | 覃鸿妮,晏萌,王召辉,等.玉米籽粒中花色苷和黑色素含量的QTL分析[J].作物学报,2012,38(2):275-284. |
| QIN H N, YAN M, WANG Z H, et al.. QTL mapping for anthocyanin and melanin contents in maize kernel[J]. Acta Agron. Sin., 2012, 38(2): 275-284. | |
| [21] | 张丽更.玉米黄质合成关键基因表达载体的构建与玉米茎尖生长点的农杆菌介导转化[D].雅安:四川农业大学,2011. |
| [22] | LI X R, TIAN G Q, SHEN H J, et al.. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to produce zeaxanthin[J]. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2015, 42(4): 627-636. |
| [23] | 徐昌杰,张上隆.植物类胡萝卜素的生物合成及其调控[J].植物生理学通讯,2000,36(1):64-70. |
| XU C J, ZHANG S L. Biosynthesis and regulation of plant carotenoids[J]. Plant Physiol. Commun., 2000, 36(1): 64-70. | |
| [24] | WONG J C, LAMBERT R J, WURTZEL E T, et al.. QTL and candidate genes phytoene synthase and ζ-carotene desaturase associated with the accumulation of carotenoids in maize[J]. Theor. Appl. Genet., 2004, 108(2): 349-359. |
| [25] | CHANDER S, GUO Y Q, YANG X H, et al.. Using molecular markers to identify two major loci controlling carotenoid contents in maize grain[J]. Theor. Appl. Genet., 2008, 116(2): 223-233. |
| [26] | YAN J, KANDIANIS C B, HARJES C E, et al.. Rare genetic variation at Zea mays crtRB1 increases β-carotene in maize grain[J]. Nat. Genet., 2010, 42(4): 322-327. |
| [27] | KANDIANIS C B, STEVENS R, LIU W, et al.. Genetic architecture controlling variation in grain carotenoid composition and concentrations in two maize populations[J]. Theor. Appl. Genet., 2013, 126(11): 2879-2895. |
| [28] | OWENS B F, LIPKA A E, MAGALLANES-LUNDBACK M, et al.. A foundation for provitamin A biofortification of maize: genome-wide association and genomic prediction models of carotenoid levels[J]. Genetics, 2014, 198(4): 1699-1716. |
| [29] | FU J, CHENG Y, LINGHU J, et al.. RNA sequencing reveals the complex regulatory network in the maize kernel[J/OL]. Nat. Commun., 2013, 4: 2832[2025-07-10]. . |
| [30] | 吕律,金黎明, Lee Michael,等.黄色玉米籽粒颜色相关性状的QTL定位[J].种子,2019,38(2):37-40. |
| LYU L, JIN L M, LEE M, et al.. QTL mapping of seed color-related traits in yellow maize[J]. Seed, 2019, 38(2): 37-40. | |
| [31] | DONG E, BAI Y, QIN L, et al.. Identification and epistasis analysis of quantitative trait loci for zeaxanthin concentration in maize kernel across different generations and environments[J]. Breed Sci., 2020, 70(2): 212-220. |
| [32] | LIU J, KANG Y, LIU K, et al.. Maize carotenoid gene locus mining based on conditional Gaussian Bayesian network[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 15223-15231. |
| [33] | 贾海涛,张士龙,黄益勤,等.基于甜玉米重组自交系群体的玉米黄质QTL定位[J/OL].分子植物育种,2022:1-8[2022-10-31]. . |
| JIA H T, ZHANG S L, HUANG Y Q, et al.. Quantitative genetic loci mapping of zeaxanthin based on recombined inbred lines of sweet maize[J/OL]. Mol. Plant Breed., 2022: 1-8[2022-10-31]. . | |
| [34] | ZHANG Y, TANG Y, JIN W, et al.. QTL mapping of zeaxanthin content in sweet corn using recombinant inbred line population across different environments[J/OL]. Plants, 2023, 12(19): 3506[2025-07-10]. . |
| [35] | CHEN W, ZHANG X, LU C, et al.. Genome-wide association study of carotenoids in maize kernel[J/OL]. Plant Genome, 2024, 17(3): e20495[2025-07-10]. . |
| [36] | 周琳,梁轩铭,赵磊.天然类胡萝卜素的生物合成研究进展[J].生物技术通报,2022,38(7):119-127. |
| ZHOU L, LIANG X M, ZHAO L. Biosynthesis of natural carotenoids: progress and perspective[J]. Biotechnol. Bull., 2022, 38(7): 119-127. | |
| [37] | 张晓薇,冯佳茵.不同植物中类胡萝卜素的提取和含量比较[J].光明中医,2021,36(23):3986-3988. |
| ZHANG X W, FENG J Y. Extraction and content comparison of carotenoids from different Chinese medicinal materials[J]. Guangming J. Chin. Med., 2021, 36(23): 3986-3988. | |
| [38] | SPANOS G A, CHEN H, SCHWARTZ S J. Supercritical CO2 extraction of β-carotene from sweet potatoes[J]. J. Food Sci., 1993, 58(4): 817-820. |
| [39] | ALEXANDER W S, BRUSEWITZ G H, MANESS N O. Pecan oil recovery and composition as affected by temperature, pressure, and supercritical CO2 flow rate[J]. J. Food Sci., 1997, 62(4): 762-766. |
| [40] | TZIMA S, GEORGIOPOULOU I, LOULI V, et al.. Recent advances in supercritical CO2 extraction of pigments, lipids and bioactive compounds from microalgae[J/OL]. Molecules, 2023, 28(3): 1410[2025-07-10]. . |
| [41] | ÇINAR İ. Effects of cellulase and pectinase concentrations on the colour yield of enzyme extracted plant carotenoids[J]. Process. Biochem., 2005, 40(2): 945-949. |
| [42] | KAO L, CHEN C R, CHANG C J. Supercritical CO2 extraction of turmerones from turmeric and high-pressure phase equilibrium of CO2 turmerones[J]. J. Supercrit. Fluids, 2007, 43(2): 276-282. |
| [43] | 龚琳琳.来曲唑原料药的含量测定及有机杂质分析[J].化学与粘合,2024,46(3):317-321. |
| GONG L L. Content determination and organic impurity analysis of letrozole APIs[J]. Chem. Adhes., 2024, 46(3): 317-321. | |
| [44] | 杨文花.玉米黄素的分析检测[J].中国西部科技,2009,8(24):23-24. |
| [45] | 惠伯棣,李京,裴凌鹏.应用C30-HPLC-PDA分离与鉴定食品中全反式叶黄素和玉米黄素[J].食品科学,2006,27(9):151-154. |
| HUI B D, LI J, PEI L P. Separation and identification of all e-lutein and E-zeaxanthin in foods with C30-HPLC-PDA[J]. Food Sci., 2006, 27(9): 151-154. | |
| [46] | 朱航,崔方庆,卢传礼,等.不同籽粒颜色玉米自交系类胡萝卜素含量分析[J].作物杂志,2022(5):62-68. |
| ZHU H, CUI F Q, LU C L, et al.. Analysis of carotenoid content in maize inbred lines with different color grains[J]. Crops, 2022(5): 62-68. | |
| [47] | 朱莉,徐晓萍,黄婷.紫外-可见分光光度法测定破壁灵芝孢子粉中总三萜及多糖含量[J].食品安全导刊,2020(30):85-87. |
| ZHU L, XU X P, HUANG T. Determination of total triterpenoids and polysaccharides in spore powder of broken Ganoderma lucidum by UV-vis spectrophotometry[J]. China Food Saf. Mag., 2020(30): 85-87. | |
| [48] | 付晓伟,吴晓,姜莉莉,等.紫外分光光度法测定水果中维生素C含量[J].山东化工,2020,49(24):102-103. |
| FU X W, WU X, JIANG L L, et al.. Deter mination of vita Min C in fruits by UV spectrophotometry[J]. Shandong Chem. Ind., 2020, 49(24): 102-103. | |
| [49] | 蒲翔,谢宇,罗君,等.紫外可见分光光度法测定丹眠颗粒中总皂苷的含量[J].贵州中医药大学学报,2020,42(2):35-37. |
| PU X, XIE Y, LUO J, et al.. Determination of total saponins in danmian granules by UV spectrophotometry[J]. J. Guizhou Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med., 2020, 42(2): 35-37. | |
| [50] | 梁爱仙,陈颜清,庞赛,等.紫外-可见分光光度计性能确认方法的建立[J].中国药业,2022,31(5):86-88. |
| LIANG A X, CHEN Y Q, PANG S, et al.. Establishment of performance qualification method of UV-visible spectrophotometers[J]. China Pharm., 2022, 31(5): 86-88. | |
| [51] | 张宇雷,李义,丁宏标.类胡萝卜素及其在蛋鸡生产中的应用[J].饲料工业,2023,44(3):7-12. |
| ZHANG Y L, LI Y, DING H B. Carotenoids and its application in laying hen production[J]. Feed. Ind., 2023, 44(3): 7-12. | |
| [52] | 蔡靳,惠伯棣,蒋继志.玉米黄素及在食品中的应用研究进展[J].中国食品添加剂,2012,23(3):200-207. |
| CAI J, HUI B D, JIANG J Z. Progress on research in zeaxanthin and its application in foods[J]. China Food Addit., 2012, 23(3): 200-207. | |
| [53] | 俞国伟.胶红酵母发酵生产类胡萝卜素的研究[D].杭州:浙江工业大学,2014. |
| [54] | 张霁月,张俭波,郑江歌,等.食品添加剂玉米黄标准研制研究[J].中国食品添加剂,2021,32(2):35-41. |
| ZHANG J Y, ZHANG J B, ZHENG J G, et al.. Establishment of product standard for food additive corn yellow[J]. China Food Addit., 2021, 32(2): 35-41. | |
| [55] | KARBAS FOROUSHAN S, SHOKRI-NAEI S, MALAEKEH-NIKOUEI A, et al.. Antidotal properties of zeaxanthin as a functional food and one of the most common carotenoids in nature: a review[J/OL]. J. Funct. Foods, 2024, 121: 106436[2025-07-10]. . |
| [56] | 卢艳杰,龚院生,周展明,等.玉米黄色素抗氧化特性的初步探讨[J].郑州工程学院学报,2001,22(1):57-59. |
| LU Y J, GONG Y S, ZHOU Z M, et al.. Study on the antioxidant activity of maize yellow pigment[J]. J. Zhengzhou Grain Coll., 2001, 22(1): 57-59. | |
| [57] | MARES-PERLMAN J A, FISHER A I, KLEIN R, et al.. Lutein and zeaxanthin in the diet and serum and their relation to age-related maculopathy in the third national health and nutrition examination survey[J]. Am. J. Epidemiol., 2001, 153(5): 424-432. |
| [58] | SANTOCONO M, ZURRIA M, BERRETTINI M, et al.. Influence of astaxanthin, zeaxanthin and lutein on DNA damage and repair in UVA-irradiated cells[J]. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, 2006, 85(3): 205-215. |
| [59] | 程静.叶黄素、玉米黄质、虾青素的活性研究与开发[D].天津:天津科技大学,2020. |
| [60] | LI H, HUANG C, ZHU J, et al.. Lutein suppresses oxidative stress and inflammation by Nrf2 activation in an osteoporosis rat model[J]. Med. Sci. Monit., 2018, 24: 5071-5075. |
| [61] | JOHRA F T, BEPARI A K, BRISTY A T, et al.. A mechanistic review of β-carotene, lutein, and zeaxanthin in eye health and disease[J/OL]. Antioxidants, 2020, 9(11): 1046[2025-07-10]. . |
| [62] | CHANG D, ZHANG X, RONG S, et al.. Serum antioxidative enzymes levels and oxidative stress products in age-related cataract patients[J/OL]. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev., 2013, 2013: 587826[2025-07-10]. . |
| [63] | KAUR J, KUKREJA S, KAUR A, et al.. The oxidative stress in cataract patients[J]. J. Clin. Diagn. Res., 2012, 6(10): 1629-1632. |
| [64] | MOELLER S M, VOLAND R, TINKER L, et al.. Associations between age-related nuclear cataract and lutein and zeaxanthin in the diet and serum in the carotenoids in the age-related eye disease study, an ancillary study of the women's health initiative[J]. Arch. Ophthalmol., 2008, 126(3): 354-364. |
| [65] | BOUYAHYA A, OMARI NEL, HAKKUR M, et al.. Sources, health benefits, and biological properties of zeaxanthin[J]. Trends Food Sci. Technol., 2021, 118: 519-538. |
| [66] | BONE R A, LANDRUM J T, DIXON Z, et al.. Lutein and zeaxanthin in the eyes, serum and diet of human subjects[J]. Exp. Eye Res., 2000, 71(3): 239-245. |
| [67] | SCHALCH W, COHN W, BARKER F M, et al.. Xanthophyll accumulation in the human retina during supplementation with lutein or zeaxanthin-the LUXEA (lutein xanthophyll eye accumulation) study[J]. Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 2007, 458(2): 128-135. |
| [68] | PARK J S, CHEW B P, WONG T S. Dietary lutein from marigold extract inhibits mammary tumor development in BALB/c mice[J]. J. Nutr., 1998, 128(10): 1650-1656. |
| [69] | 张坤生,郝磊.玉米黄素的性质及提取研究[J].食品研究与开发,2006,27(7):217-220. |
| ZHANG K S, HAO L. The property of zeaxanthin and its extracting[J]. Food Res. Dev., 2006, 27(7): 217-220. | |
| [70] | 孟繁磊,宋志峰,牛红红,等.玉米黄素的提取分离及生理功能[J].吉林农业,2016(23):115-116. |
| MENG F L, SONG Z F, NIU H H, et al.. Extraction, separation and physiological function of zeaxanthin[J]. Agric. Jilin, 2016(23): 115-116. | |
| [71] | 孙震,苏宇杰,姚惠源.玉米蛋白粉中黄体素、玉米黄素对乳腺癌细胞增殖的影响[J].食品与机械,2005,21(2):6-8. |
| SUN Z, SU Y J, YAO H Y. Effects of lutein and zeaxanthin from corn gluten meal on proliferation of mammary cancer cell[J]. Food Mach., 2005, 21(2): 6-8. | |
| [72] | SHENG Y N, LUO Y H, LIU S B, et al.. Zeaxanthin induces apoptosis via ROS-regulated MAPK and AKT signaling pathway in human gastric cancer cells[J]. Onco. Targets Ther., 2020, 13: 10995-11006. |
| [73] | MORRIS D L, KRITCHEVSKY S B, DAVIS C E. Serum carotenoids and coronary heart disease. The lipid research clinics coronary primary prevention trial and follow-up study[J]. JAMA, 1994, 272(18): 1439-1441. |
| [74] | 国家卫计委.《食品安全国家标准 包装饮用水》(GB19298—2014)、《食品安全国家标准 食品添加剂使用标准》(GB2760—2014)等37项食品安全国家标准发布[J].饮料工业,2014,17(12):46-47. |
| [75] | 刁卫楠,朱红菊,刘文革.蔬菜作物中类胡萝卜素研究进展[J].中国瓜菜,2021,34(1):1-8. |
| DIAO W N, ZHU H J, LIU W G. Research progress on carotenoids in vegetable crops[J]. China Cucurbits Veg., 2021, 34(1): 1-8. | |
| [76] | 刘源,赵冉,卢振芳,等.植物类胡萝卜素生物代谢途径及其功能研究进展[J].生物技术通报,2025,41(5):23-31. |
| LIU Y, ZHAO R, LU Z F, et al.. Research progress in the biological metabolic pathway and functions of plant carotenoids[J]. Biotechnol. Bull., 2025, 41(5): 23-31. |
| [1] | 李豆,王珊珊. 葡萄籽中原花青素的提取及应用现状[J]. 生物技术进展, 2015, 5(5): 335-339. |
| [2] | 曹建,孙学辉,路铁刚. 一份水稻矮杆小粒突变体的形态特征和基因定位[J]. 生物技术进展, 2014, 4(3): 186-191. |
| [3] | 石雅丽,张锐,孟志刚,郭三堆. 一种高效提取棉花RNA的改良方法[J]. 生物技术进展, 2011, 1(3): 219-222. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||